
On September 13, 2024, during the 9th China Vascular Conference (CVC 2024), Professor Shu Chang from the Department of Vascular Surgery at Fuwai Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, shared the 2024 China Vascular Disease Medical Quality Report. He summarized the status of vascular disease treatment in China in 2023 and provided new insights for the future.

National Vascular Disease Medical Quality Control Platform Development
•January 2018: Establishment of the Expert Committee on Vascular Surgery under the National Cardiovascular Disease Professional Quality Control Center.
•November 2023: Establishment of the National Peripheral Vascular Interventional Technique Quality Control Center (in preparation).
•January 2024: Establishment of the Expert Committee of the National Peripheral Vascular Interventional Technique Quality Control Center (including five sub-specialty expert groups for venous diseases, lower extremity arterial diseases, carotid artery diseases, aortic diseases, and visceral artery diseases).
National-Level Vascular Disease Medical Quality Data Publication
Since 2020, participation in the compilation and publication of the National Medical Services and Quality Safety Report: Cardiovascular Disease Specialty and the vascular surgery section of the China Cardiovascular Health and Disease Report. In 2024, led the compilation of the National Peripheral Vascular Interventional Technique Medical Quality Report. This report comprehensively reflects and evaluates the current state of vascular disease treatment in China and was released during the 2024 China Heart Congress (CHC) & China Vascular Conference (CVC).
Data Sources for the Vascular Disease Medical Quality Report
The medical quality evaluation data is derived from the National Hospital Quality Monitoring System (HQMS). In 2023, a total of 8,119 hospitals were included, comprising 2,549 tertiary hospitals and 5,570 secondary hospitals. In 2023, 76.498 million cardiovascular inpatients were registered, of which 18.237 million (23.8%) had a primary diagnosis of cardiovascular disease, and 58.261 million (76.2%) had a secondary diagnosis of cardiovascular disease.
Current Status of Aortic Disease Treatment in China
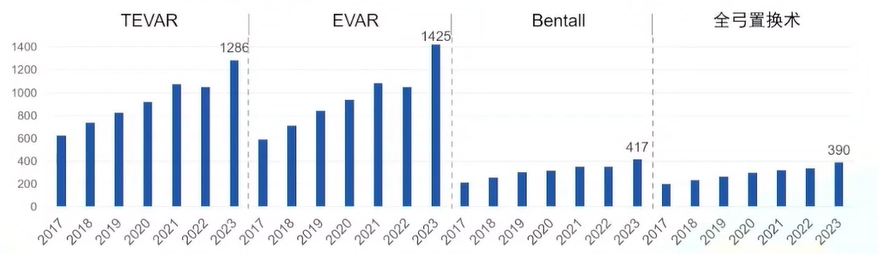
Four representative procedures for aortic disease are TEVAR, EVAR, Bentall, and total arch replacement. From 2017 to 2023, the number of procedures showed an overall growth trend, with minor fluctuations during the pandemic:
•TEVAR: Increased from 13,709 cases to 30,852 cases (+125.0%).
•EVAR: Increased from 7,611 cases to 25,936 cases (+240.8%).
•Bentall: Increased from 3,105 cases to 8,044 cases (+159.1%).
•Total Arch Replacement: Increased from 3,707 cases to 12,823 cases (+245.9%).

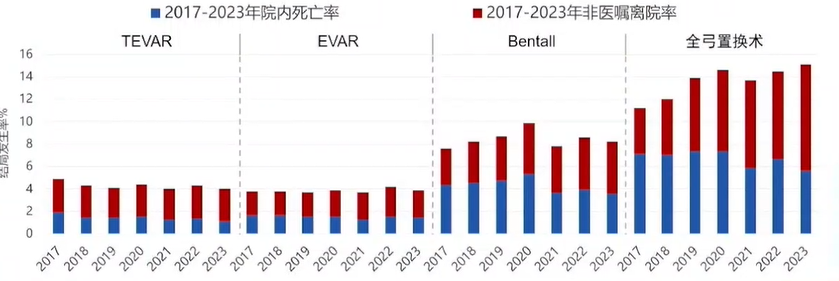
Key Changes in Aortic Surgery from 2017 to 2023
•TEVAR: Mortality rate decreased to 1.2%; non-recovery discharge rate decreased to 4.0%.
•EVAR: Mortality rate decreased to 1.5%; non-recovery discharge rate decreased to 3.9%.
•Bentall: Mortality rate decreased to 3.6%; non-recovery discharge rate decreased to 8.2%.
•Total Arch Replacement: Mortality rate decreased to 5.7%; non-recovery discharge rate increased to 15.1%.
The number of hospitals performing aortic surgeries has shown an upward trend overall. By 2023, 1,663 hospitals (20.5%) performed endovascular aortic surgeries, and 590 hospitals (7.3%) performed open aortic surgeries.
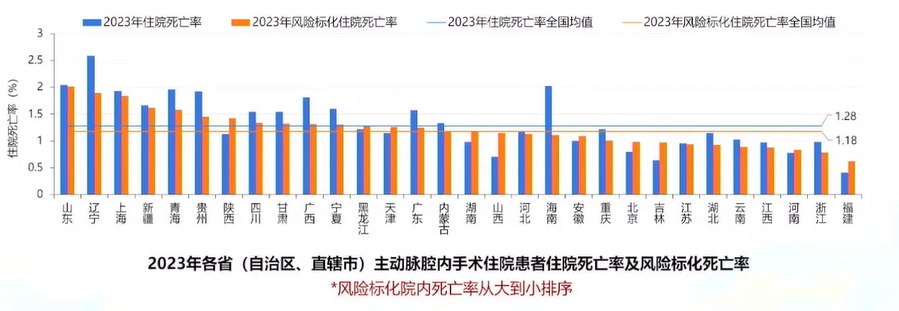
2023 National Average Quality Metrics for Aortic Endovascular Surgery
•National average in-hospital mortality rate: 1.28% (decreased).
•Risk-adjusted in-hospital mortality rate: 1.18% (decreased).
16 provinces had a risk-adjusted mortality rate higher than the national average, while 14 provinces had a rate lower than the national average.
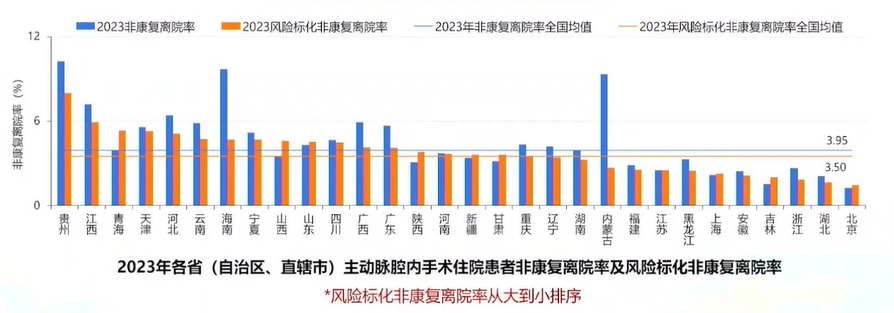
•National average non-recovery discharge rate: 3.50% (decreased).
•Risk-adjusted non-recovery discharge rate: 3.95%.
17 provinces had a risk-adjusted non-recovery discharge rate higher than the national average, while 13 provinces had a rate lower than the national average.
Summary
The following four trends can be observed in vascular disease treatment in China:
1. Stable Development: The number of vascular surgeries is increasing yearly, with endovascular procedures growing more rapidly.
2. Hospital Distribution Variations: The distribution of surgeries varies significantly between hospitals, with a small number of hospitals performing a large proportion of surgeries.
3. Importance of Technical Guidance: Surgical quality correlates with surgical volume, highlighting significant differences in a small number of hospitals.
4. Overall Quality Improvement: The diverse types of peripheral vascular diseases benefit from a unified platform for quality control.


