
During the 9th China Vascular Conference (CVC 2024) on September 12, Professor Wang Hao from the Vascular Surgery Department of Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, shared a case of subdiaphragmatic abdominal aorta–left external iliac artery bypass for the treatment of an infected abdominal aortic aneurysm.

Case Sharing
Patient Information (Male, Middle-aged)
Chief Complaint: Intermittent abdominal pain for 8 years, worsened and accompanied by fever for 1 week.
Past Medical History: Type 2 diabetes for over 10 years, managed with regular insulin therapy, but poor blood glucose control. The patient resided long-term in Bayannur City, Inner Mongolia, and had a history of extensive livestock farming.
Physical Examination: A pulsatile mass was palpable slightly to the left below the umbilicus.
Preoperative Tests:
•Preoperative white blood cell and neutrophil counts were within normal range.
•Moderate anemia with hemoglobin at 99 g/L.
•Liver and kidney function and blood electrolytes showed no significant abnormalities.
•CRP: 40.37 mg/L; PCT: 0.1 ng/ml; IL-6: 38.6 pg/ml.
Pathogen Indicators:
•Brucella Agglutination Test: Positive.
•Widal Test: Negative.
•Weil-Felix Test: Negative.
•T-SPOT Test: Negative.
•Consecutive 3-day blood cultures: Negative.
Preoperative CTA: Infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysm with mural hematoma and multiple collateral branches.
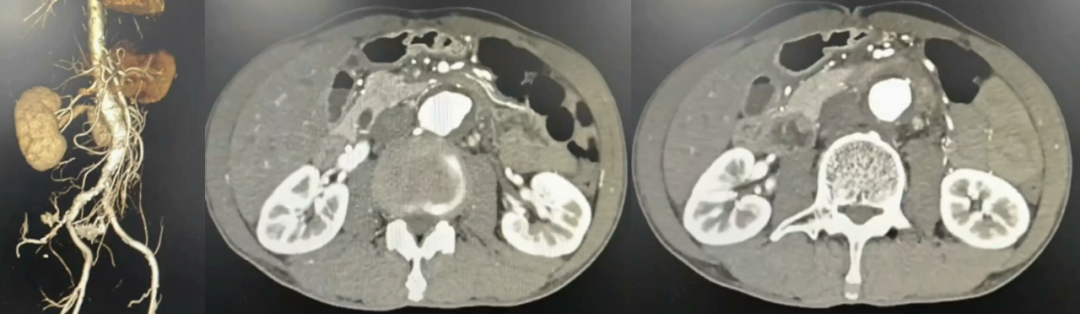
Preoperative Diagnosis: Infected abdominal aortic aneurysm, Brucella infection.
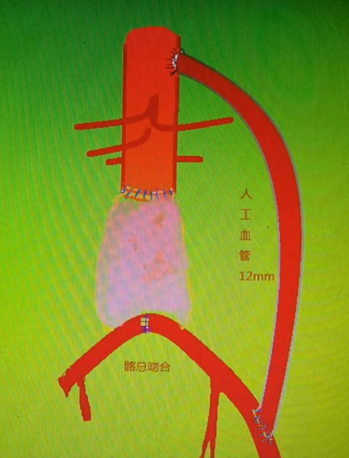
Surgical Plan: Subdiaphragmatic abdominal aorta–left external iliac artery bypass with an artificial graft.
Surgical Procedure
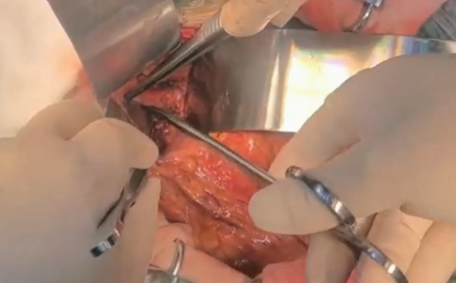
Procedure 1: Opened the abdomen and exposed the subdiaphragmatic abdominal aorta.
Procedure 2: Created a left retroperitoneal tunnel and used a 12 mm × 30 cm artificial graft.
Procedure 3: Side-clamped the subdiaphragmatic abdominal aorta.
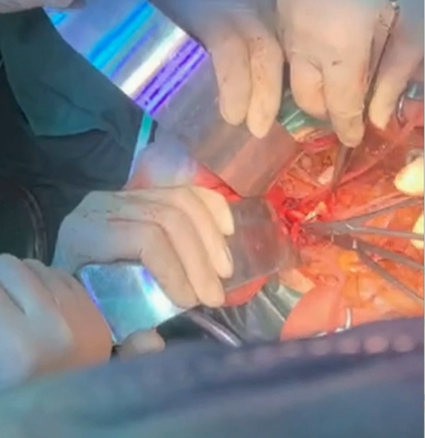
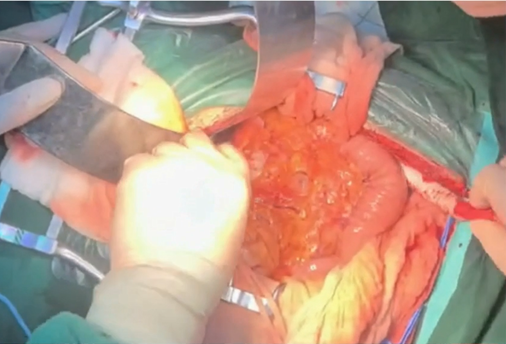
Procedure 4: Completed proximal and distal vascular anastomoses, closed the retroperitoneal tunnel at both ends.
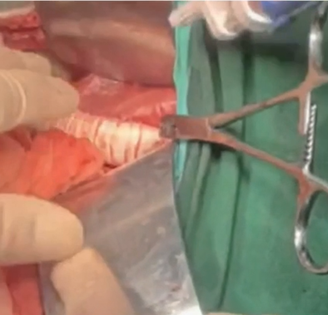
Procedure 5: Clamped the infrarenal abdominal aorta and performed aneurysm resection.
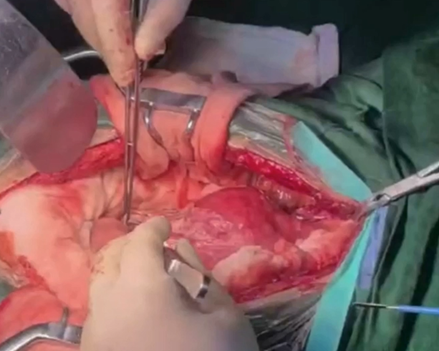
Procedure 6: Ligation of proximal and distal stumps.
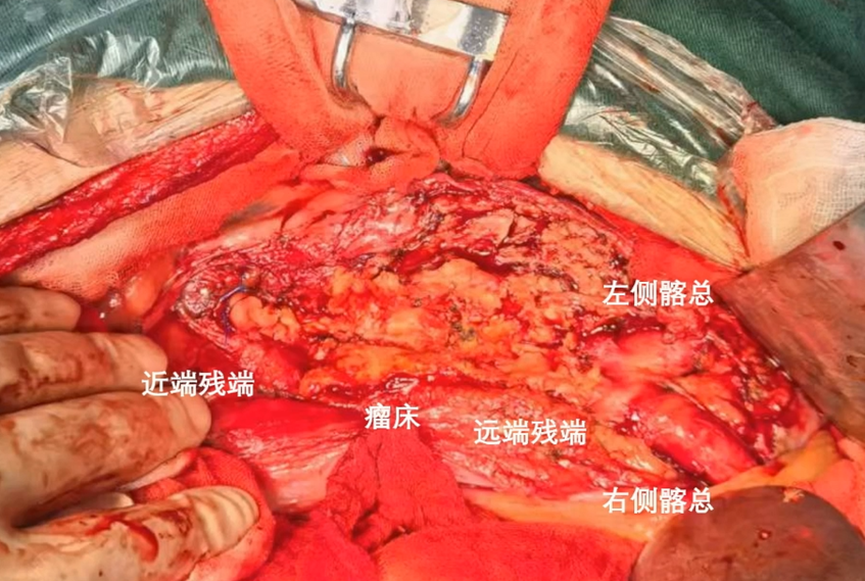
Postoperative Follow-Up
Postoperative CTA: The artificial graft was patent, and no endoleak was observed at the stump.
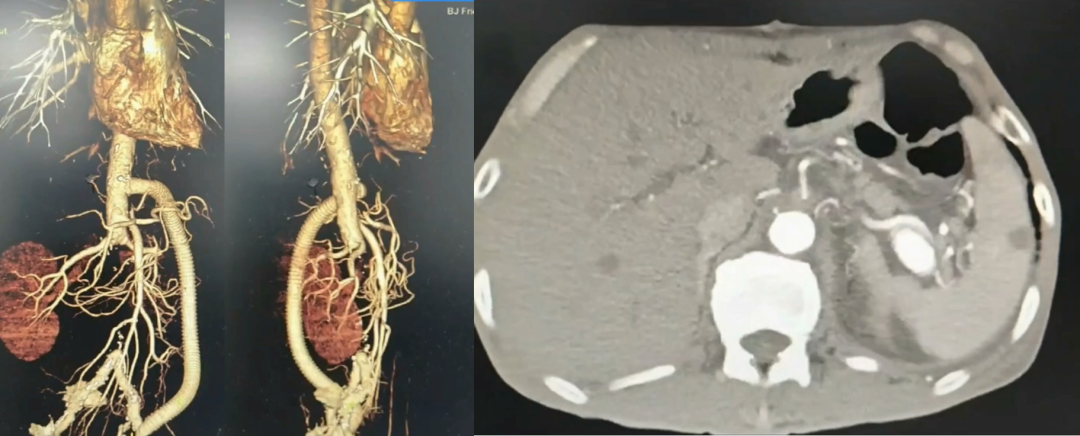
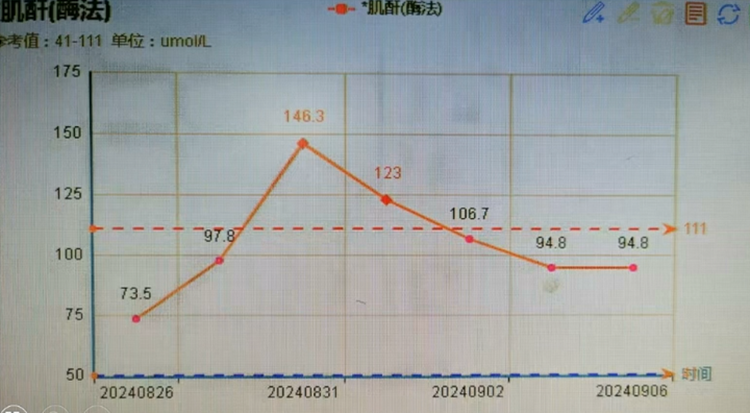
The patient experienced transient postoperative creatinine elevation, likely due to incomplete suprarenal clamping during surgery (approximately 20 minutes).
Case Insights
For the surgical treatment of infected abdominal aortic aneurysms, our department adheres to three basic principles:
1.Located in an Absolute Sterile Zone.
2.Localized Proximity Principle: Anatomical reconstruction should be as close as possible to the original anatomy.
3.Surgical Approach: If the abdominal cavity has an abscess or hematoma, an axillary-to-bifemoral bypass using an artificial graft is preferred.
For confirmed “infected AAAs,” no materials should be used for in-situ replacement or bypass grafting.


