
Patients with Type B dissection combined with distal malperfusion have a poor prognosis. Enhancing distal true lumen remodeling and improving perfusion are current challenges in the endovascular treatment of Type B dissection. On May 15, 2024, at the 2nd Tianfu Vascular Conference (TFS 2024), Professor Hu Jia’s surgical team from the Cardiac and Vascular Surgery Department of West China Hospital, Sichuan University, shared a live surgery case using the PETTICOAT technique to manage a Type B dissection with distal malperfusion.
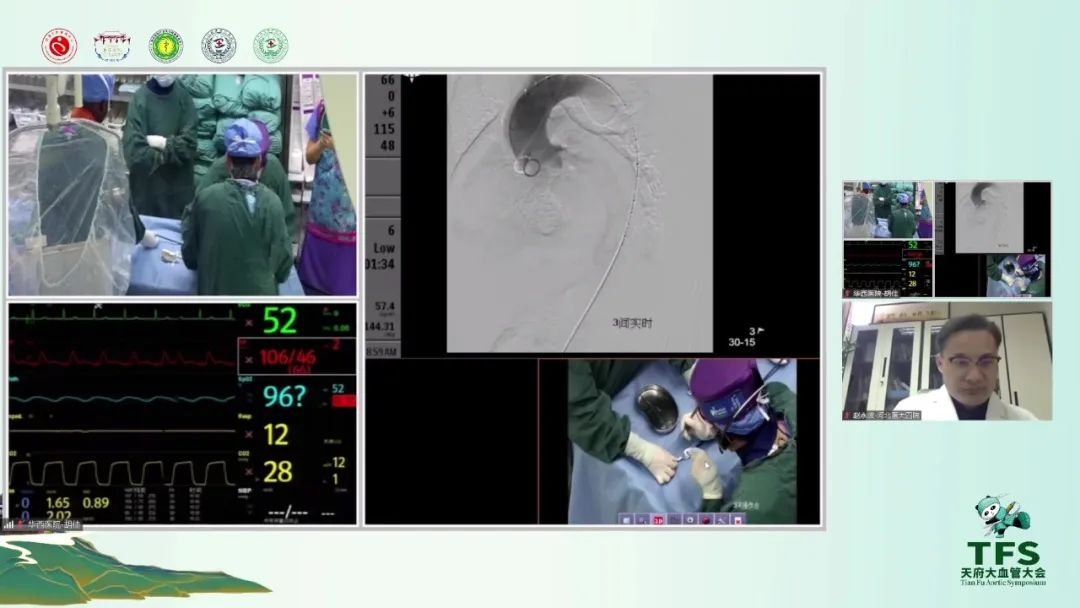
Live Surgery:
Patient Data (Male, 32 years old)
• Chief Complaint: Recurrent cough and chest pain for over 2 months.
• Medical History: The patient experienced recurrent cough and chest pain without obvious cause, accompanied by paroxysmal exacerbations, pallor, slight sweating, and nocturnal dyspnea. There were no symptoms of nausea, dizziness, syncope, lower limb pain or numbness, hemoptysis, productive cough, retrosternal pressure, diarrhea, melena, oliguria, anuria, or hematuria.
• Echocardiography: Detected intimal flap echoes in the aortic arch extending to the abdominal aorta.
• Aortic CTA: Revealed Type B aortic dissection with severe compression of the distal true lumen, ulcer on the lesser curvature, and significant left vertebral dominance. Blood supply through the true and false lumens was noted in the CA, SMA, RRA, and LRA.
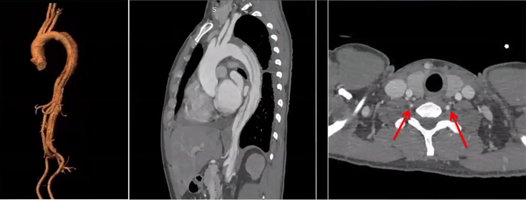
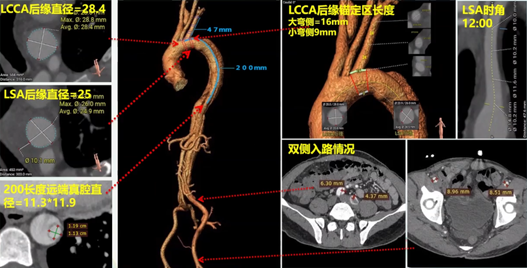
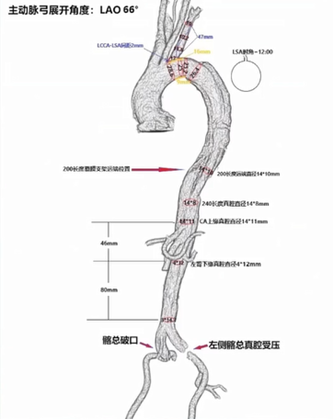
Surgical Strategy:
• Proximal: TEVAR with Ankura II 30×24×200 and external window reconstruction of the left subclavian artery using self-imaging window technology.
• Distal: Fabulous stent with PETTICOAT technique to remodel the distal true lumen.
Surgical Process:
1. Preoperative Preparation: External windowing of the Ankura II stent based on preoperative measurements, followed by reloading of the stent.
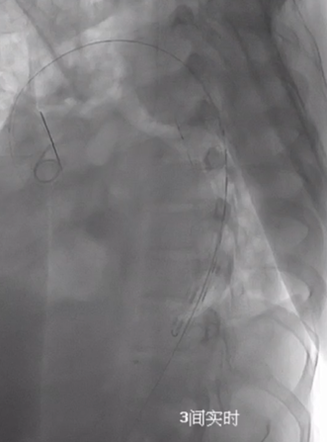
2. Initial Stent Deployment: Introduction of a restrictive stent via the femoral artery to the descending aorta and its release.
3. Main Stent Deployment: Introduction and precise positioning of the Ankura II stent, followed by its release.
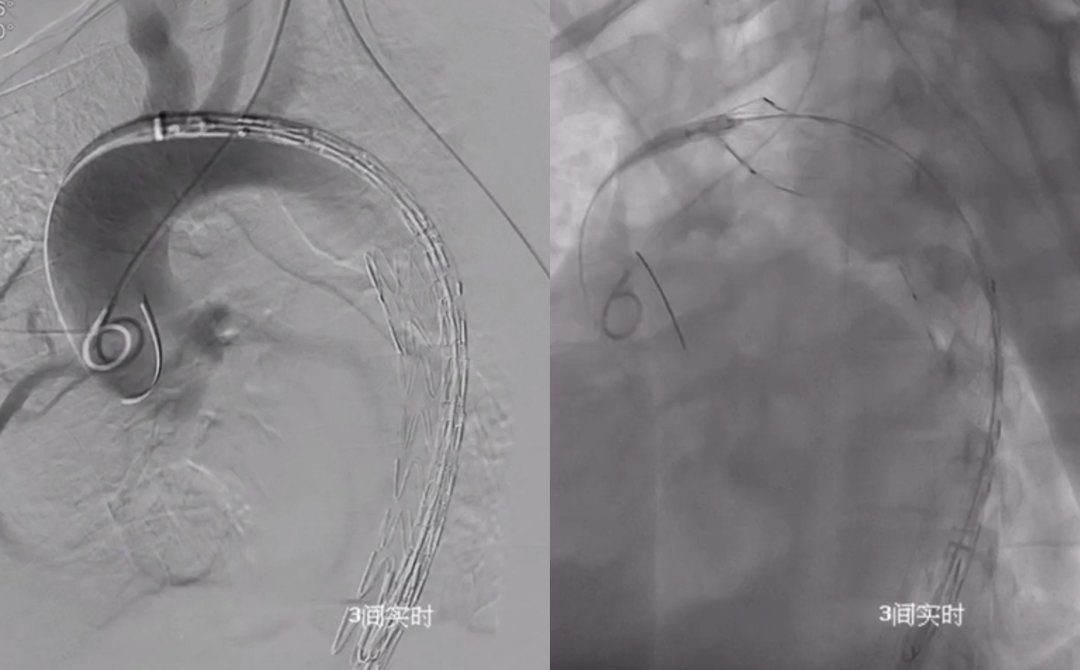
4. Proximal Stent Outcome: Angiography showed that the three branches above the arch were unobstructed, the proximal tear was completely isolated, and no endoleak was present.
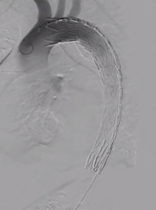
5. Distal True Lumen Narrowing: Subsequent angiography revealed narrowing of the distal true lumen.
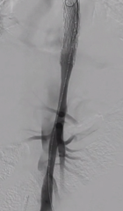
6. Distal Stent Deployment: Introduction and release of the Fabulous bare stent segment to the distal end of the restrictive stent.
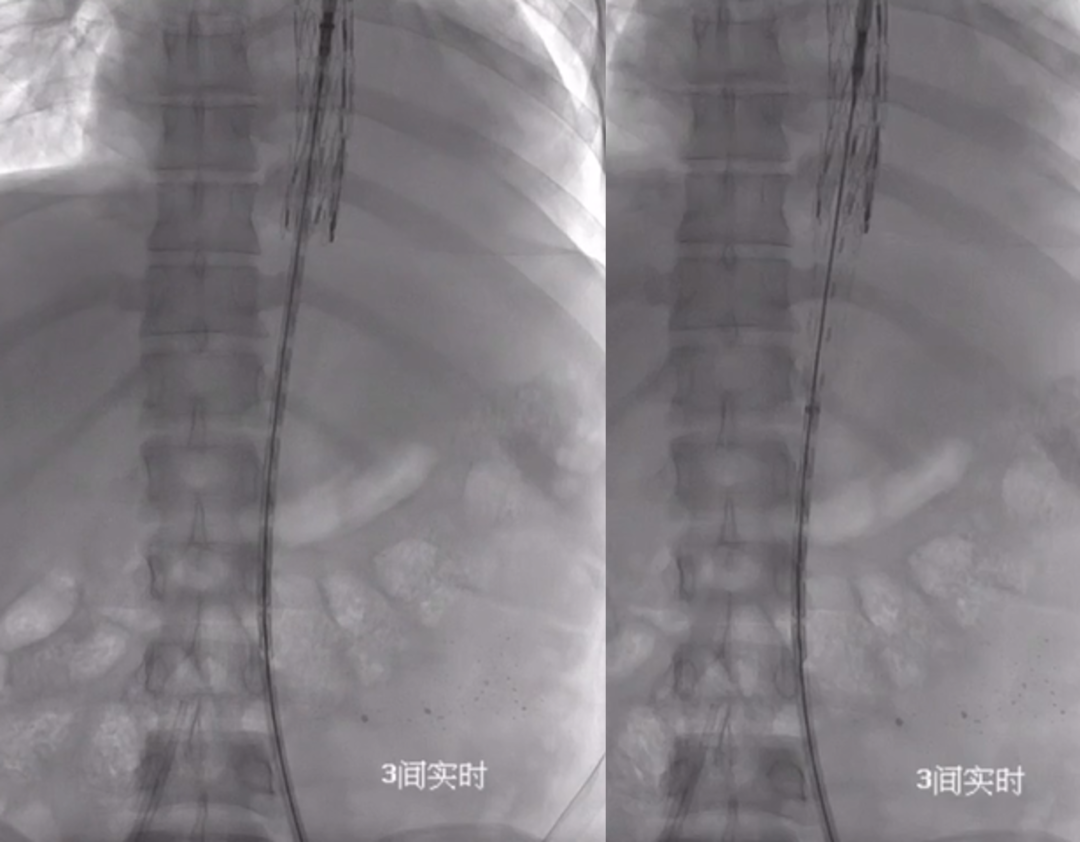
7. Final Outcome: Angiography showed restored true lumen diameter and patency of the visceral arteries.
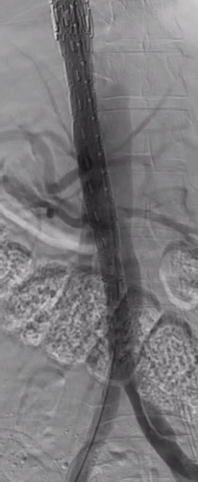
Stent Characteristics:
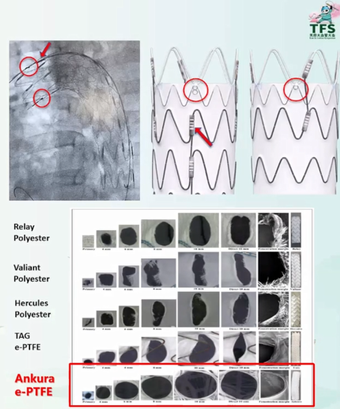
Advantages of Ankura Stent in Windowing Technology:
1. Clear self-imaging marker points for accurate positioning.
2. Self-imaging markers facilitating stent windowing.
3. e-PTFE coating with smooth cut edges and easy expansion.
4. Non-sewn e-PTFE coating eliminating pinhole endoleak.
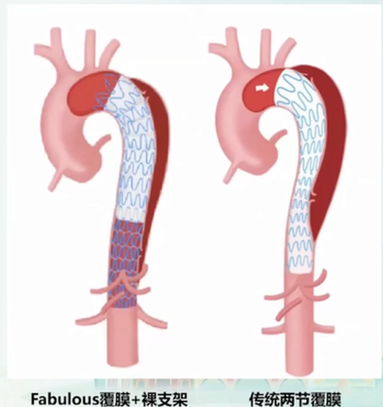
Features of Fabulous Stent:
Fabulous is the only domestic modular thoracic aortic stent system, capable of covering the eighth thoracic vertebra and visceral artery region. Compared to traditional covered stents, the Fabulous stent can cover the proximal tear and treat distal dissection without affecting blood flow to the intercostal and visceral arteries. It effectively improves organ malperfusion and enhances perioperative survival rates.
Contact Us:
We welcome further discussion and exchange on PETTICOAT technology or topics related to the Tianfu Vascular Conference. If you have any questions or interests, please leave a comment or contact us via email at endovascluar@simtomax.cn. Thank you for your attention. Let’s work together for health!


