
Advances in Endovascular Repair of Aortic Diseases
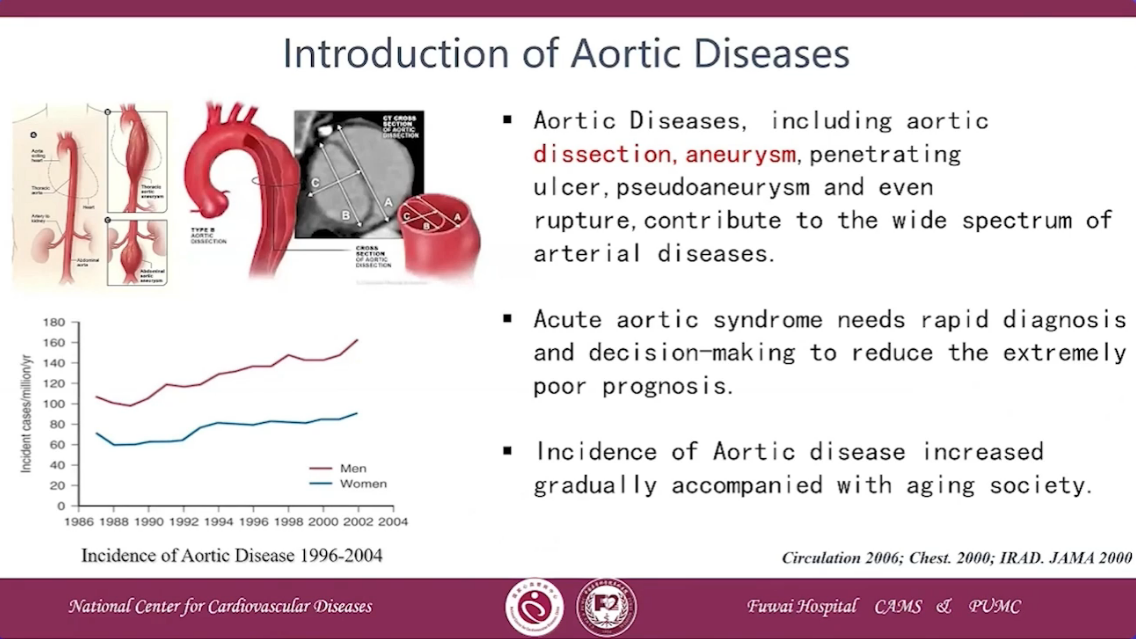
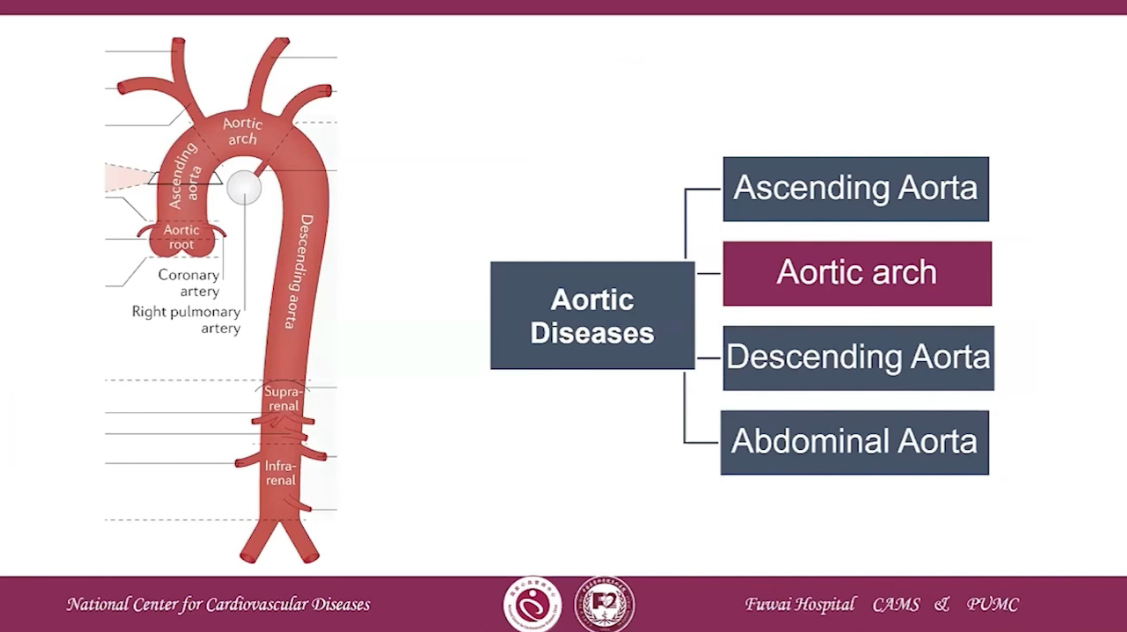
Introduction of Aortic Diseases
•Aortic Diseases, including aortic dissection,aneurysm, penetrating ulcer,pseudoaneurysm and even rupture,contribute to the wide spectrum of arterial diseases.
•Acute aortic syndrome needs rapid diagnosis and decision-making to reduce the extremely poor prognosis.
•Incidence of Aortic disease increased gradually accompanied with aging society.
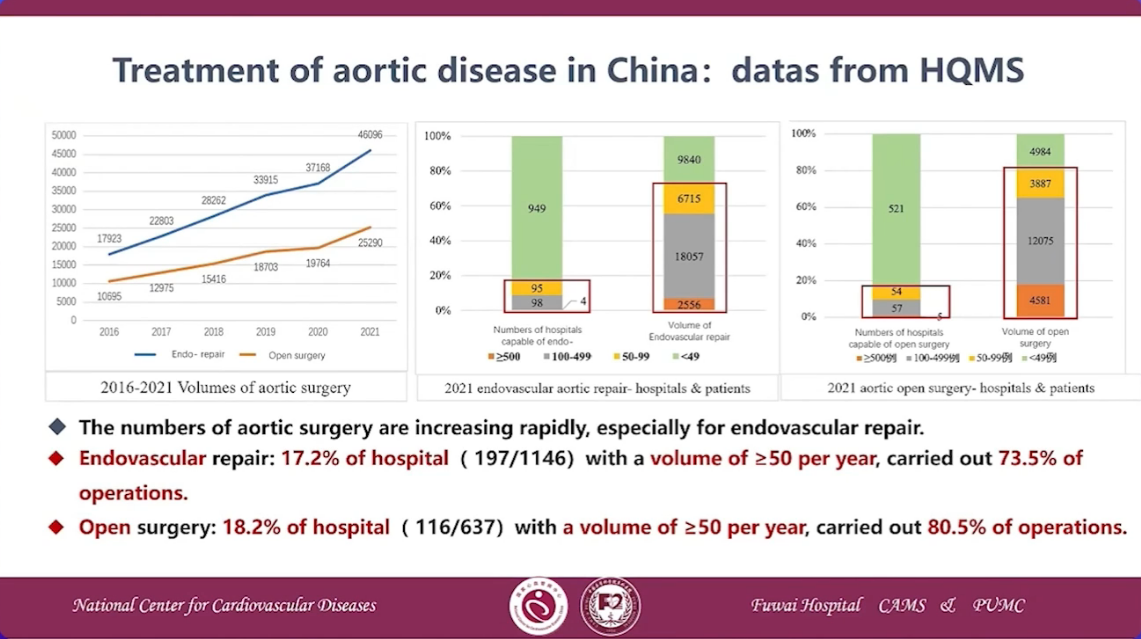
Treatment of aortic disease in China: datas from HQMS
Necessity IRAD:
•67% of acute aortic dissection is TAAD
•20% of acute TAAD not suitable to open surgery
•1996~2013,surgery rate of acute TAAD increased from 79%
•1996~2017, mortality rate of surgery of acute TAAD dicreaded from 25% to 15.3% (STS database)
•Inhospital mortality rate of conservative treatment was more than 60%
•Endovascular repair was the choise of those 20% patients who were not suitable to open surgery
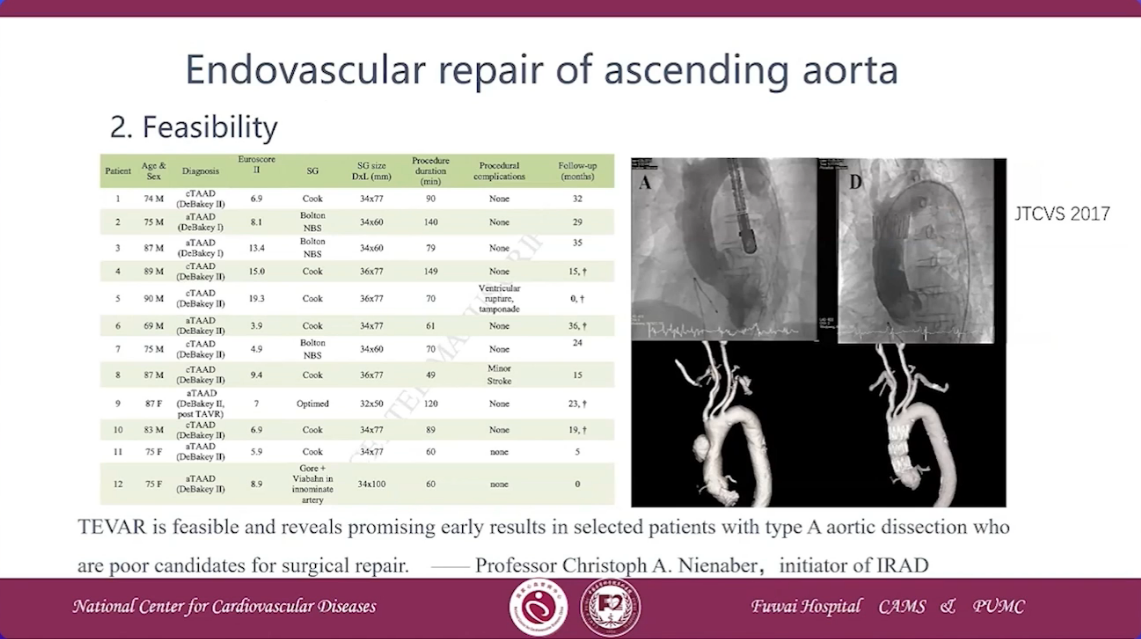
Feasibility

Complication
•The current iteration of stent-graft technology needs to be adapted to the specific features of the ascending aorta.

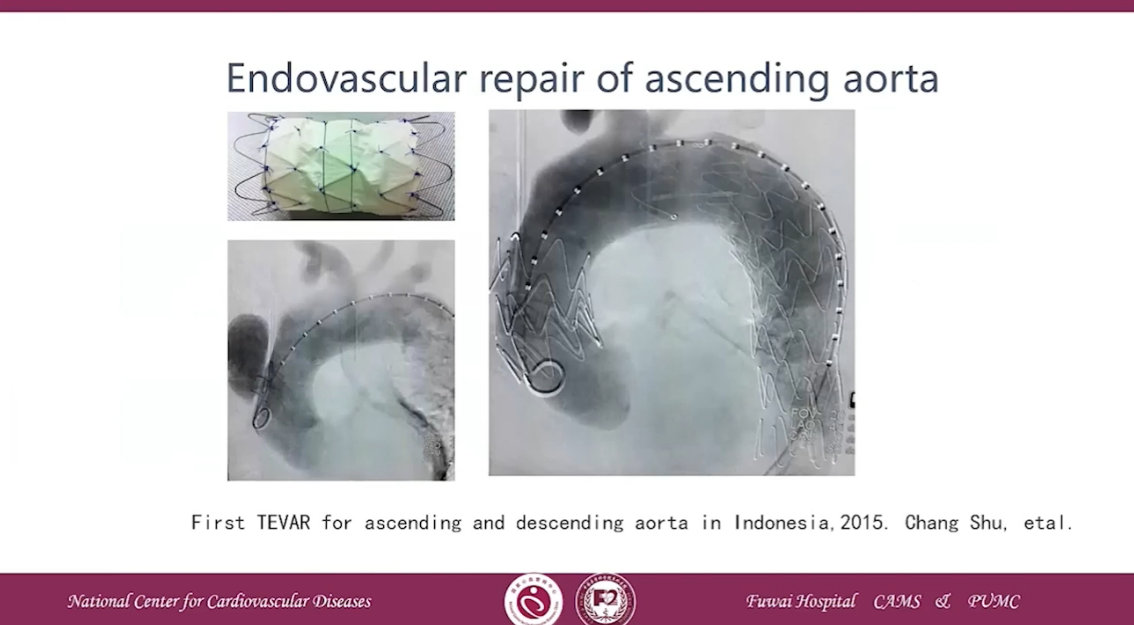


First-in-human Endo-Bentall procedure was reported in 2020
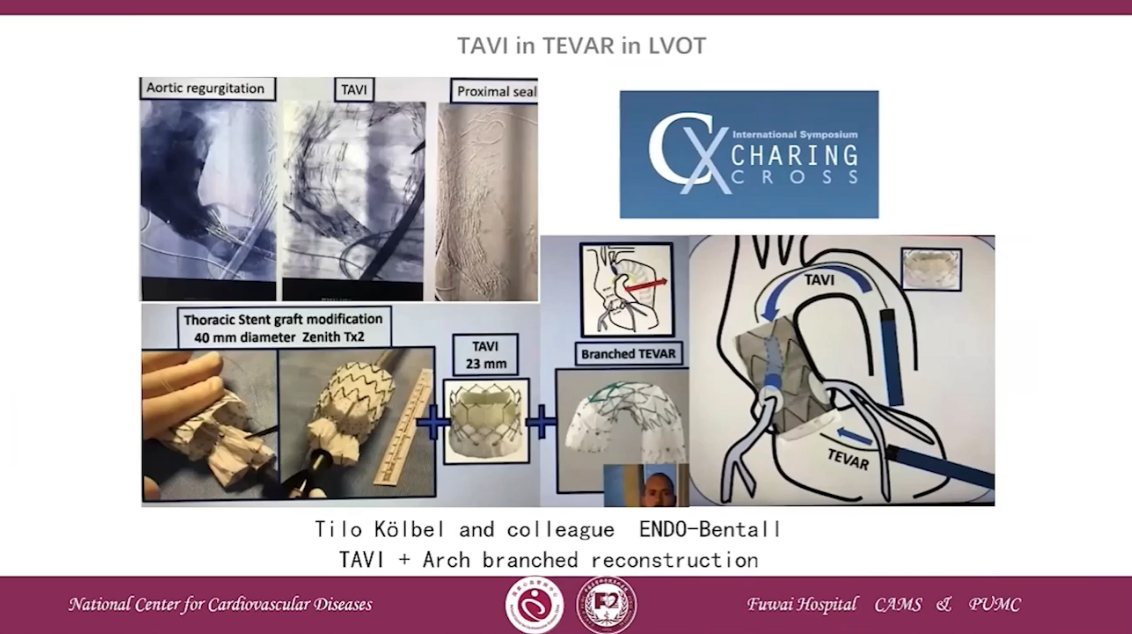
TAVI in TEVAR in LVOT
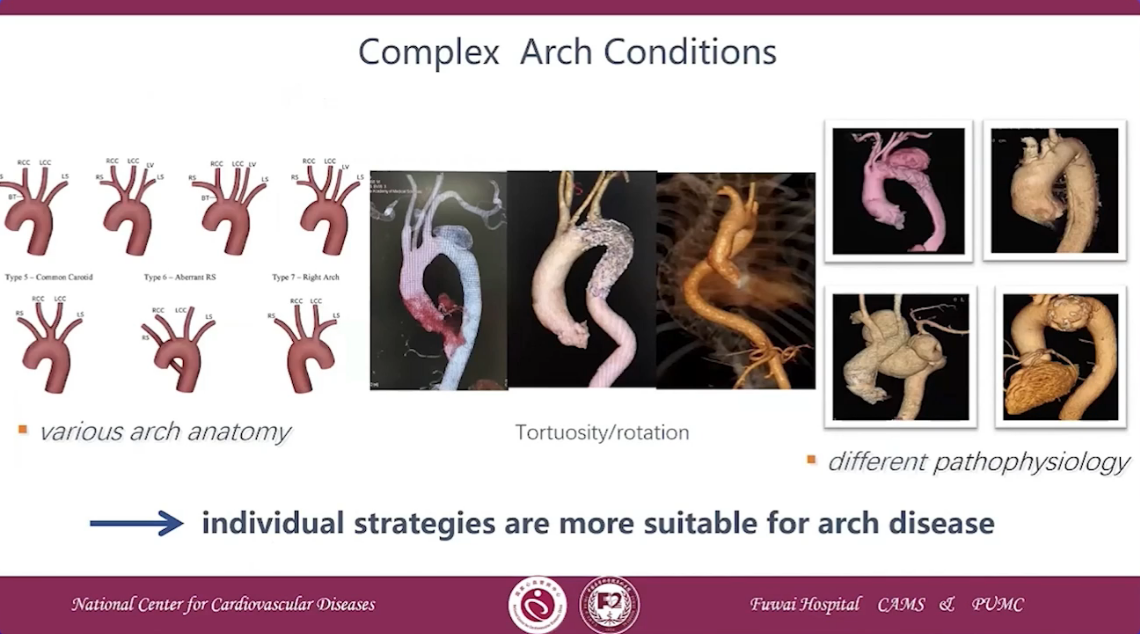
Complex Arch Conditions
•individual strategies are more suitable for arch disease
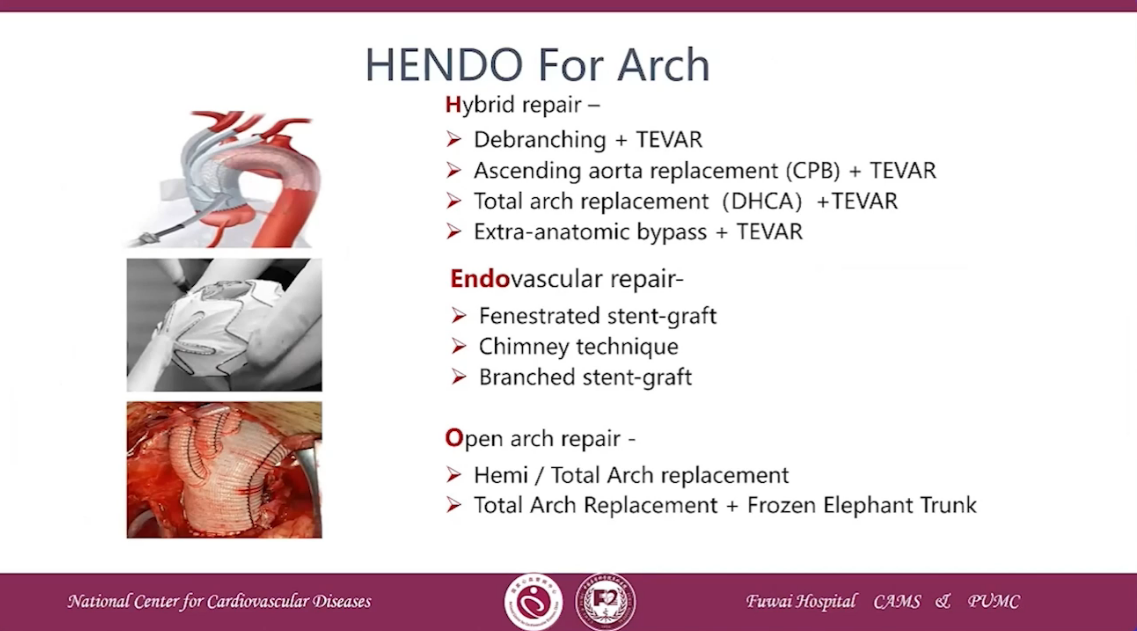
NENDO for Arch
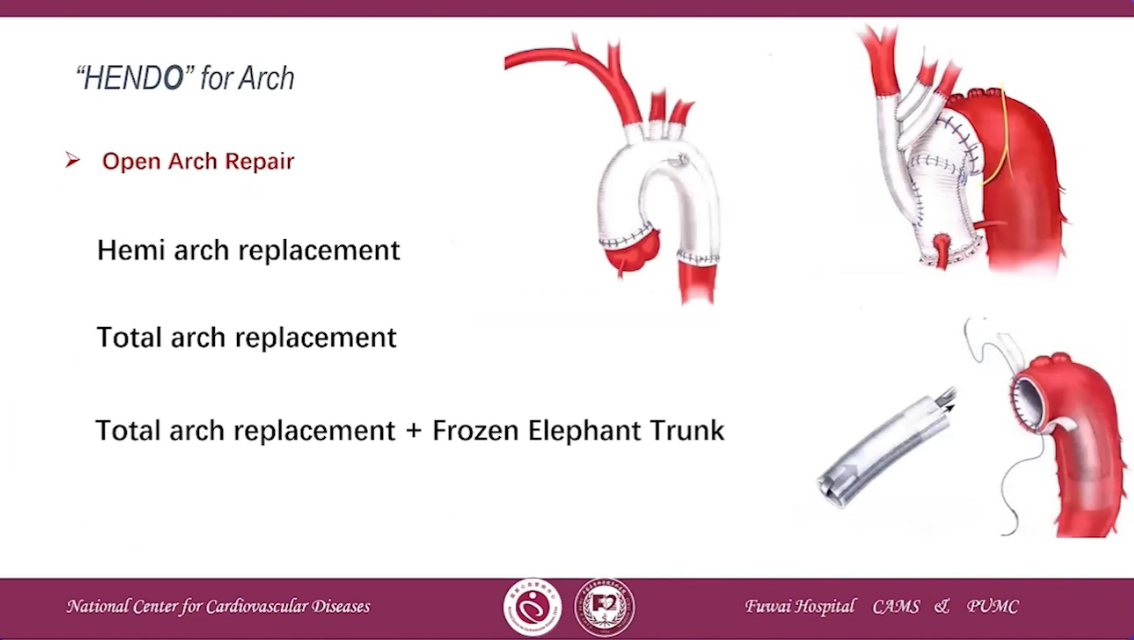
•Hemi arch replacement
•Total arch replacement
•Total arch replacement+Frozen Elephant Trunk
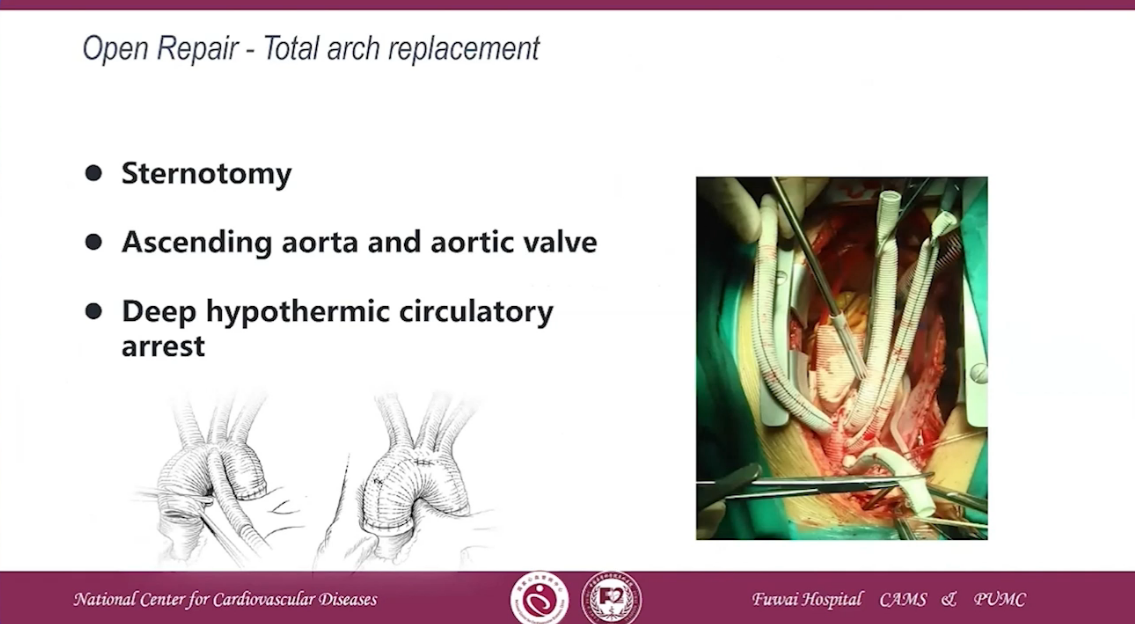
•Sternotomy
•Acending aorta and aortic valve
•Deep hypothermic circulatory arrest
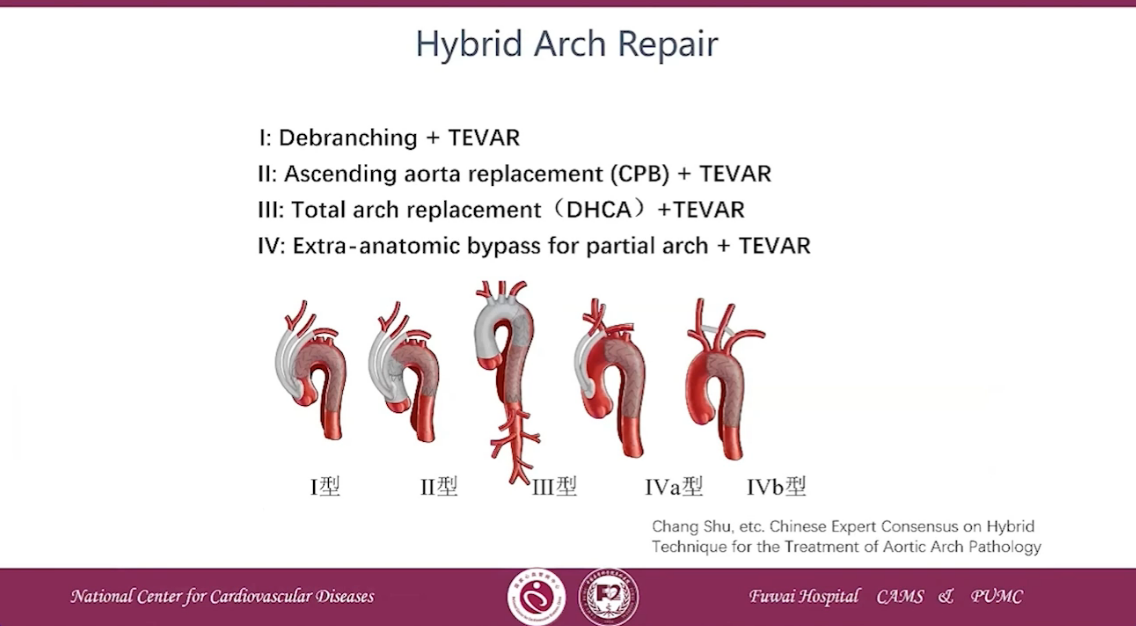
Ⅰ: Debranching + TEVAR
Ⅱ:Ascending aorta replacement(CPB)+ TEVAR
Ⅲ: Total arch replacement(DHCA)+TEVAR
Ⅳ: Extra-anatomic bypass for partial arch + TEVAR
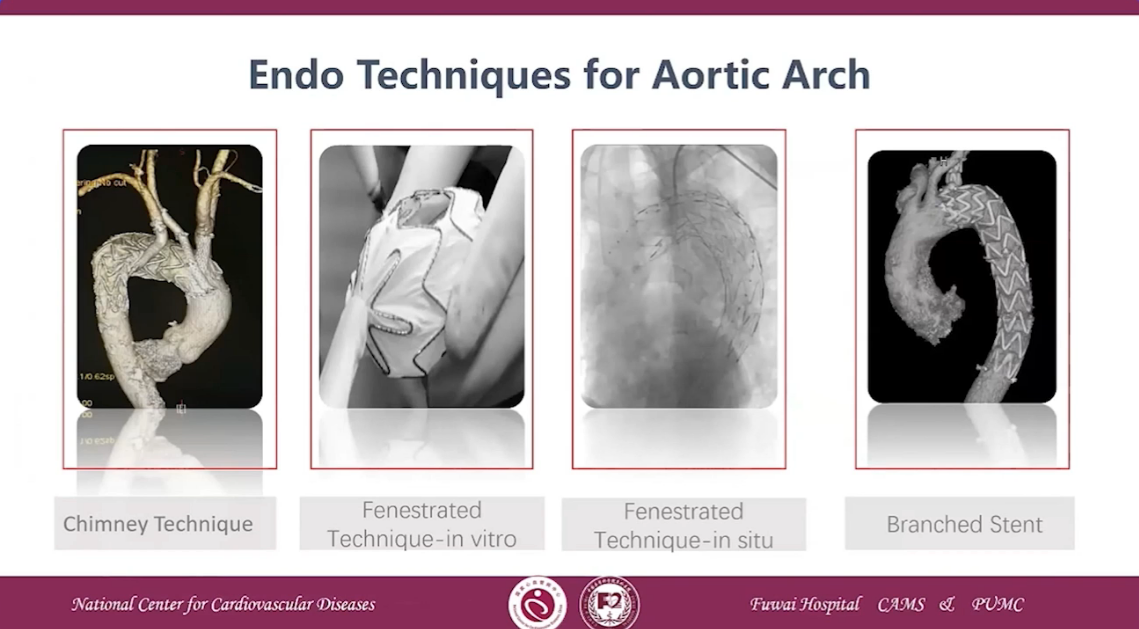
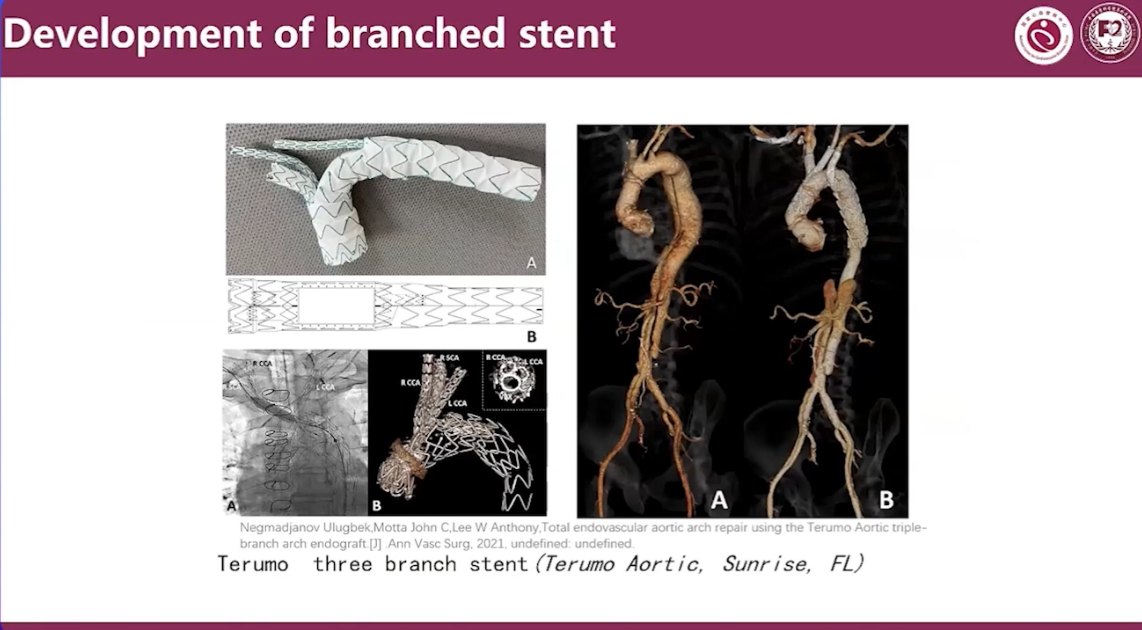
Endo Techniques for Aortic Arch
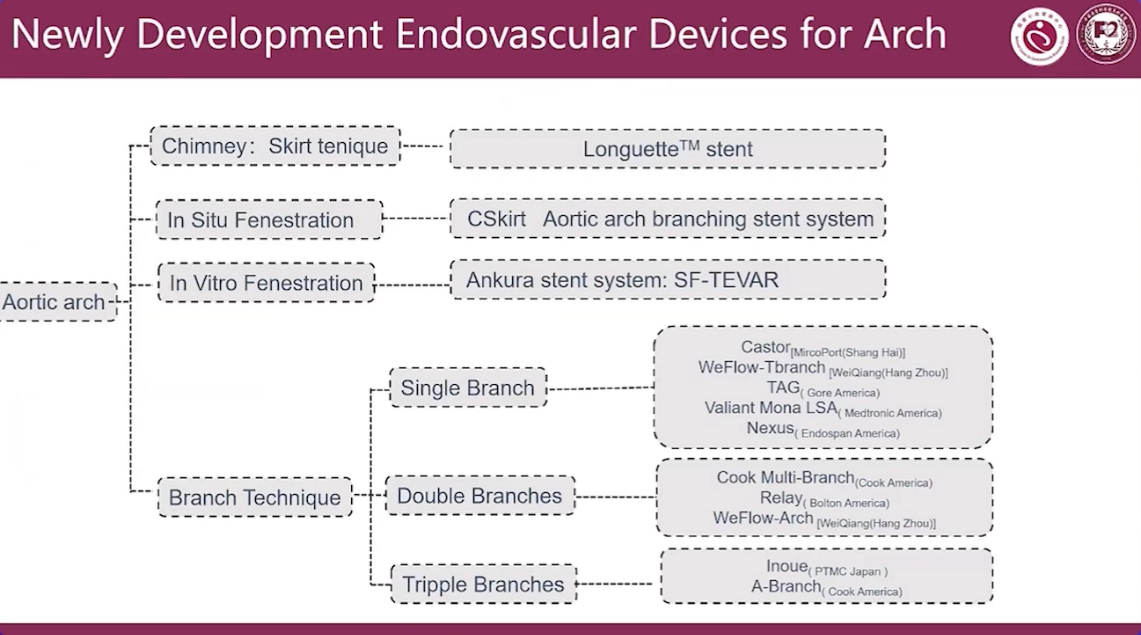
Newly Development Endovascular Devices for Arch
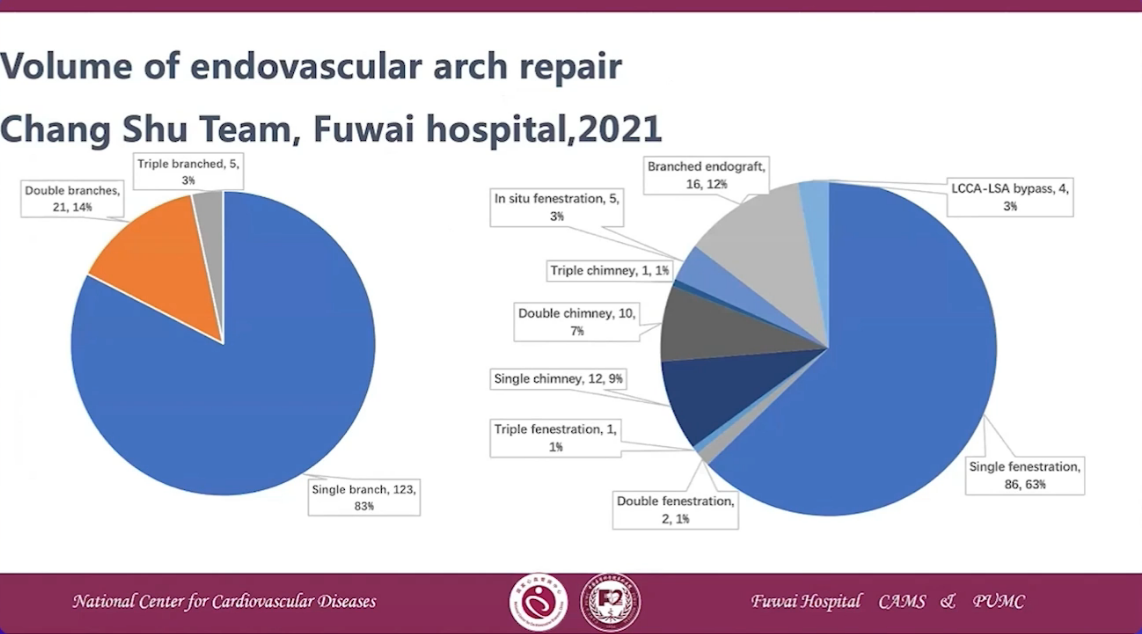
Volume of endovascular arch repair Chang Shu Team, Fuwai hopsital,2021

Endo for Arch: Chimnet technique
Chimnet technique Case 1
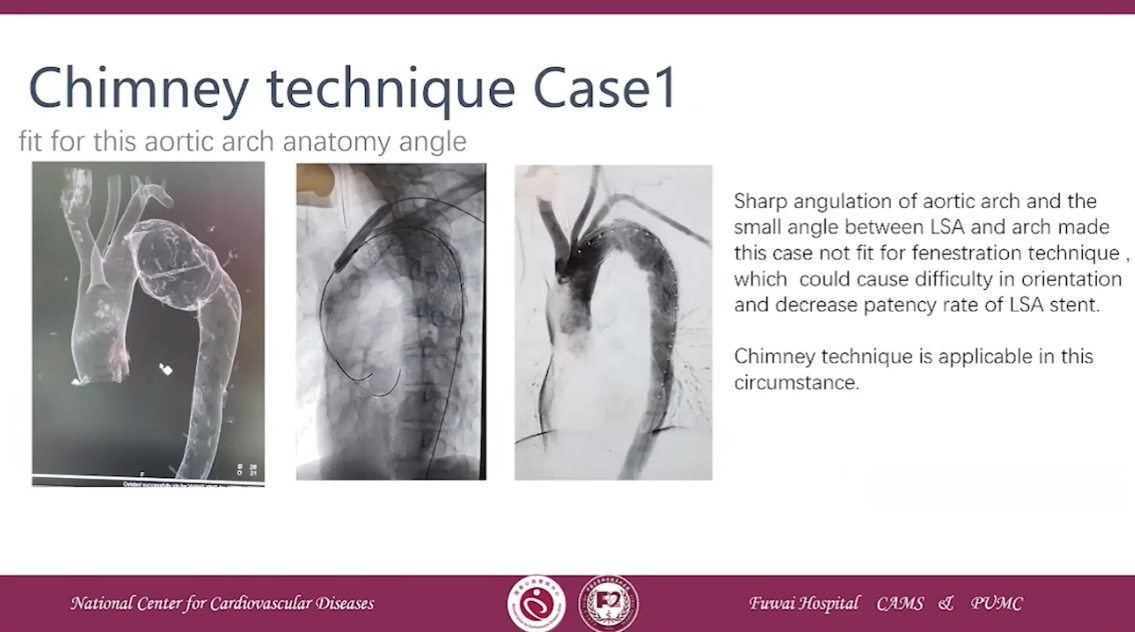
Chimney technique Case 2
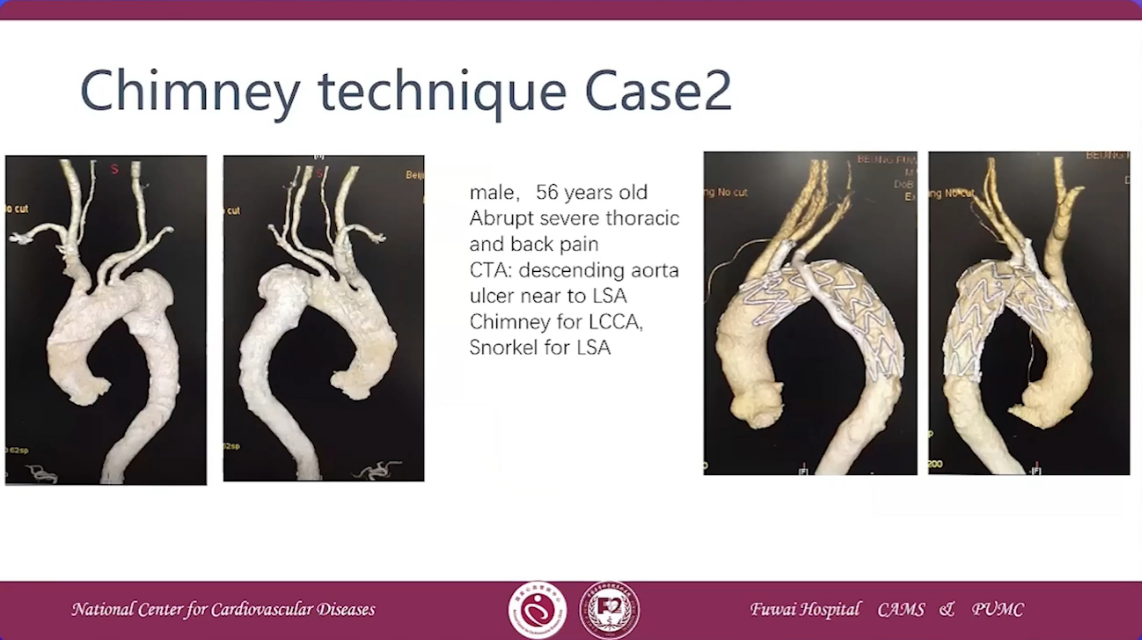
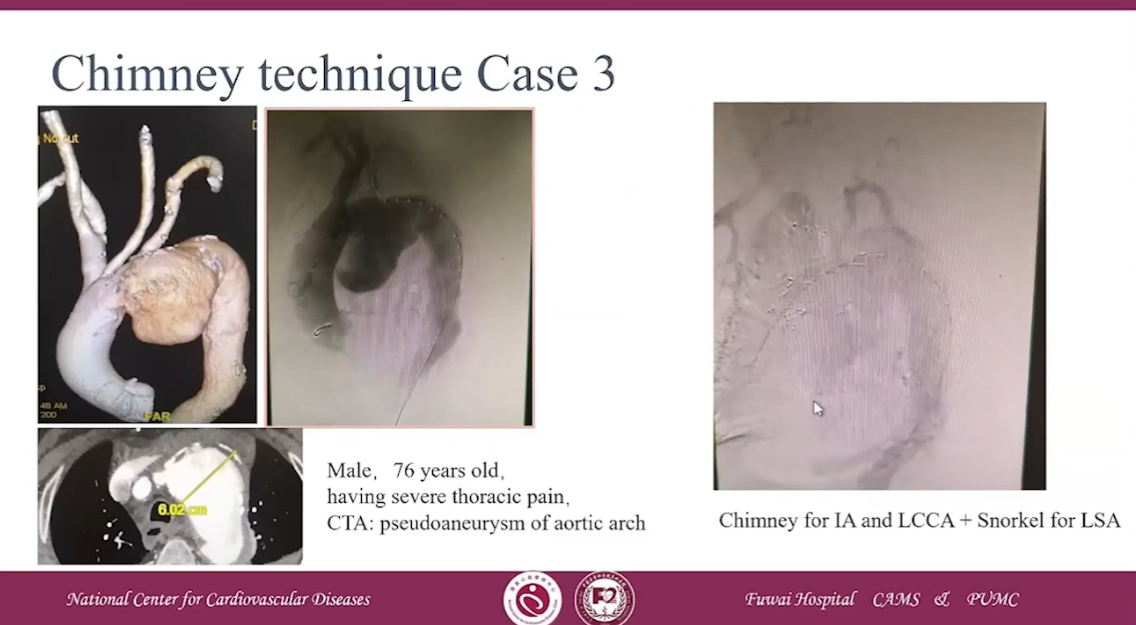
Chimney technique Case 3
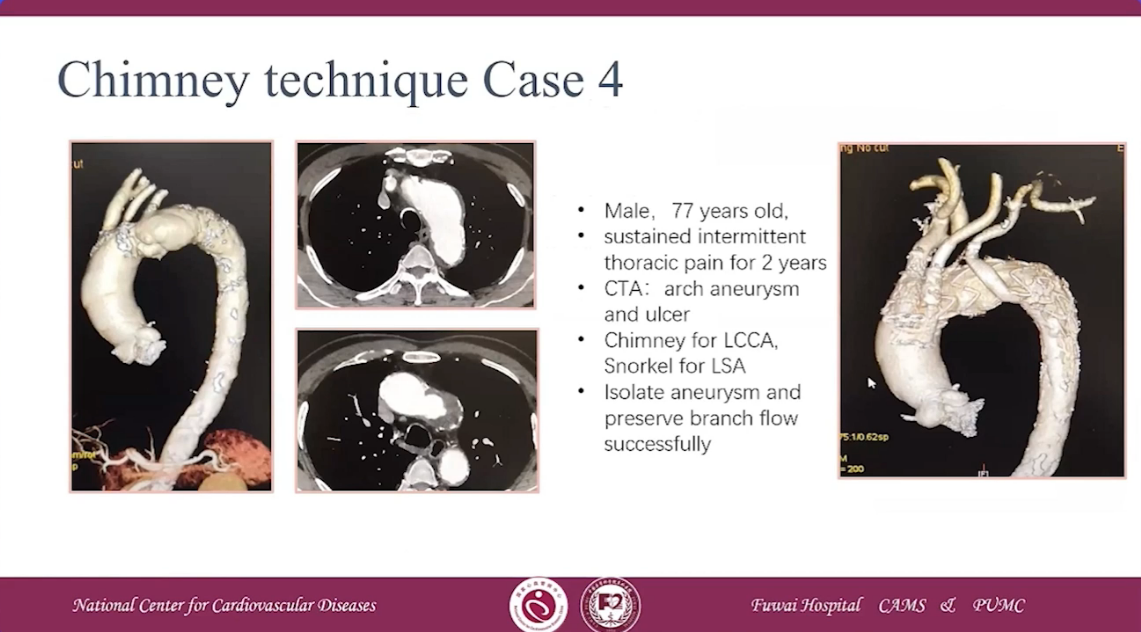
Chimney technique Case 4
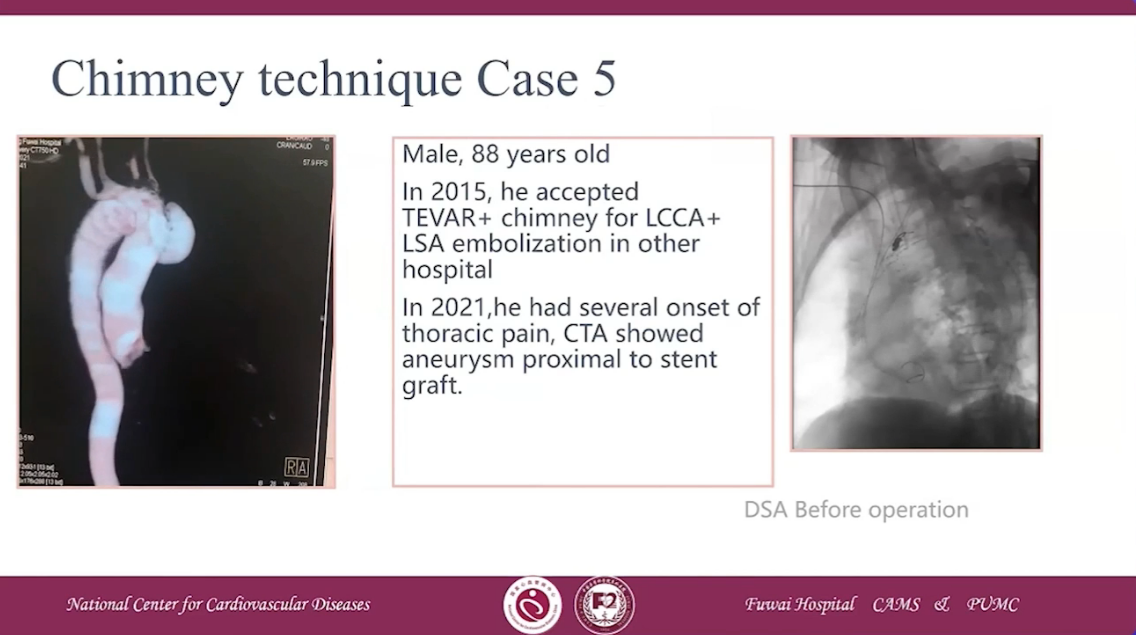
Chimney technique Case 5
Chimney technique-How to treat the endoleak?
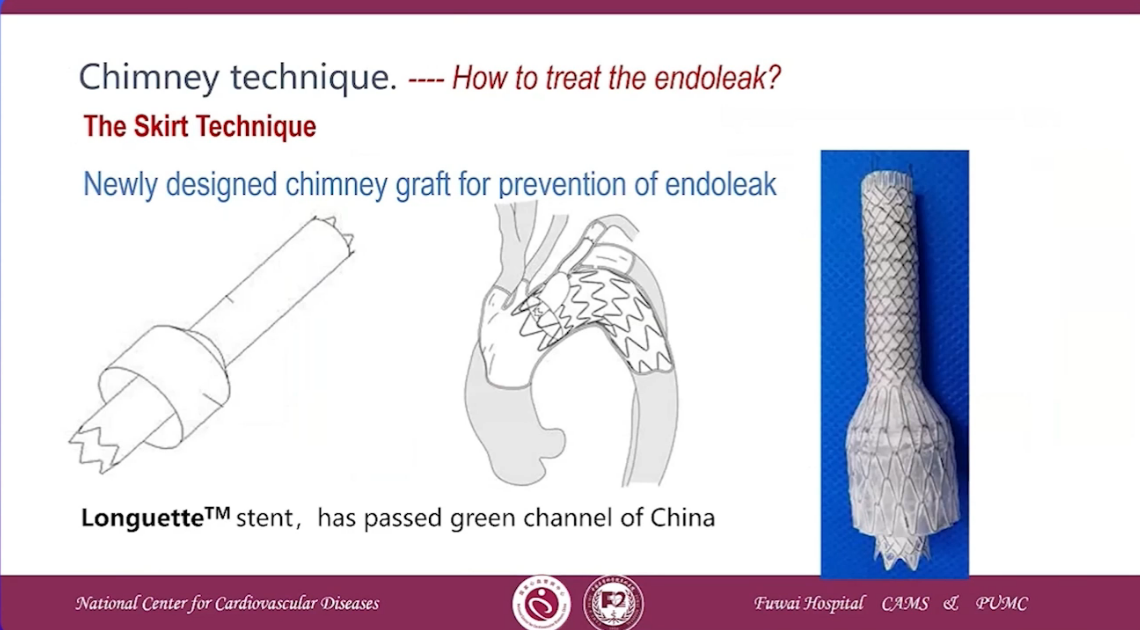
•2018-5-14, First in human implantation of Longuette Stent in National Center of Cardiovascular Disease, Indonesia
•2018-8-21, First in human implantation of Longuette Stent in Yunnan Fuwai hospital,China

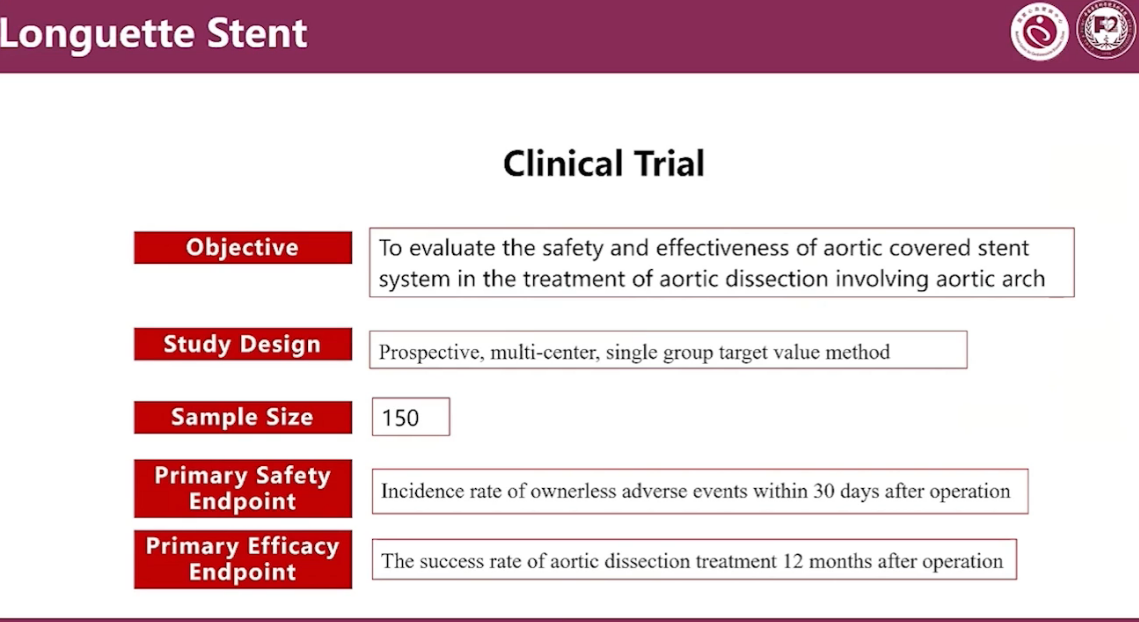
Clinical Trial
Results of Primary Safety Endpoint

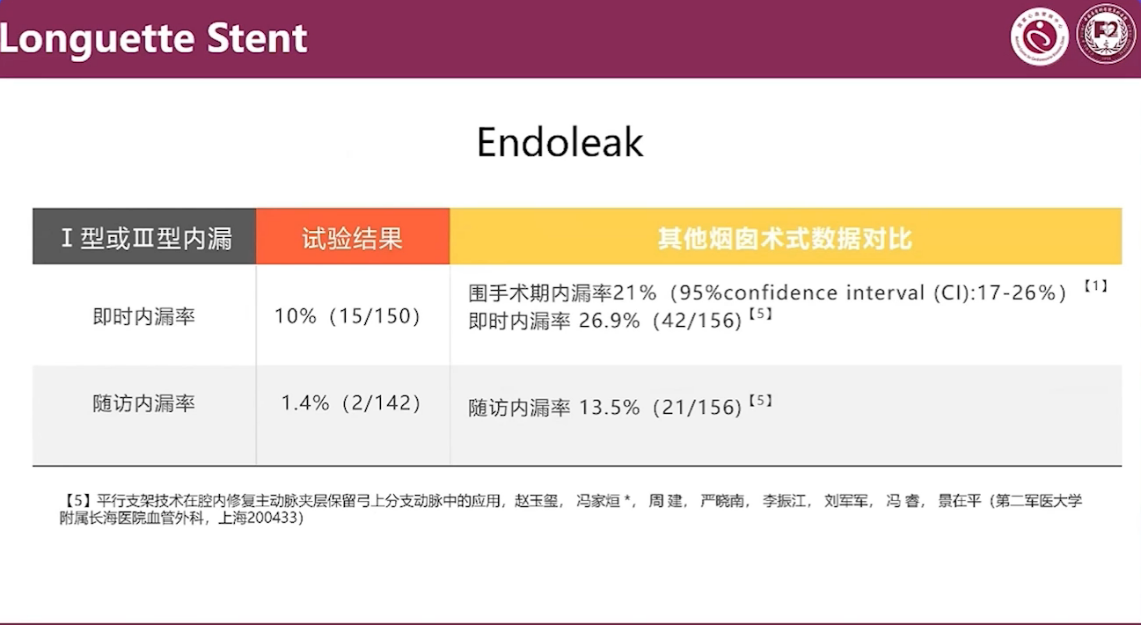
Endoleak
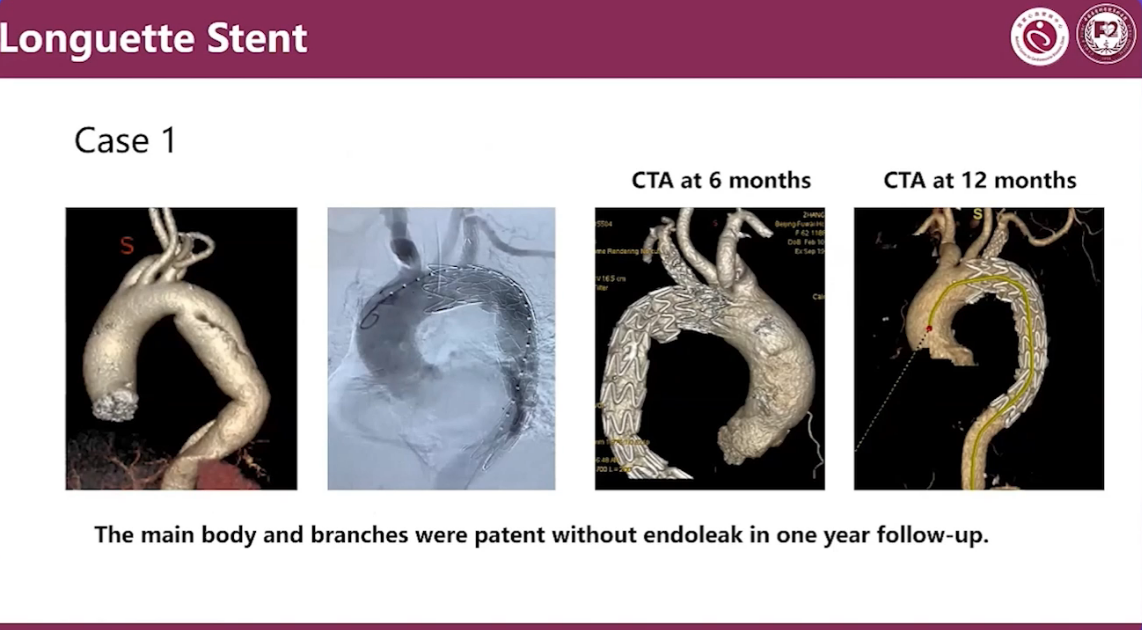
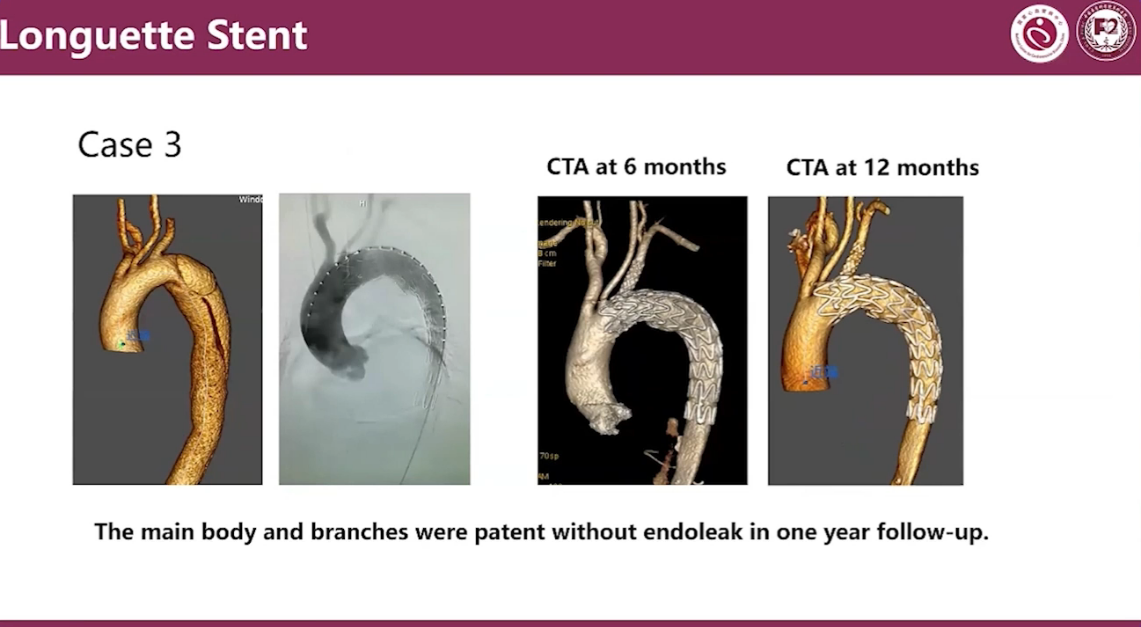
Case1
The main body and branches were patent without endoleak in one year follow-up
Case2
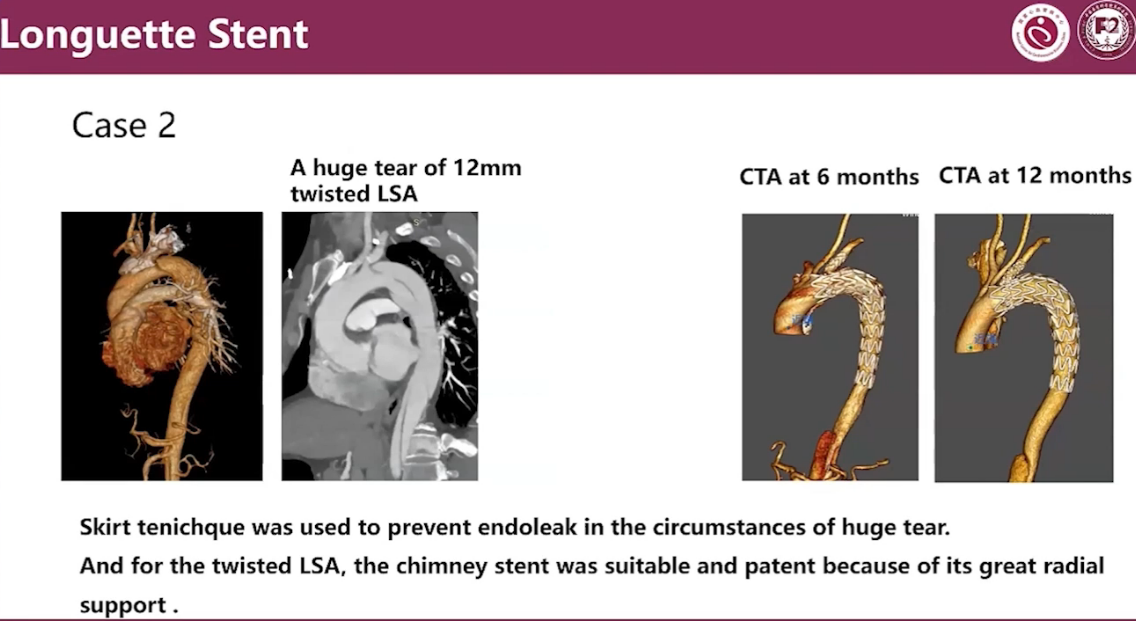
•Skirt tenichque was used to prevent endoleak in the circumstances of huge tear.
•And for the twisted LSA, the chimney stent was suitable and patent because of its great radial support.
The main body and branches were patent without endoleak in one year follow-up.
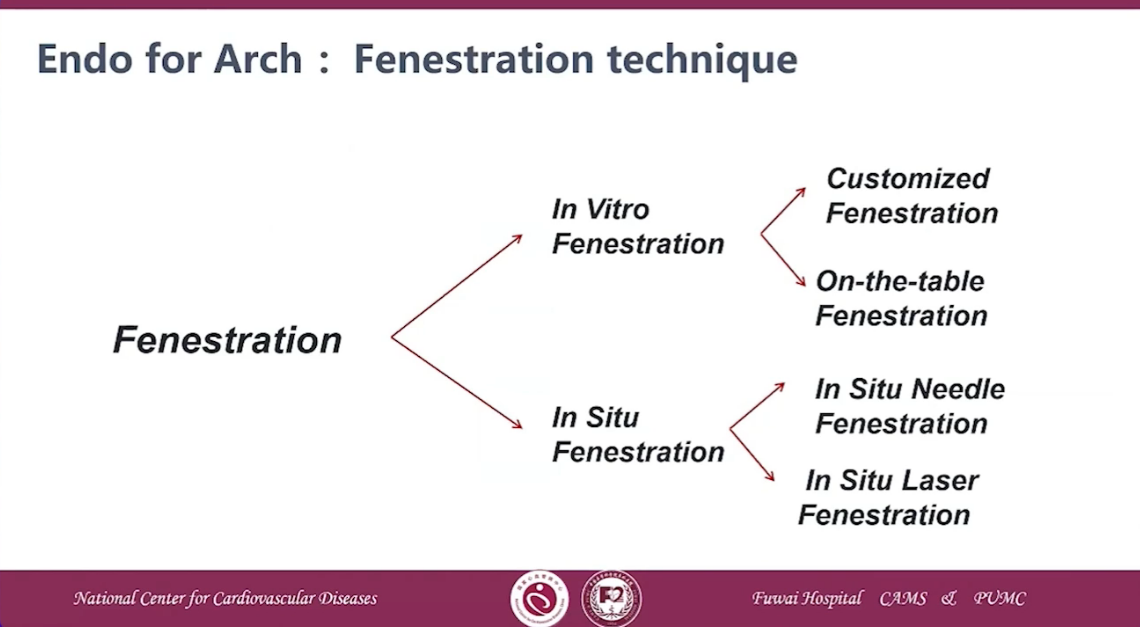
Endo for Arch: Fenestration technique

In vitro fenestration
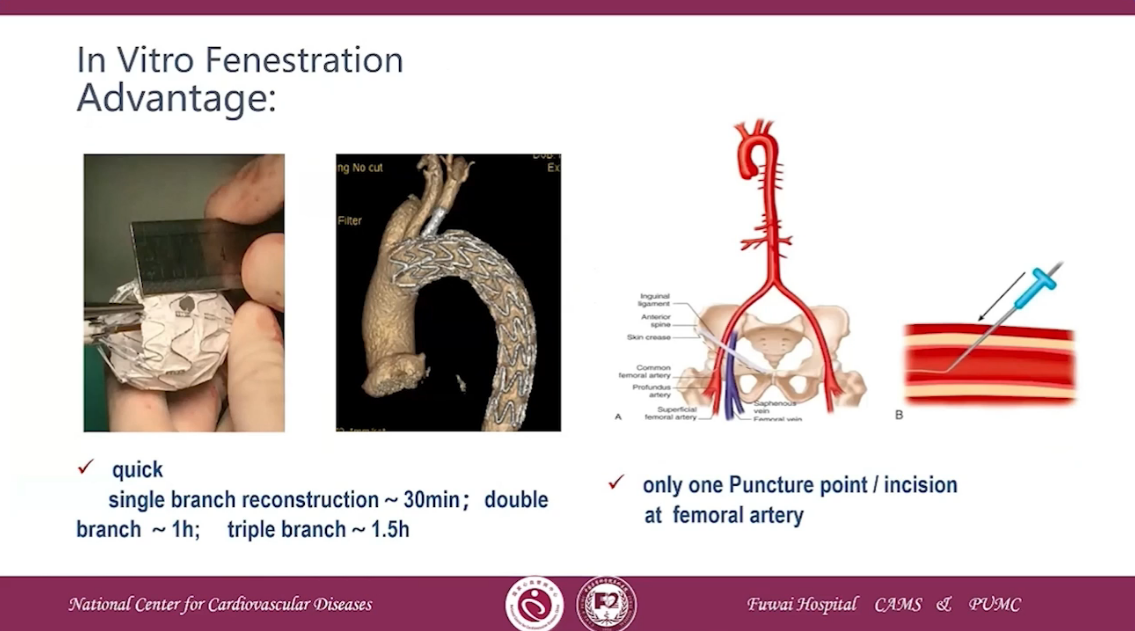
Advantage
•Quick,single branch reconstruction~30min; double branch ~1h; triple branch~1.5h
•Only one Puncture point /incision at femoral artery

Original research about SF-TEVAR
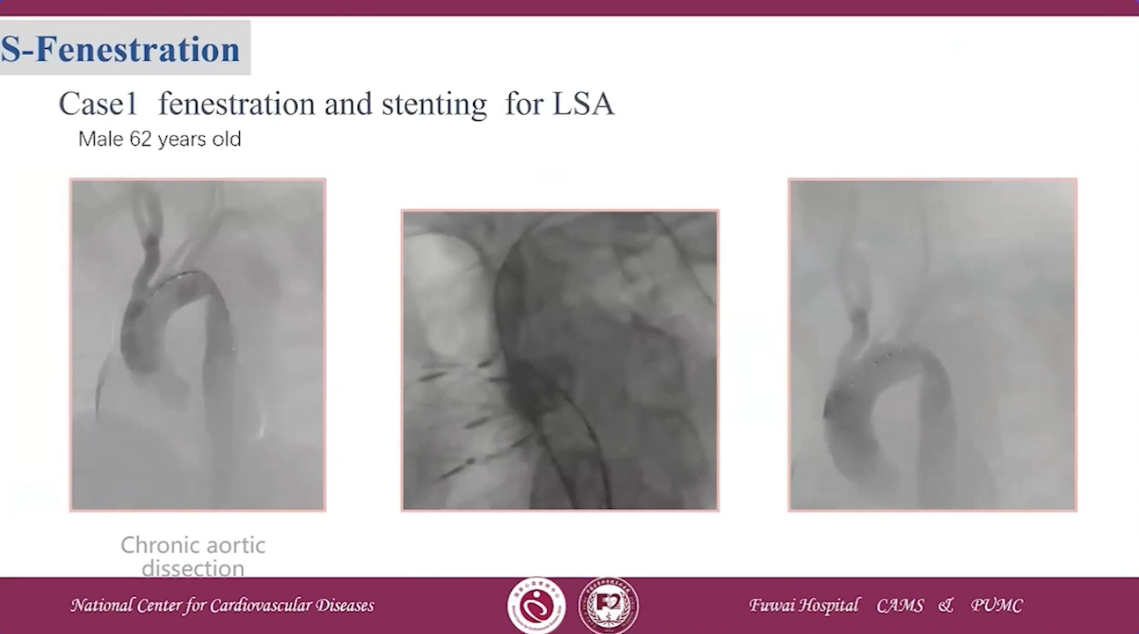
Case 1 fenestration and stenting for LSA
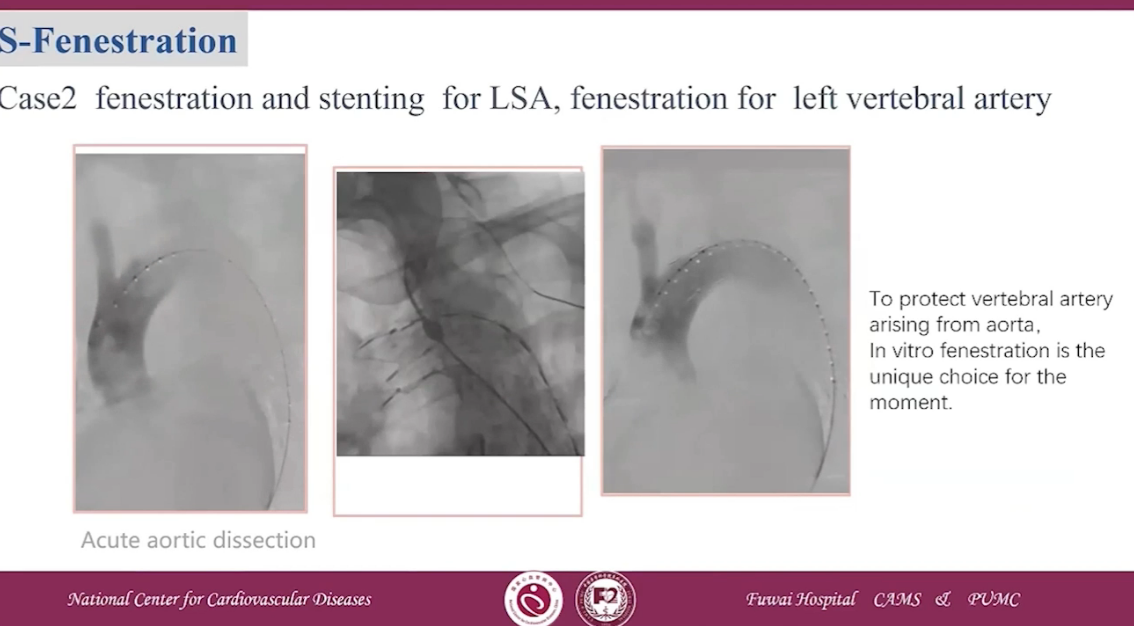
Case 2 fenestration and stenting for LSA, fenestration for left vertebral artery
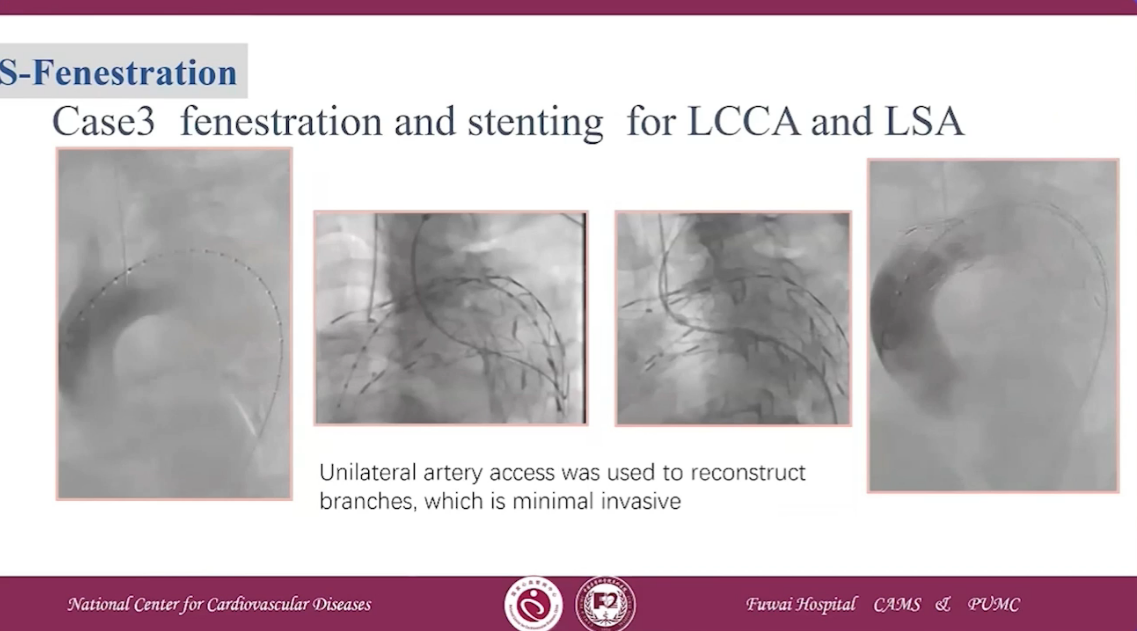
Case3 fenestration and stenting for LCCA and LSA
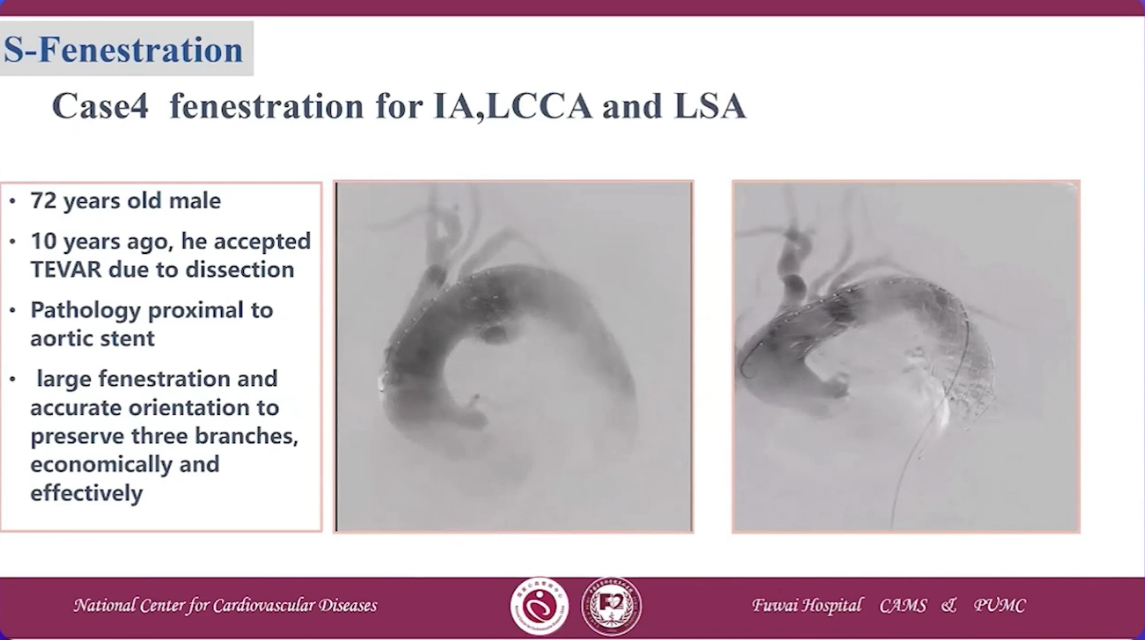
Case 4 fenestration for IA, LCCA and LSA
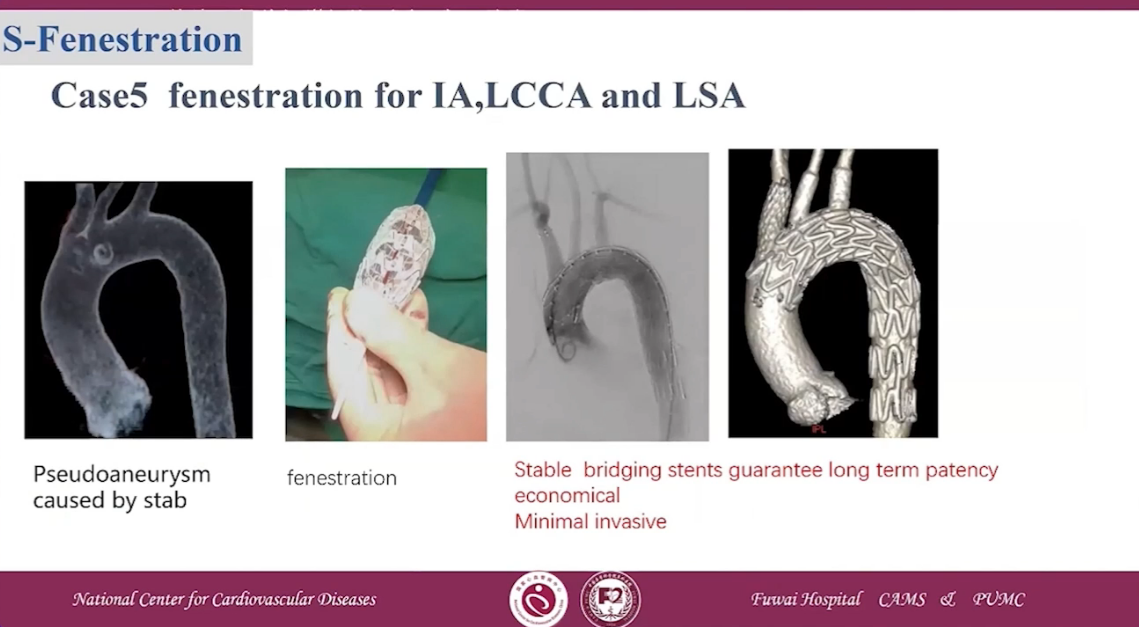
Case 5 fenestration for IA, LCCA and LSA
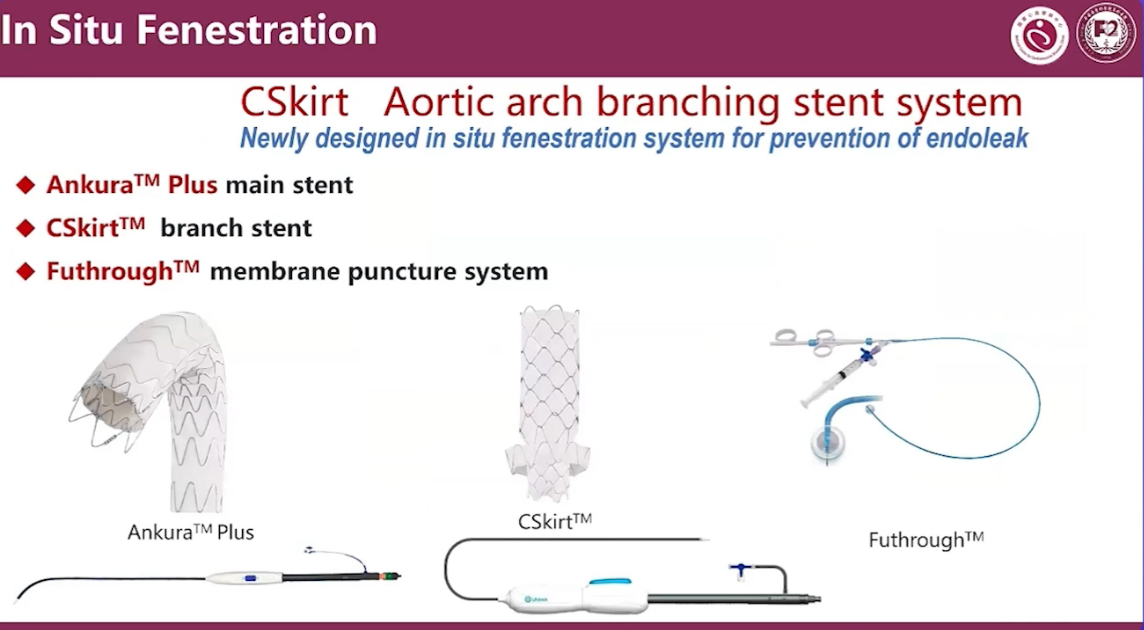
Ankurar TM Plus main stent
CSkirtrm TM branch stent
Futhrough TM membrane puncture system
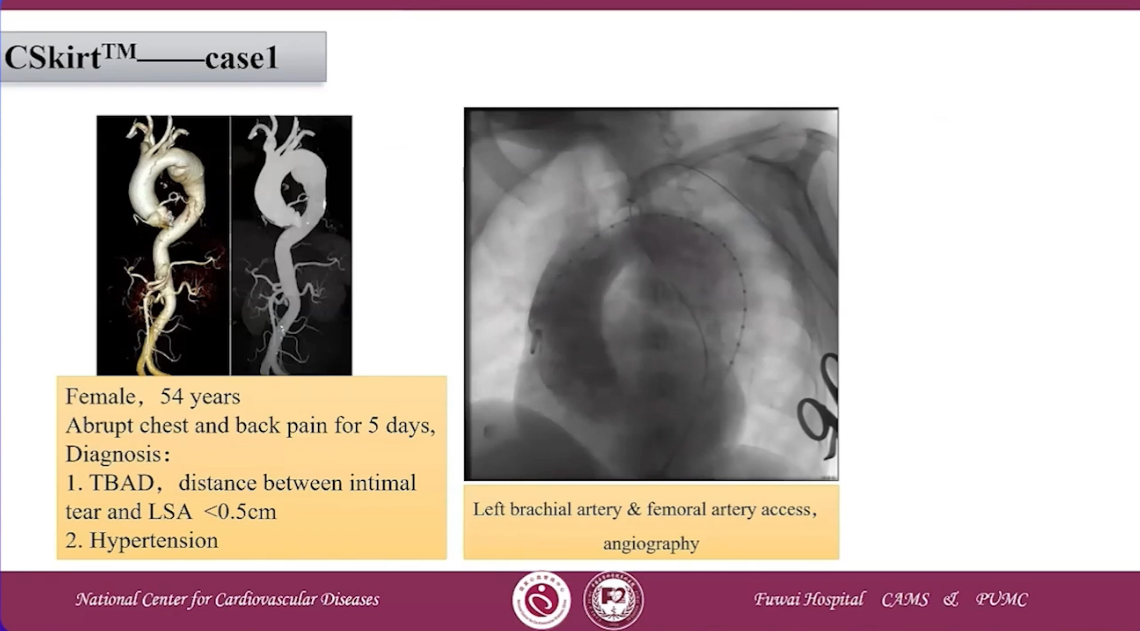
CSKirtTM case 1
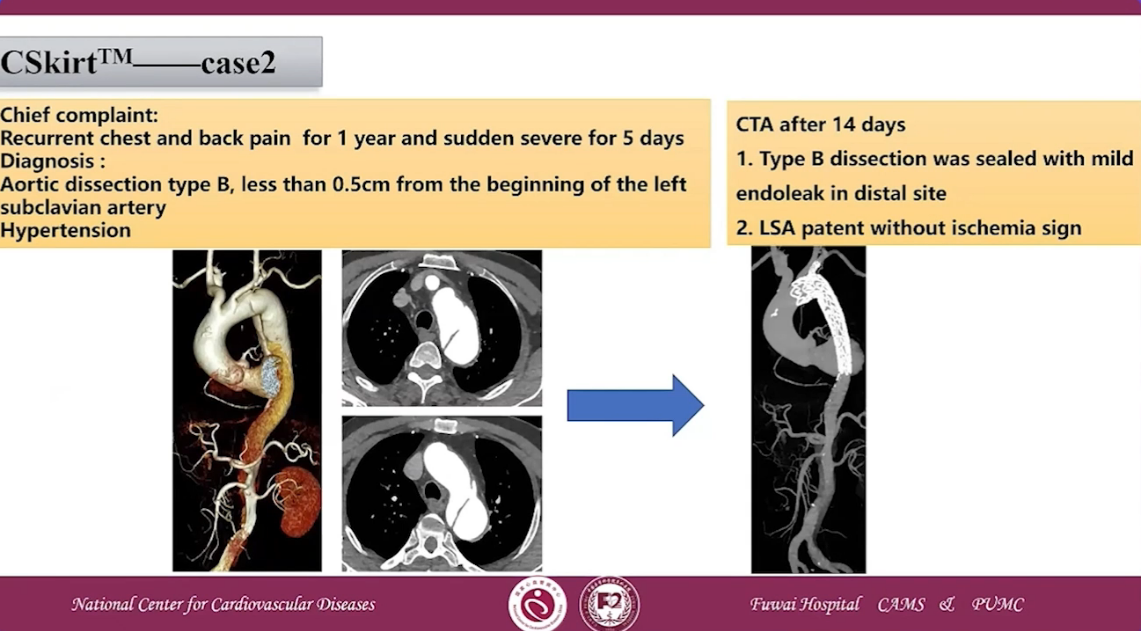
CSKirtTM case 2
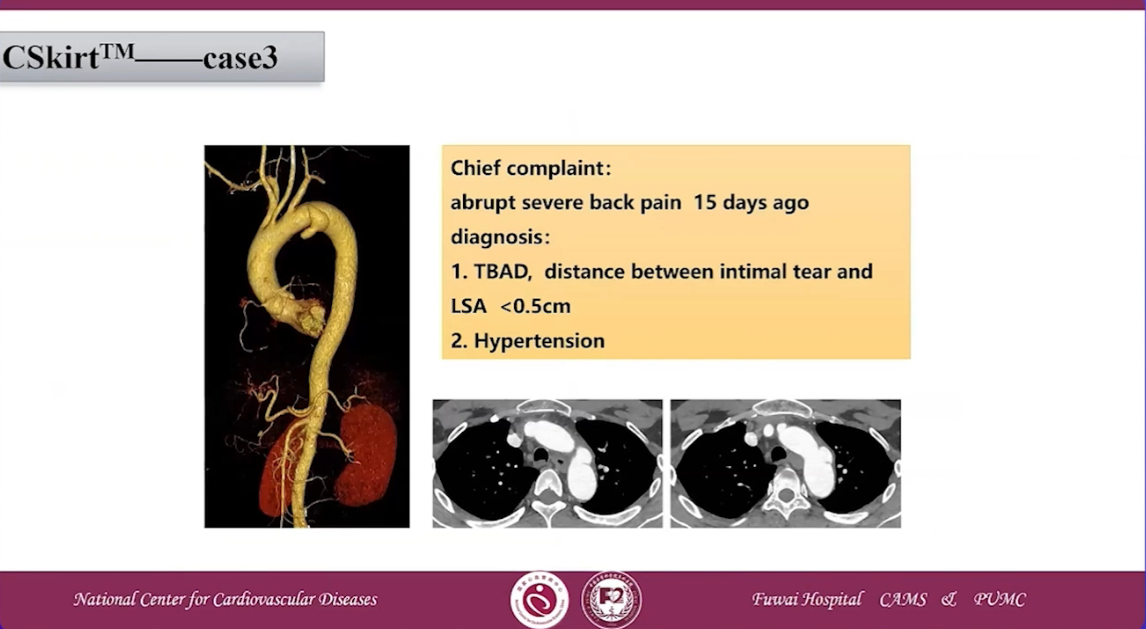
CSKirtTM case 3
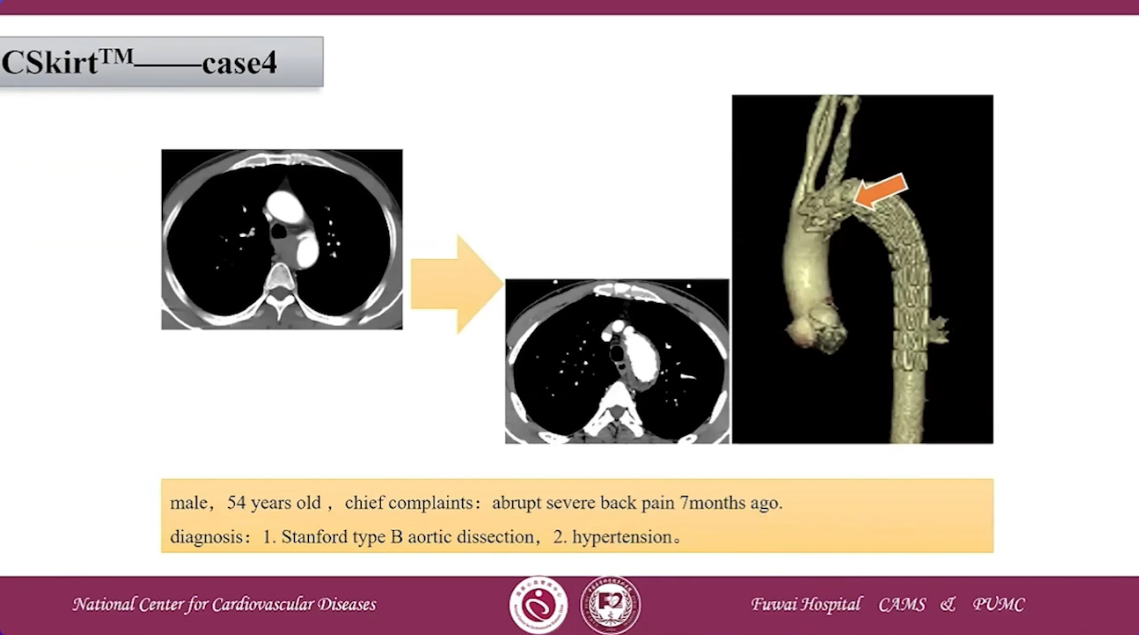
CSKirtTM case 4
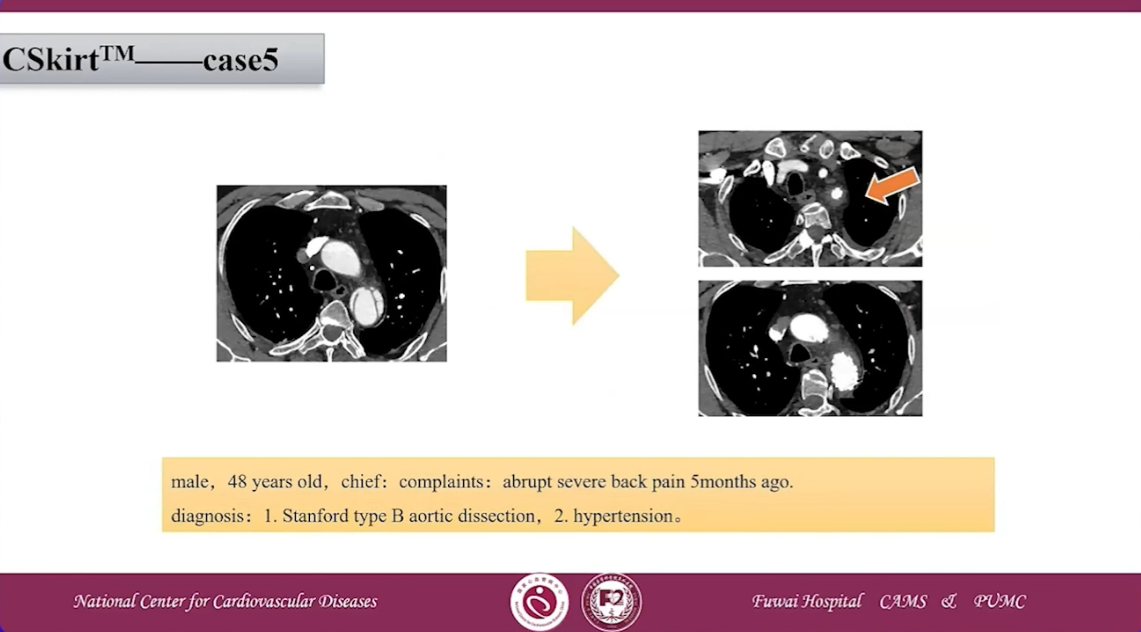
CSKirtTM case 5
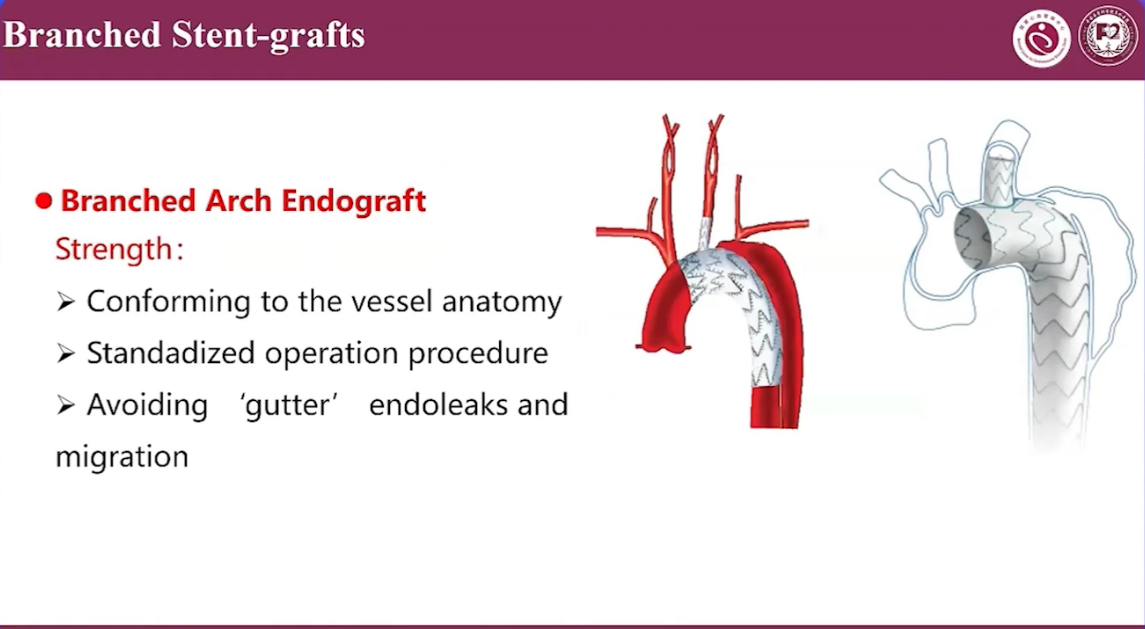
Branched Arch Endograft Strength:
•Conforming to the vessel anatomy
•Standadized operation procedure
•Avoiding 'gutter'endoleaks andmigration
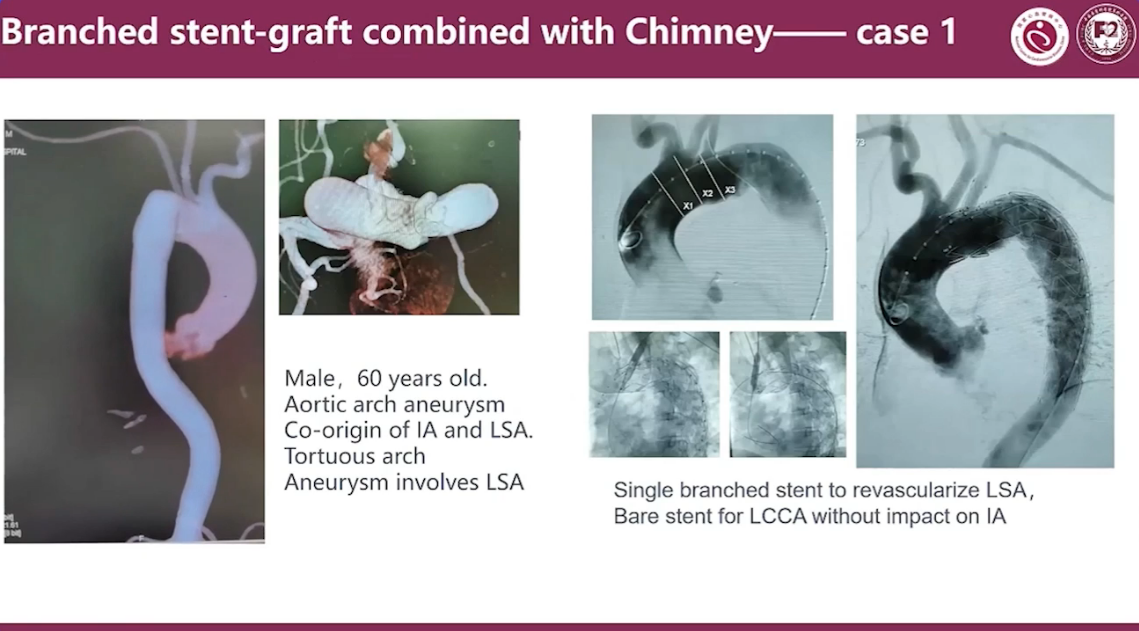
Branched stent-graft combined with Chimney Case 1
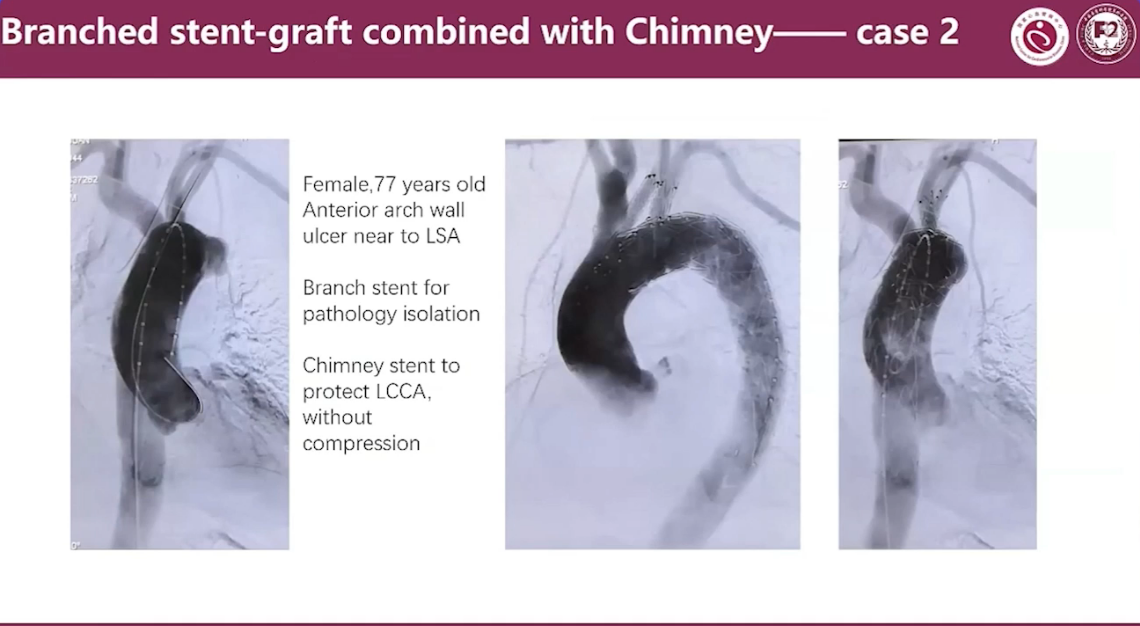
Branched stent-graft combined with Chimney Case 2
Branched stent-graft combined with Chimney Case 3
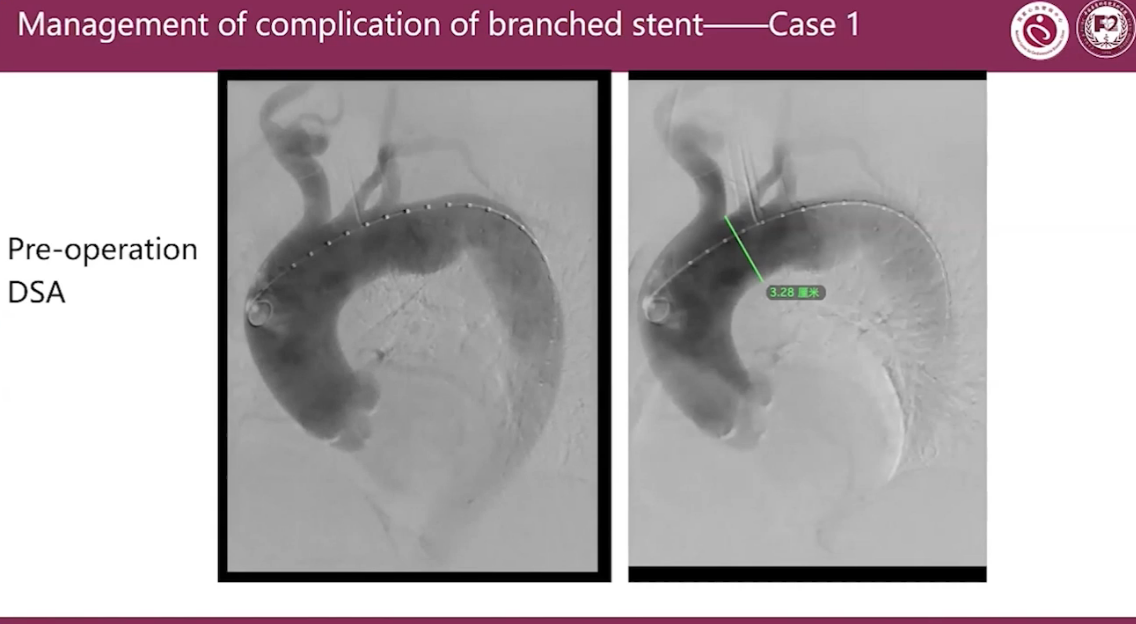
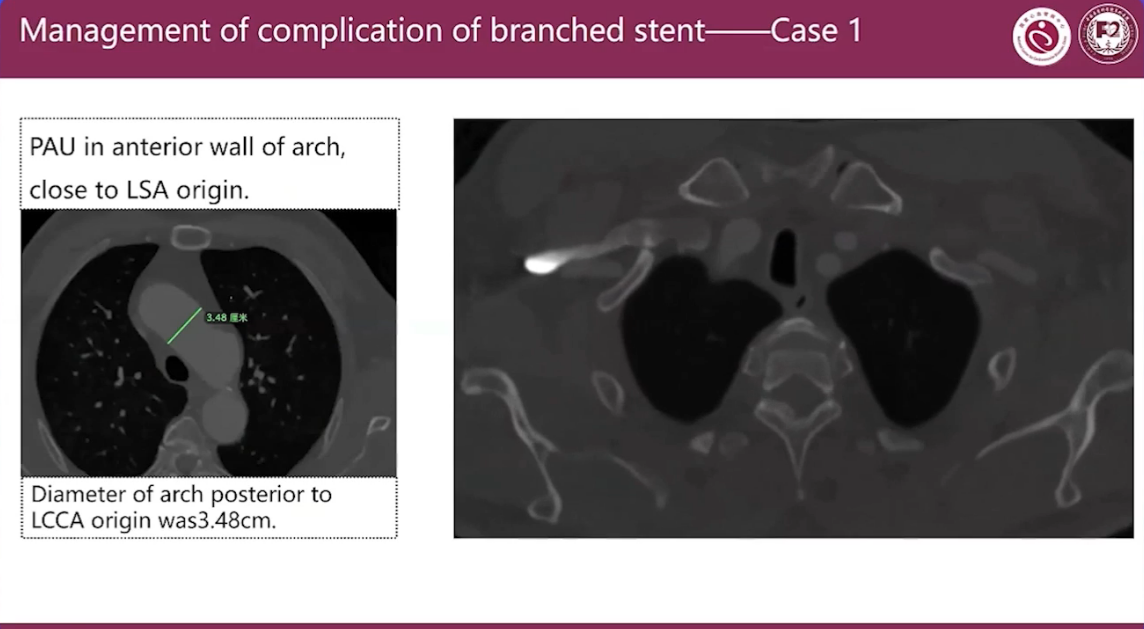
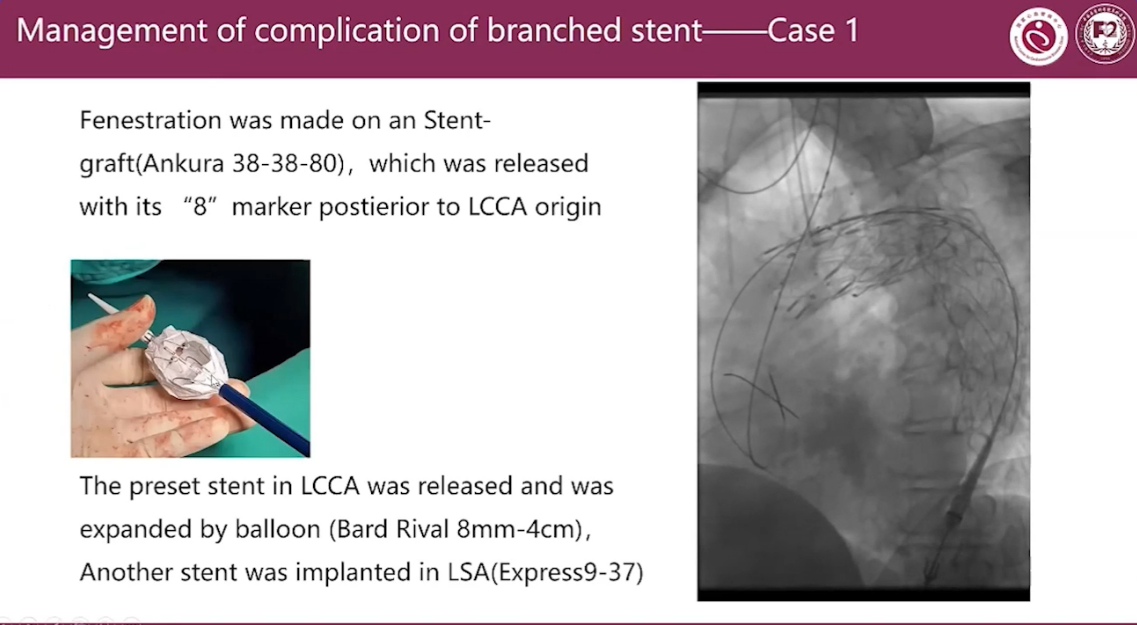
Management of complication of branched stent Case 1
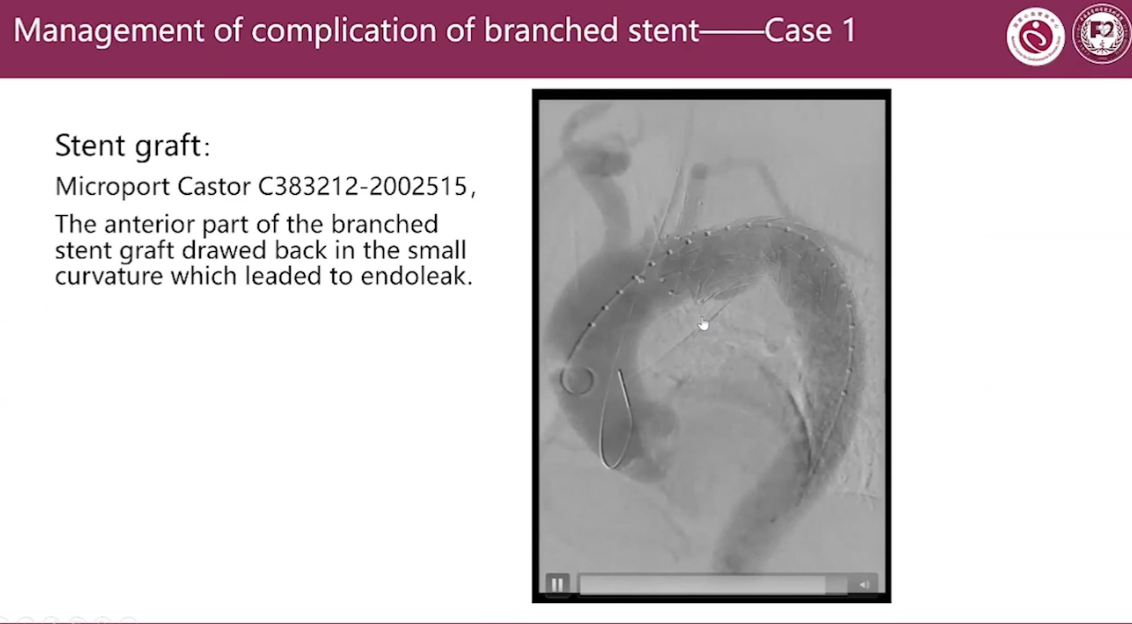
Stent graft:
Microport Castor C383212-2002515
The anterior part of the branched stent qraft drawed back in the small curvature which leaded to endoleak.
Management of complication of branched stent Case 1
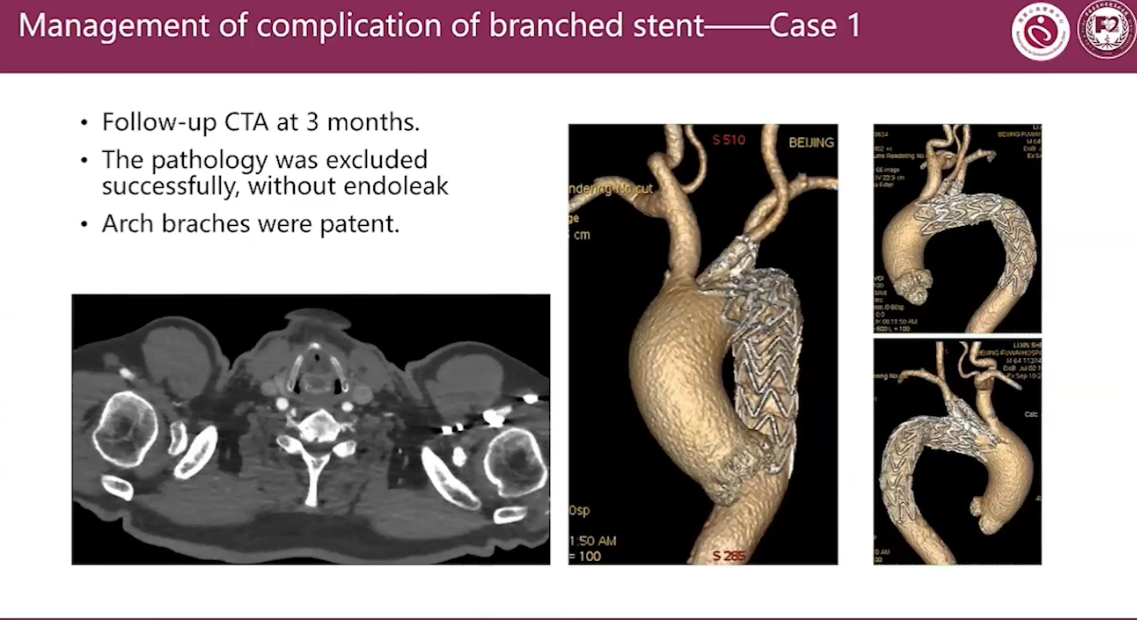
•Follow-up CTA at 3 months.
•The pathology was excluded successfully, without endoleak
•Arch braches were patent.
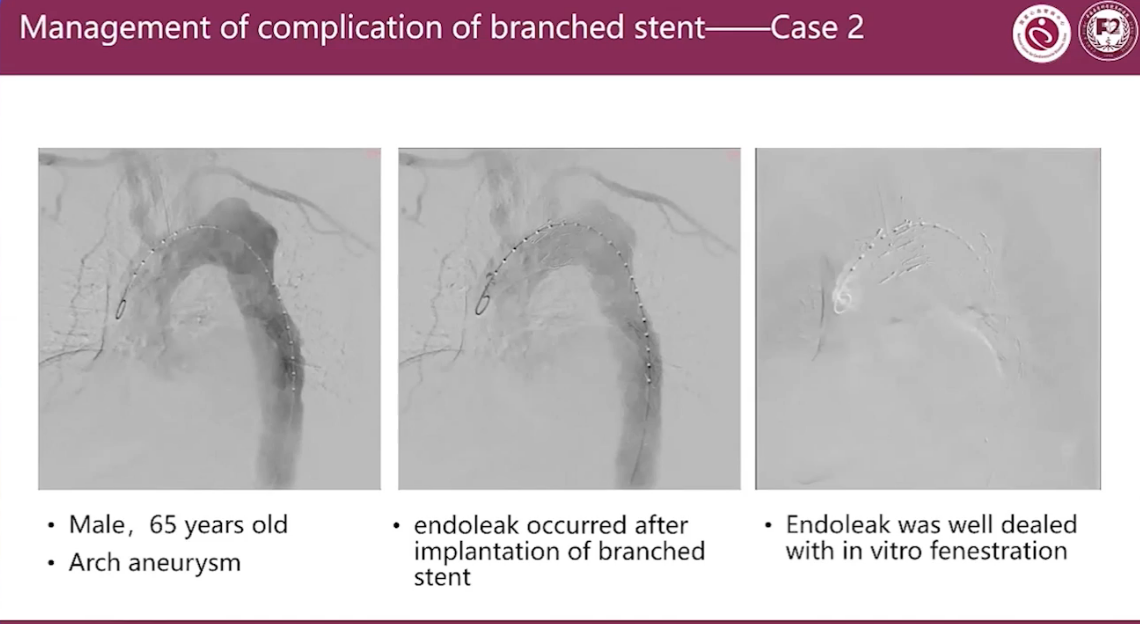
Management of complication of branched stent Case 2
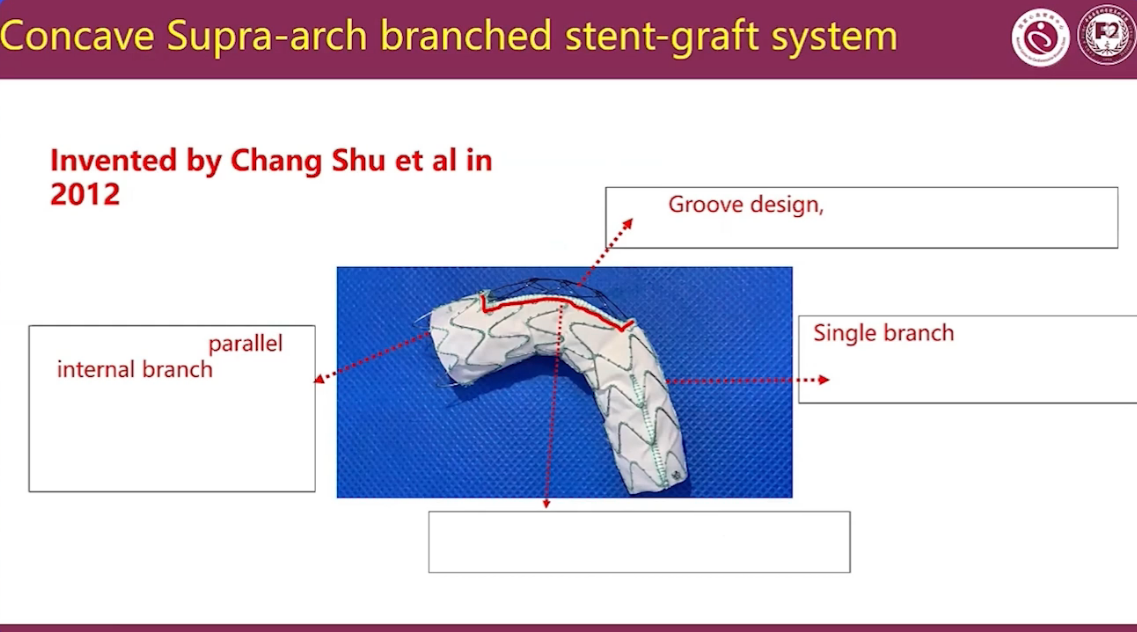
Concave Supra-arch branched stent-graft system
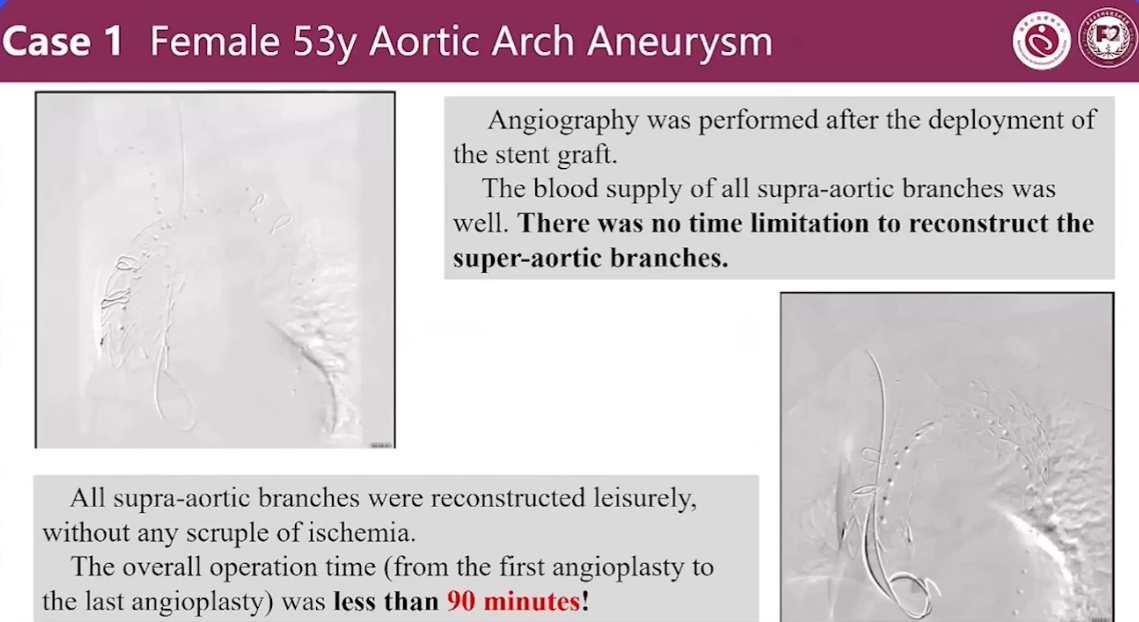
Case 1 Female 53y Aortic Arch Aneurysm
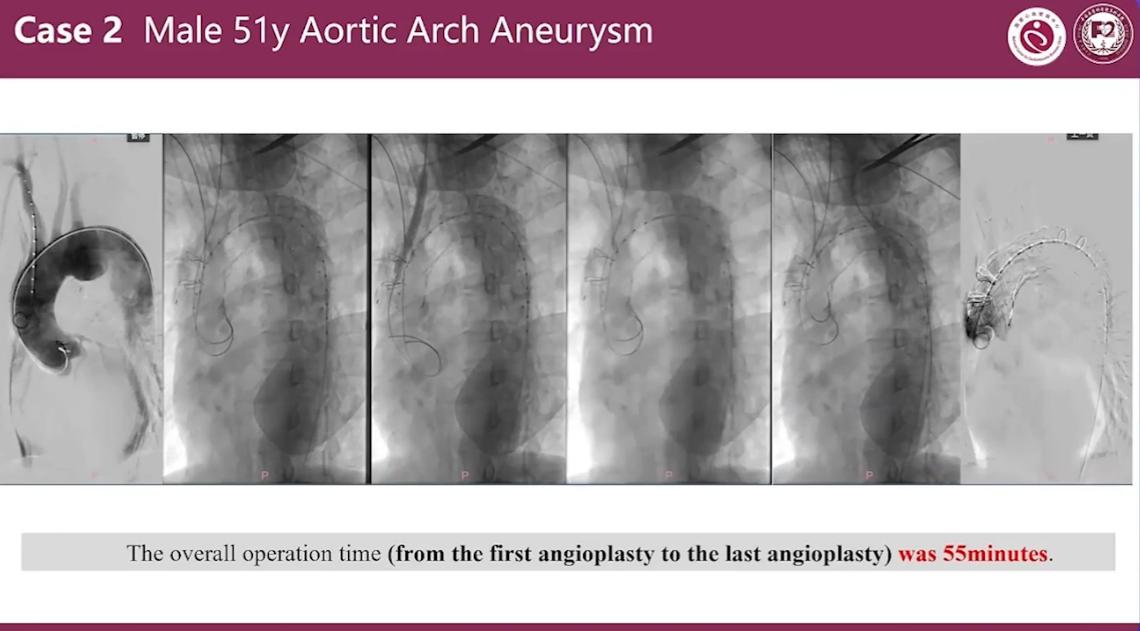
Case 2 Male 51y Aortic Arch Aneurysm
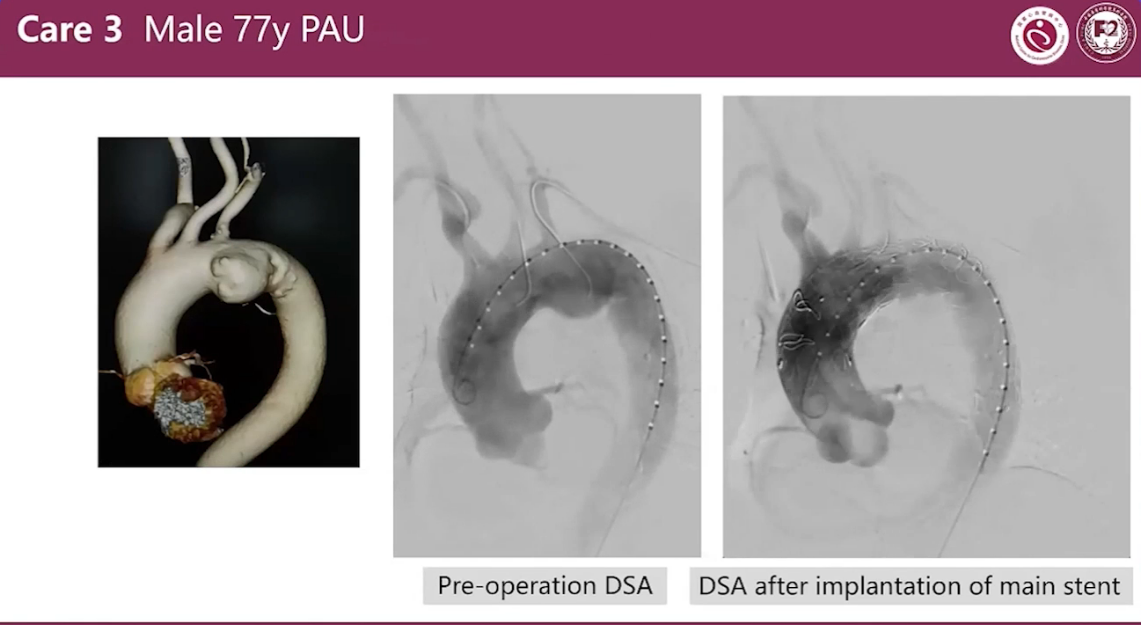
Case 3 Male 51y PAU
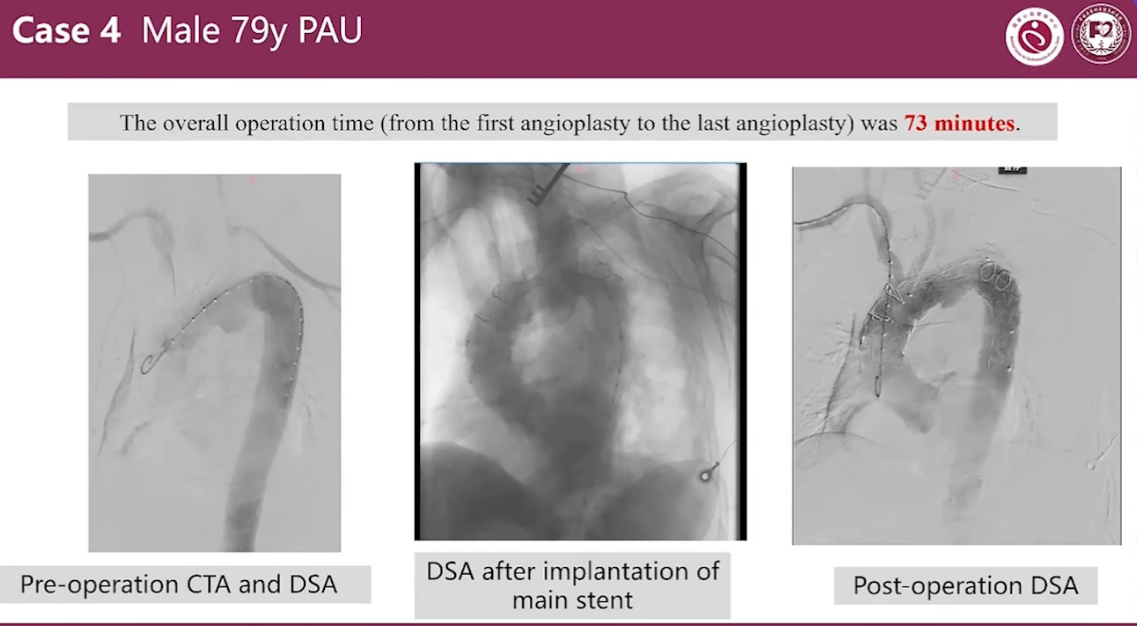
Case 4 Male 79y PAU
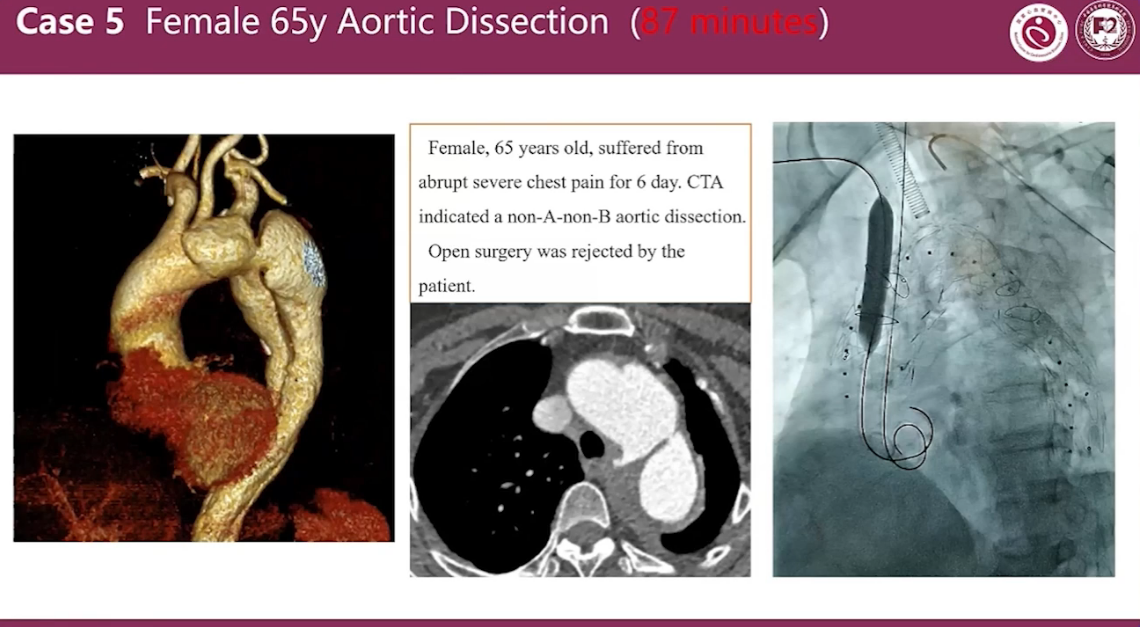
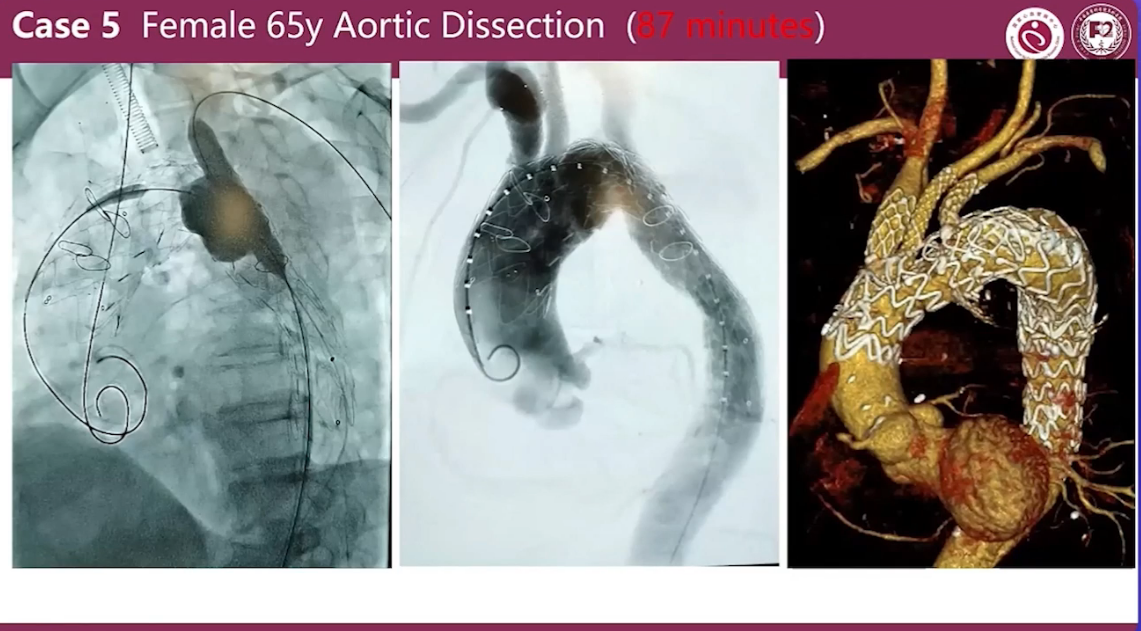
Case 5 Female 65y Aortic Dissection (87 minutes)
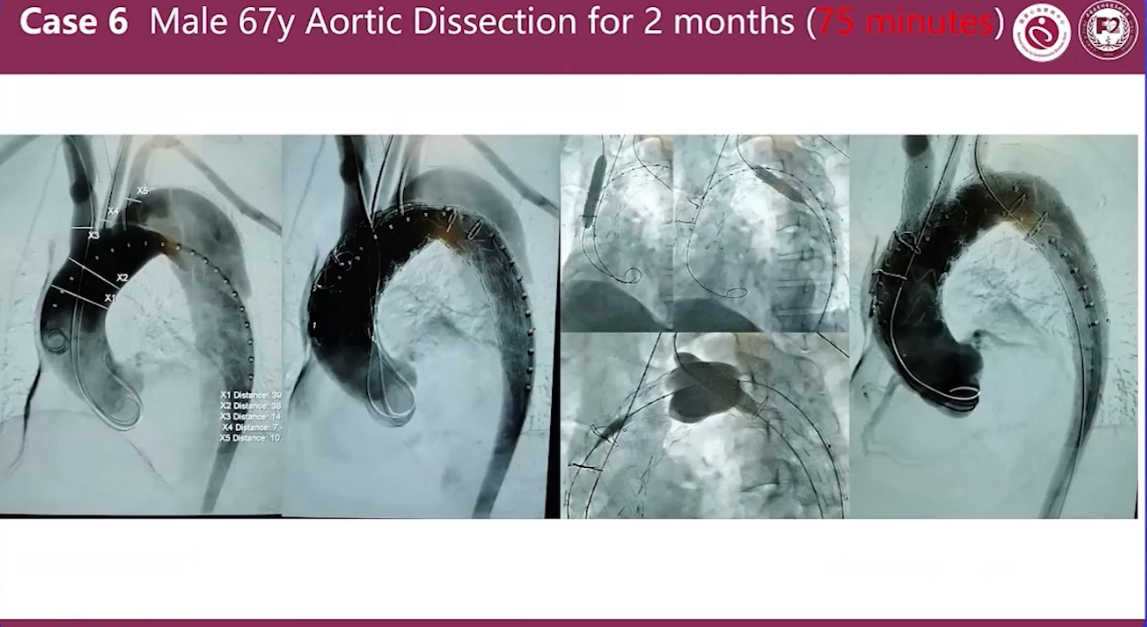
Case 6 Male 67y Aortic Dissection for 2 months (75 minutes)
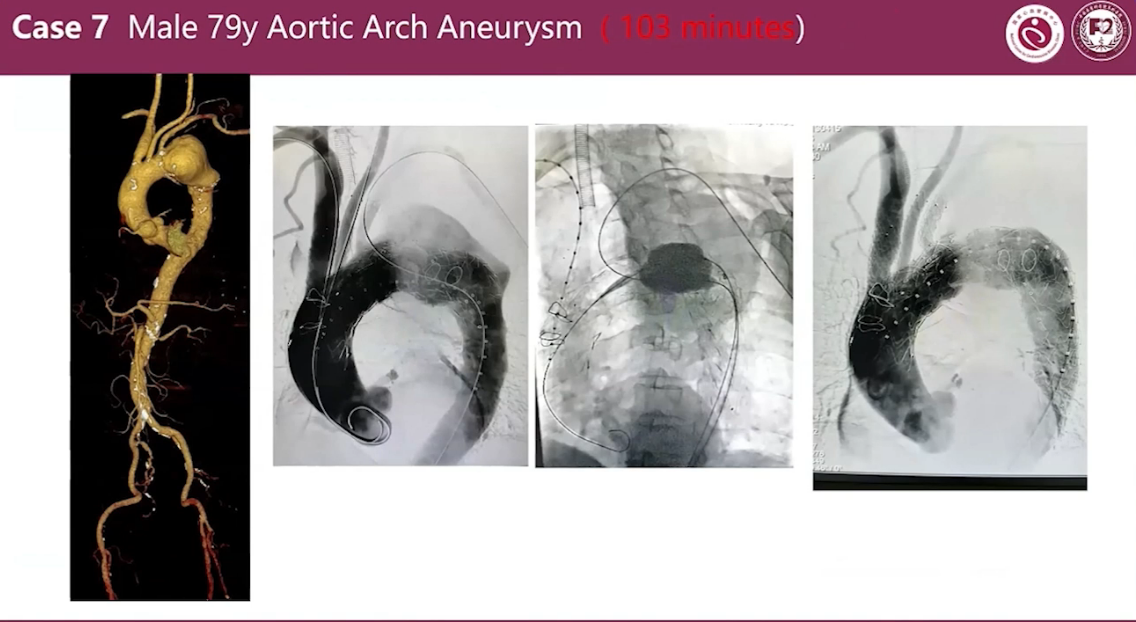
Case 7 Male 79y Aortic Arch Aneurysm (103 minutes)
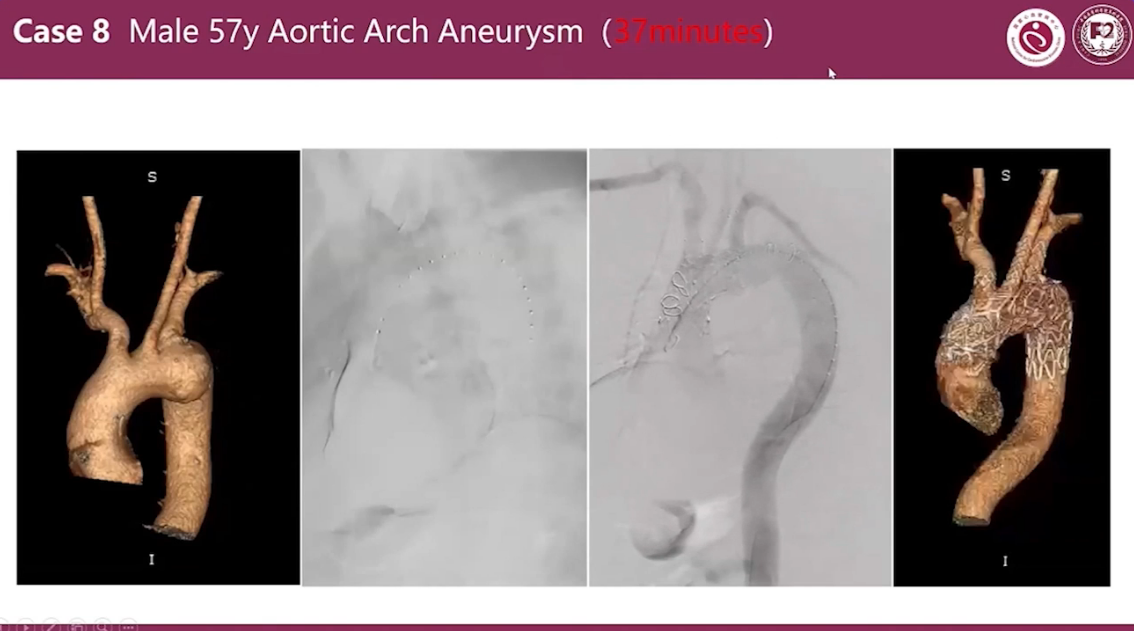
Case 8 Male 57y Aortic Arch Aneurysm (37 minutes)
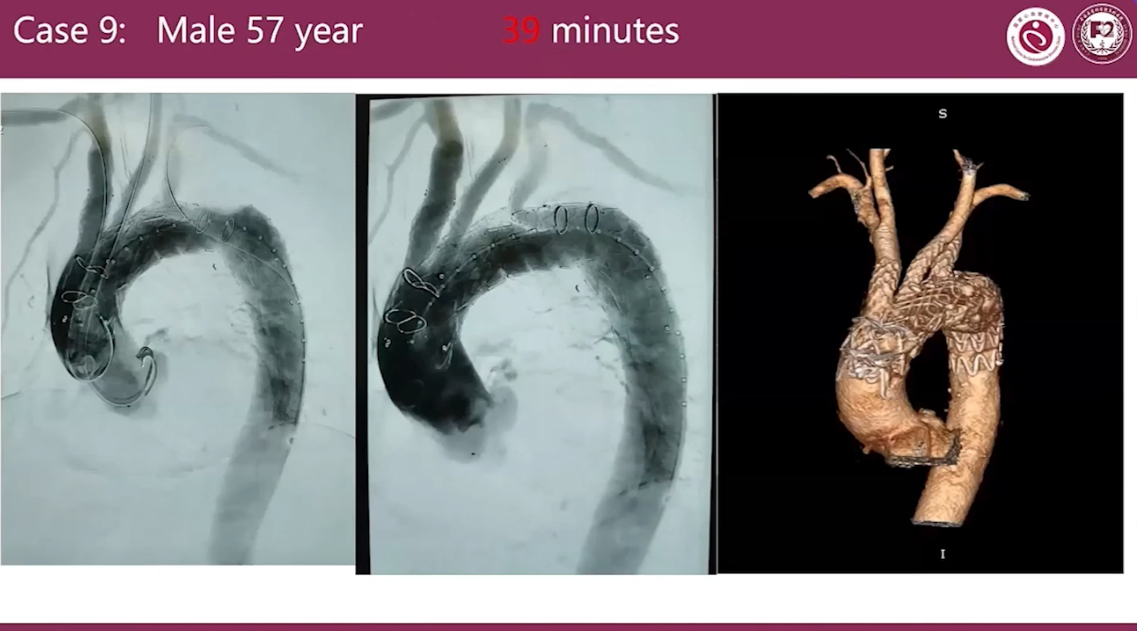
Case 9
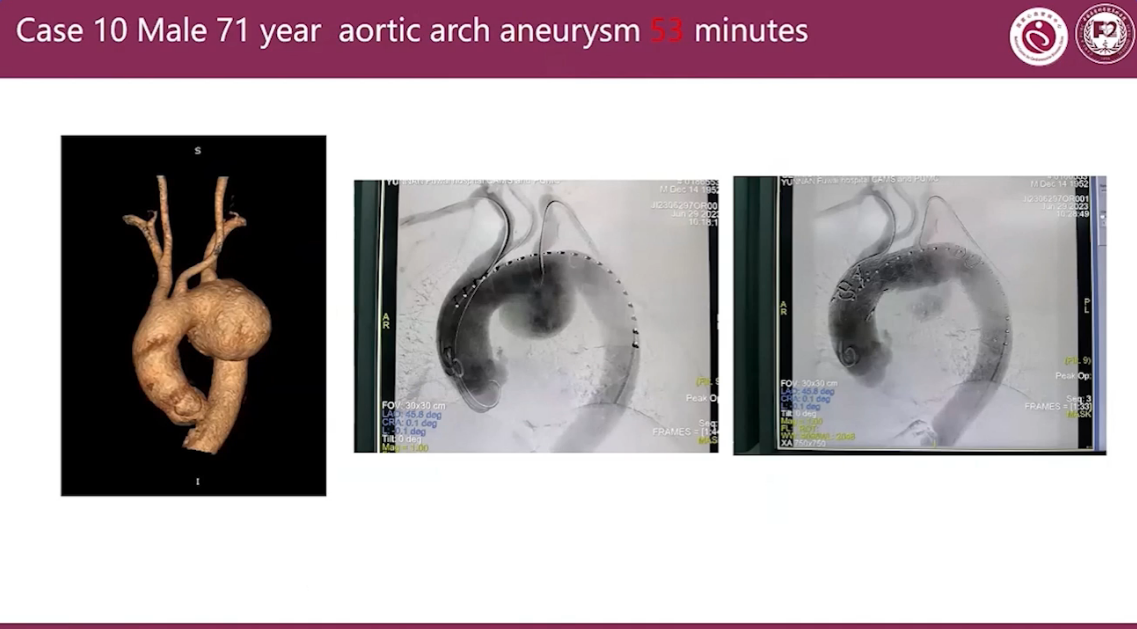
Case 10 Male 71 year aortic arch aneurysm 53 minutes
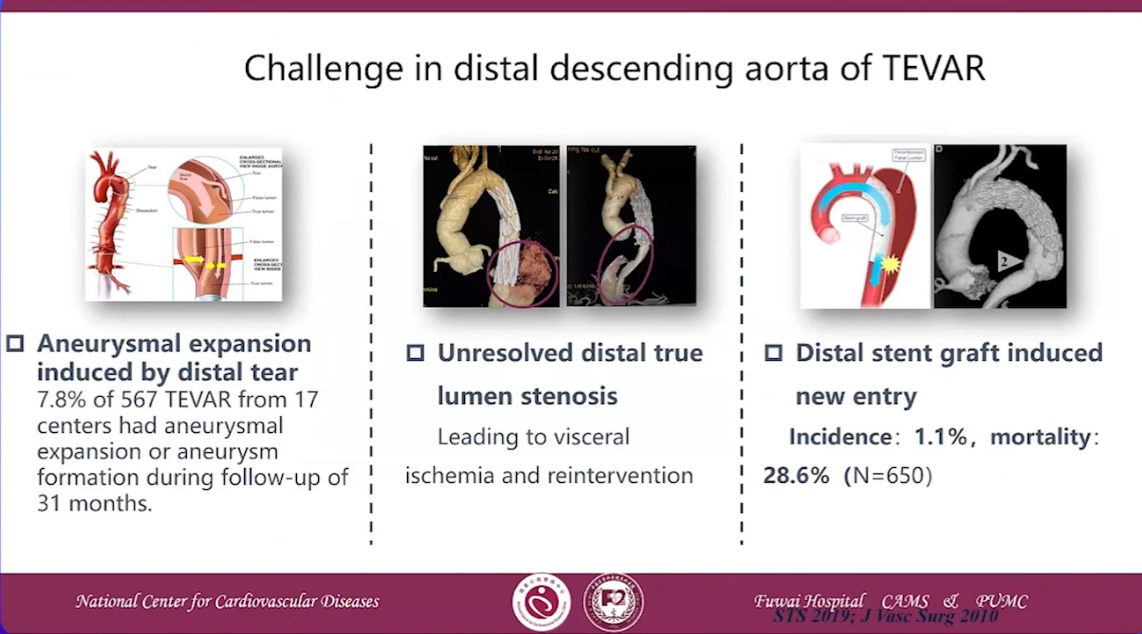
Challenge in distal descending aorta of TEVAR
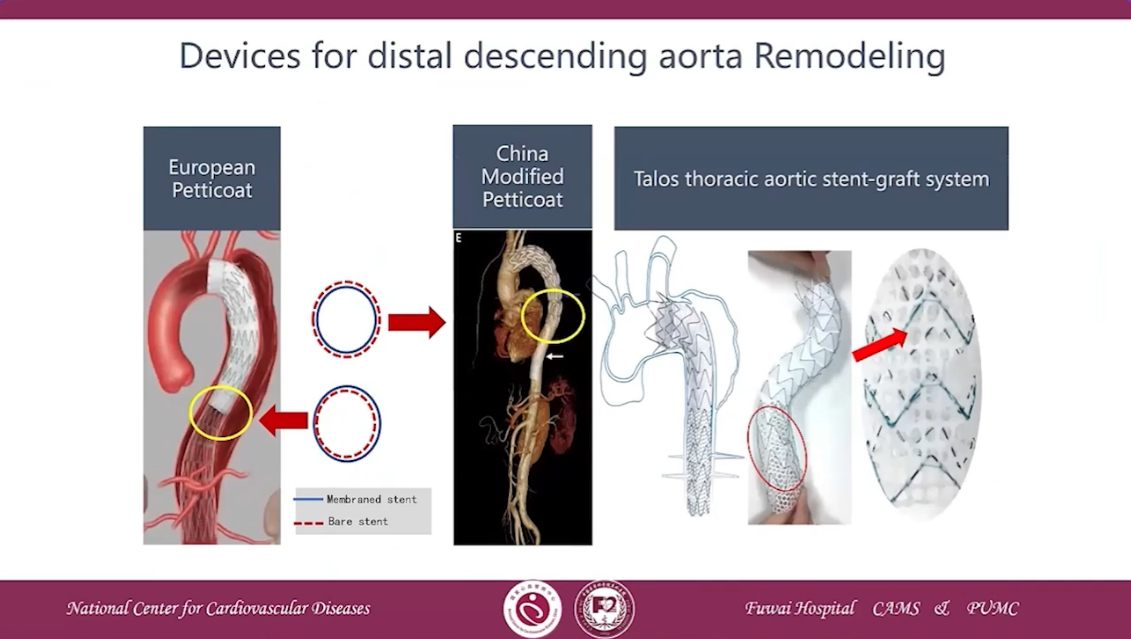
Devices for distal descending aorta Remodeling
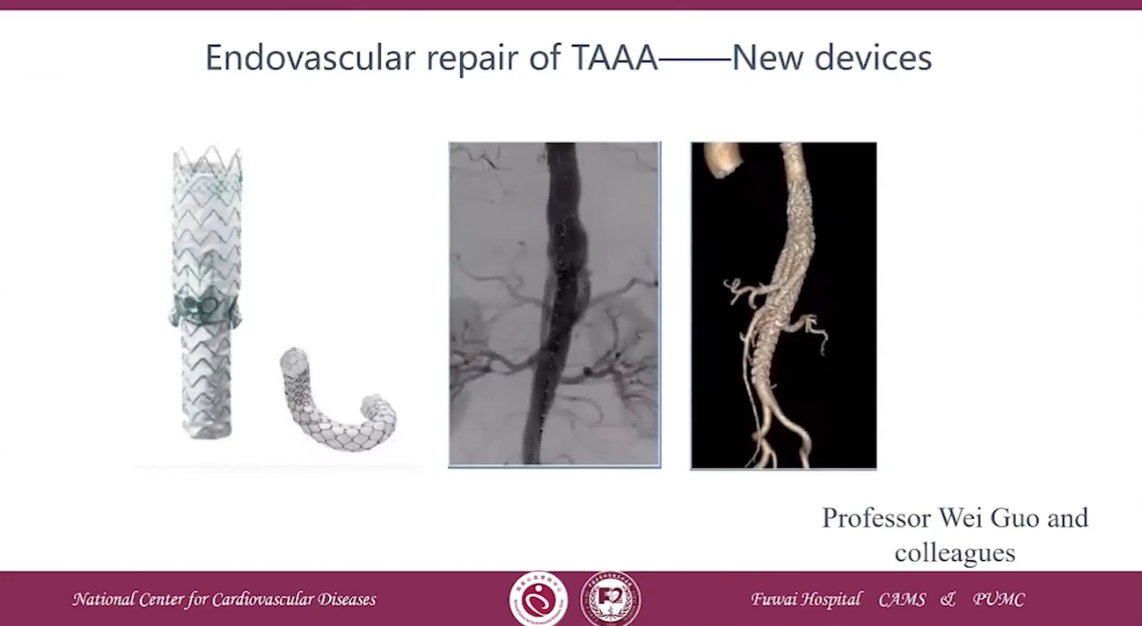
Endovascular repair of TAAA-New Devices
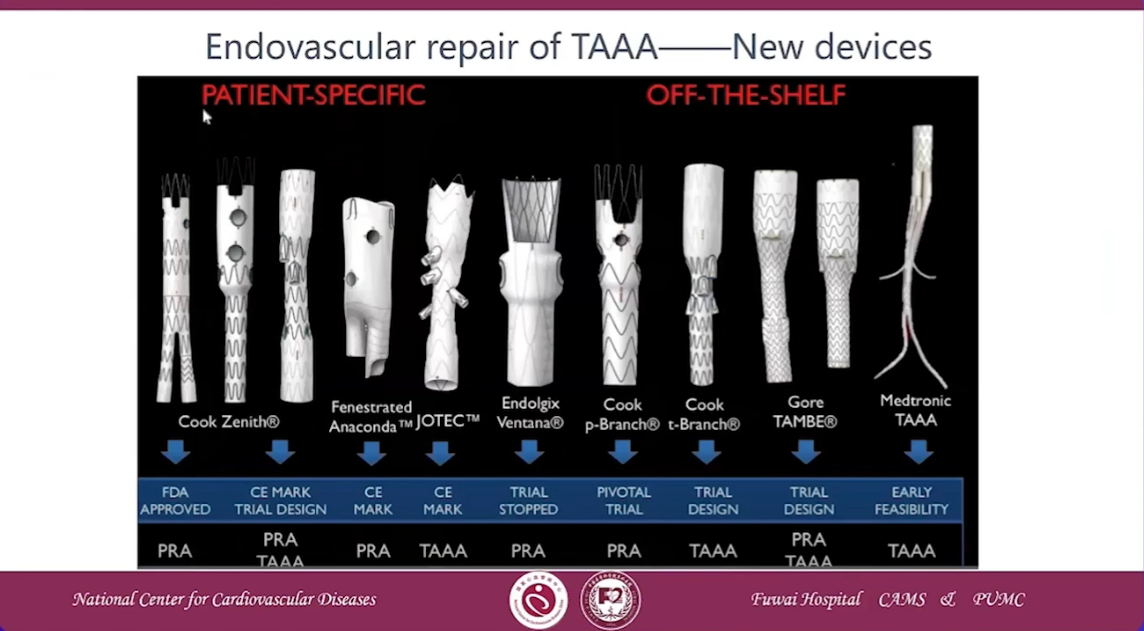
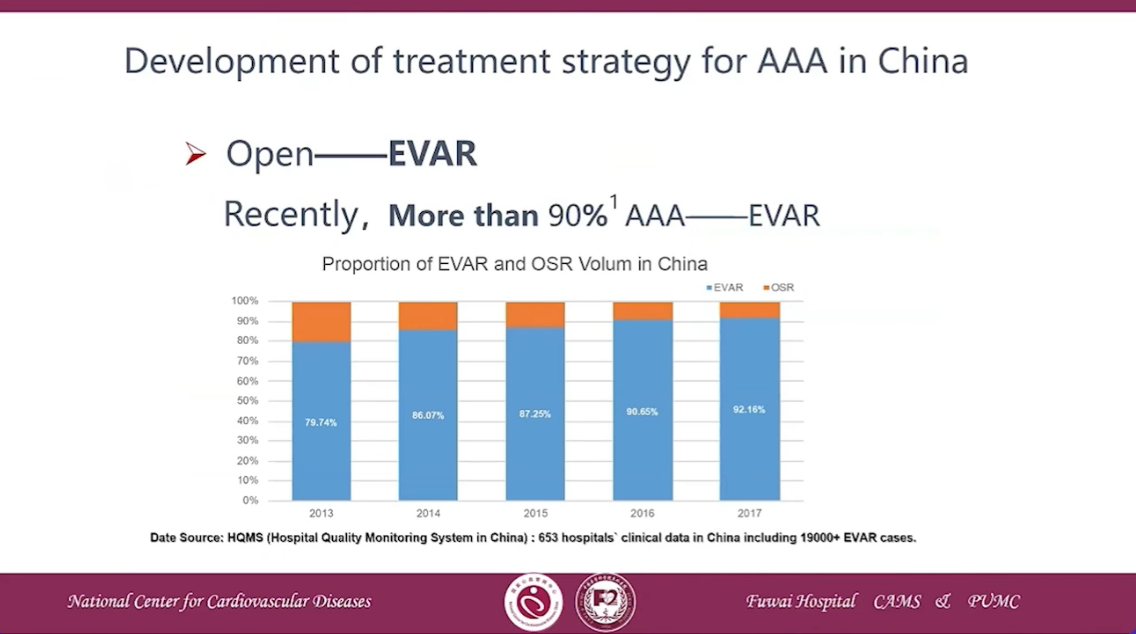
Development of treatment strategy for AAA in China

On the table fenestration
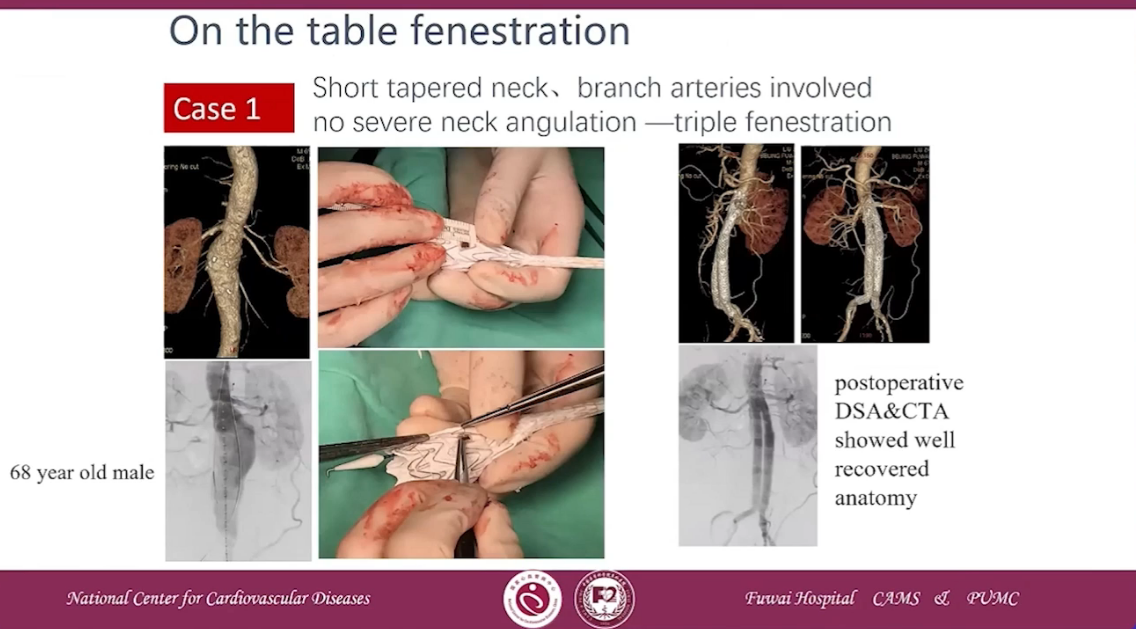
Case 1
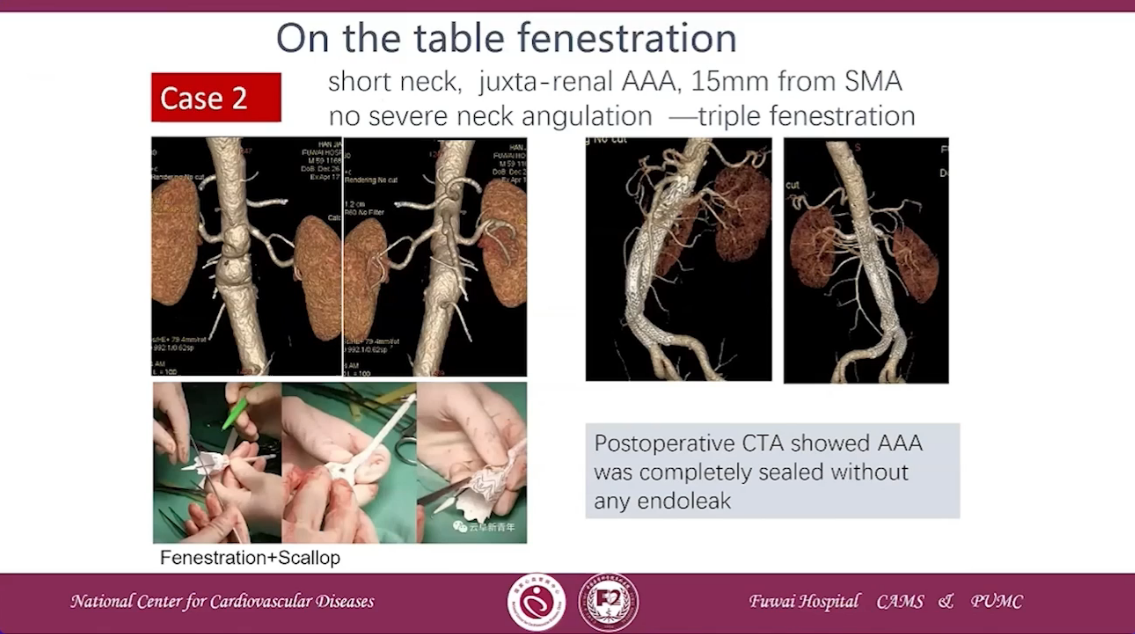
Case 2
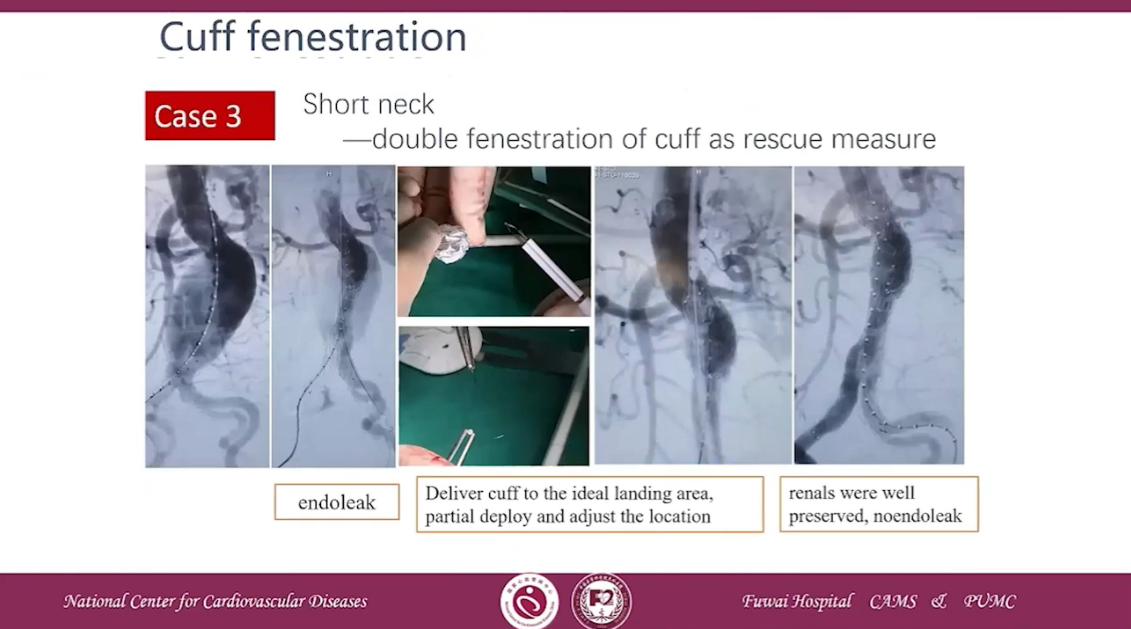
Case 3 Short neck- double fenestration of cuff as rescue measure
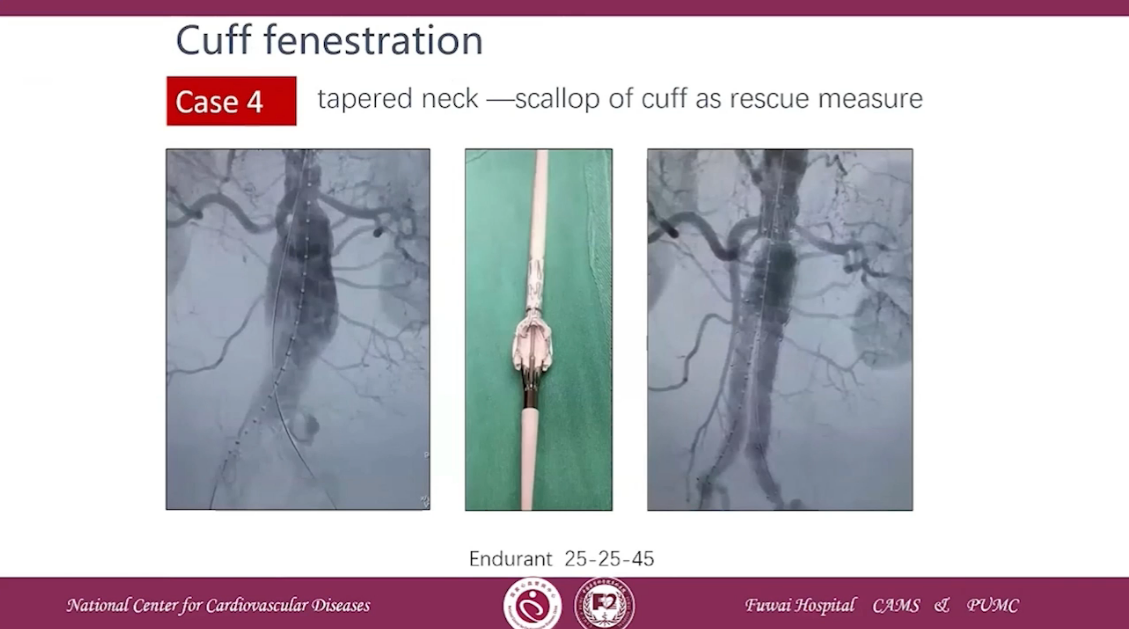
Case 4 tapered neck-scallop of cuff as rescue measure
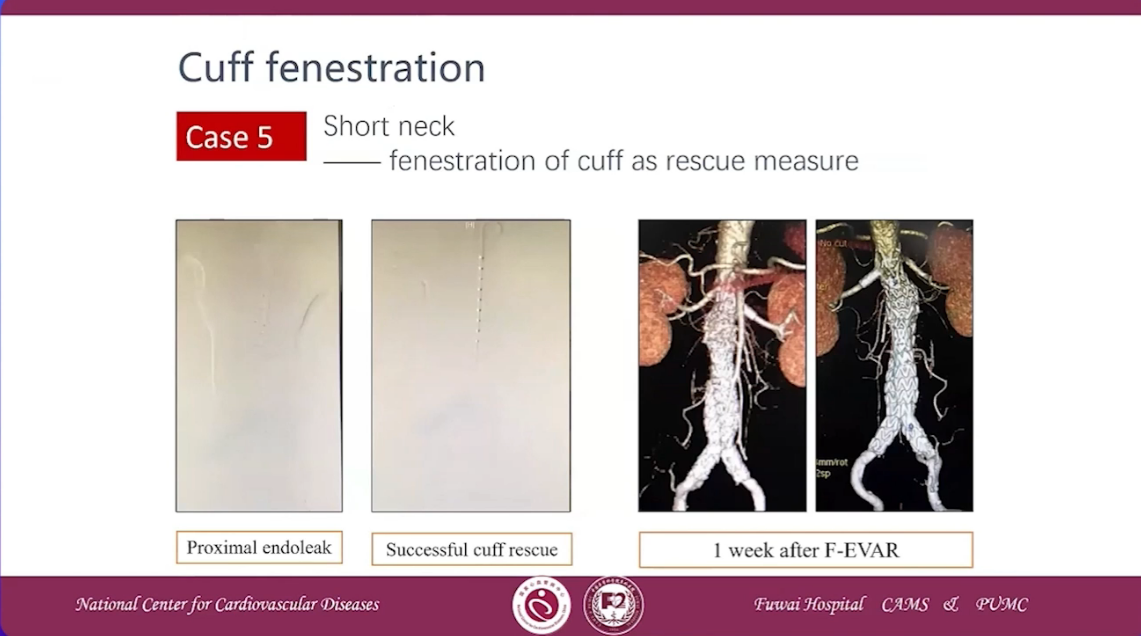
Case 5 Short neck-fenestration of cuff as rescue measure
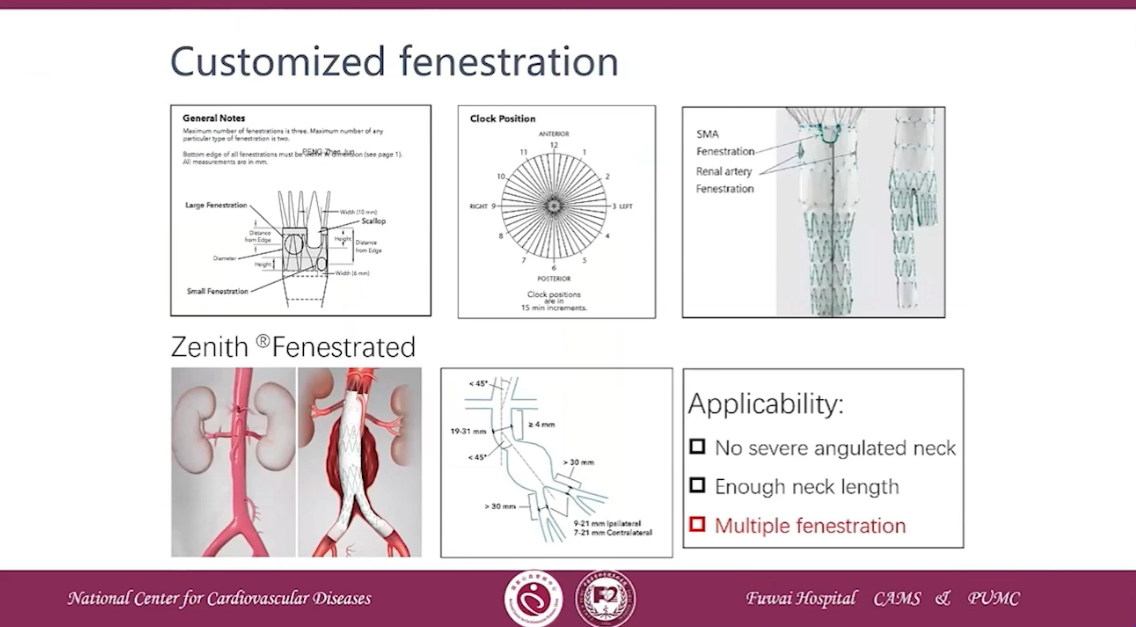
Customizeed fenestration
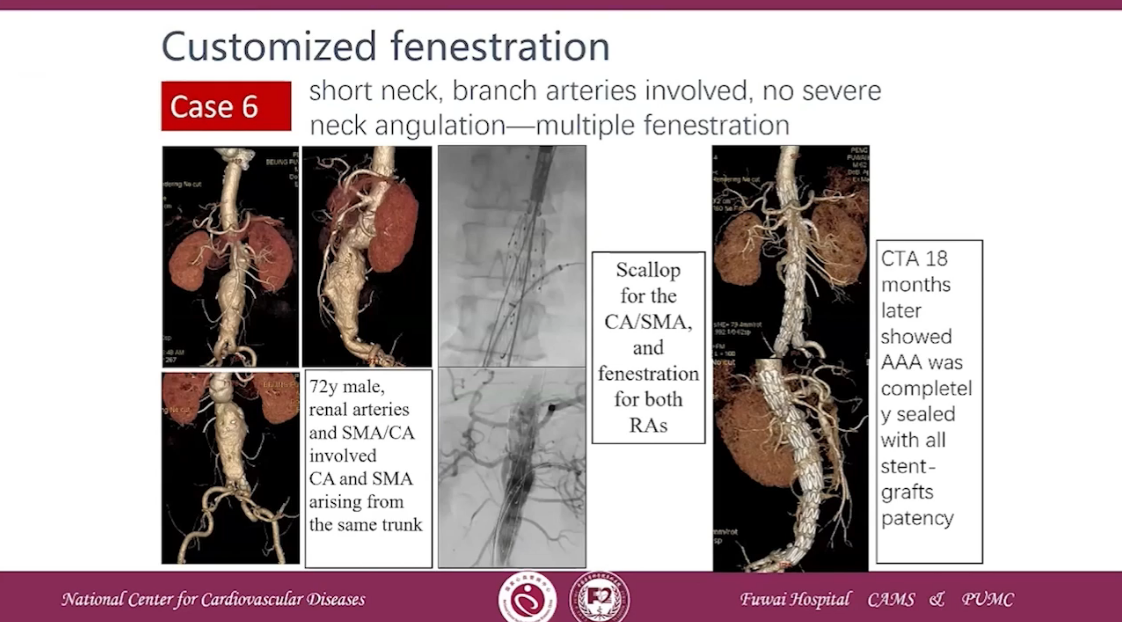
Case 6 short neck, branch arteries involved, no severe neck angulation-multiple fenestration
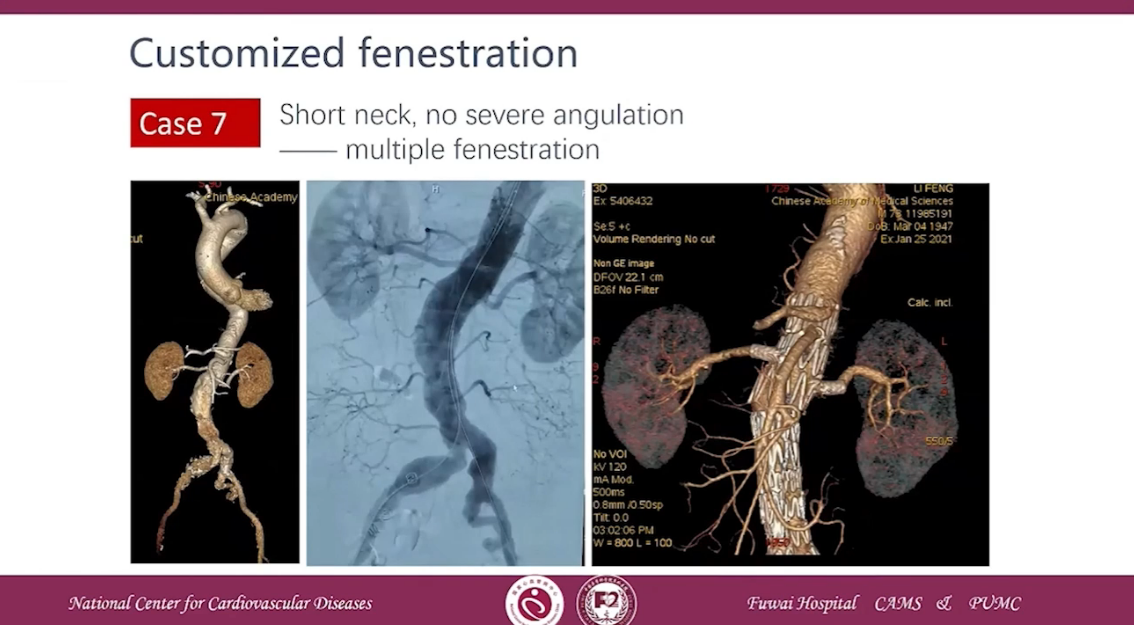
Case 7 Short neck, no severe angulation-multiple fenestration
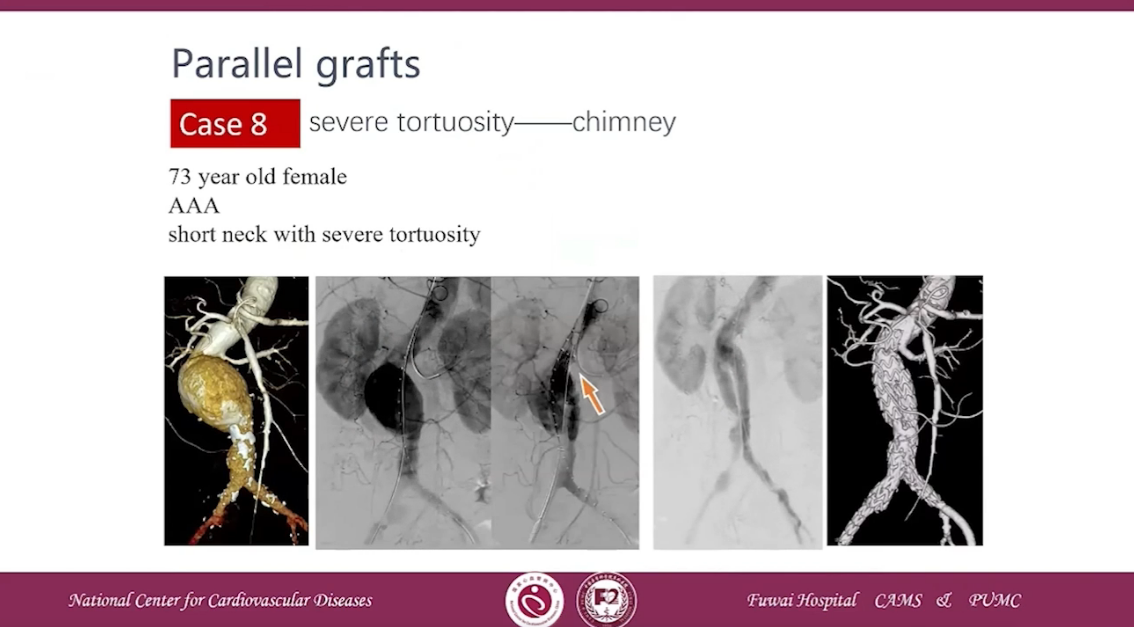
Case 8 severe tortuosity-chimney
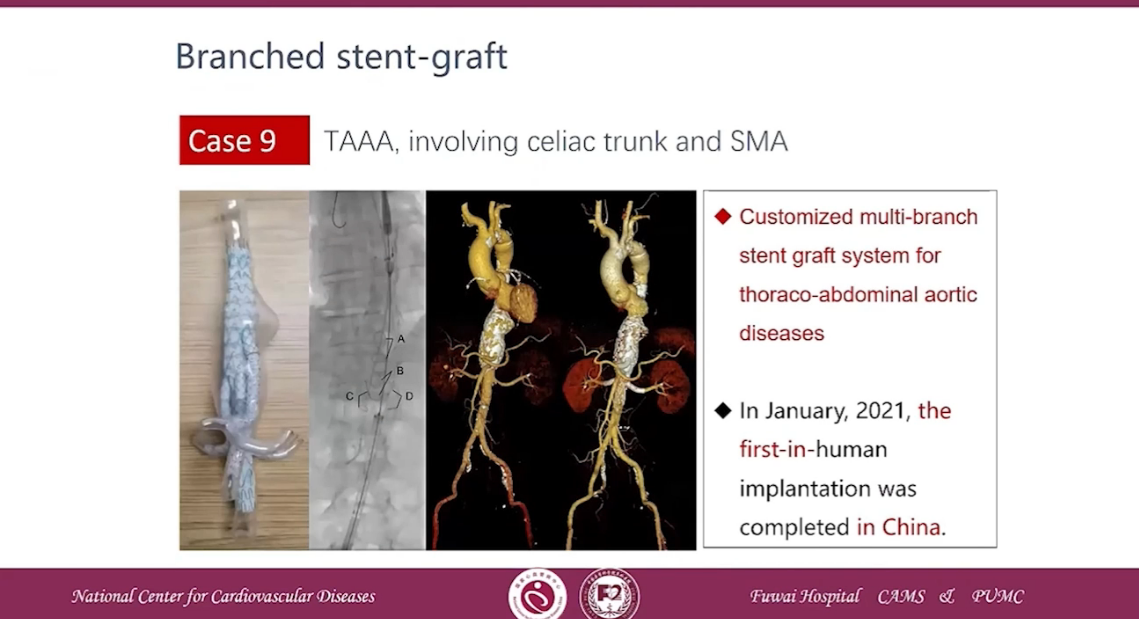
Case 9 TAAA, involving celiac trunk and SMA
•The treatment of aortic disease is gradually transitioning from open surgery to hybrid surgery and endovascular repair. Minimally invasive treatment is the trend.
•Open surgery is still the fundamental treatment option for aortic disease and gold standard for complex pathologies.
•Individualized strategy is recommended based on the various characteristcs of anatomy and pathology of aortic diseases.
•Be cautious for arch reconstruction and only performed when necessary. Many newly designed non-customized stent-grafts for single, double, and triple supra-arch branchesreconstruction are on the way, while more datas are needed on its safety and effectiveness


