
Since the establishment of the Vascular Surgery Expert Group (hereinafter referred to as the Expert Group) of the Expert Committee of the National Center for Quality Control of Cardiovascular Disease Specialties in 2018, every year since then, the Expert Group has documented in detail the Vascular Surgery section of the China Cardiovascular Disease Quality of Care Report in order to be able to reflect and evaluate the current status of the treatment of aortic diseases in China in a comprehensive and systematic manner.On September 22, 2023, at the Eighth China On September 22, 2023, during the 8th China Vascular Congress (CVC 2023) in Xi'an, Prof. Shu Chang of Fu Wai Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, presented the China Vascular Disease Treatment Quality Report 2023 in the opening keynote speech.
The National Center for Quality Control of Cardiovascular Disease Care (NCCQI) data is derived from the National Hospital Quality Management System (HQMS) and includes data on the aorta and all peripheral vascular diseases.2022 CVC patient data includes a total of 515.34 million patients in 5,647 hospitals (2,169 tertiary hospitals and 3,478 secondary hospitals) across China.

Current status of aortic disease treatment in China
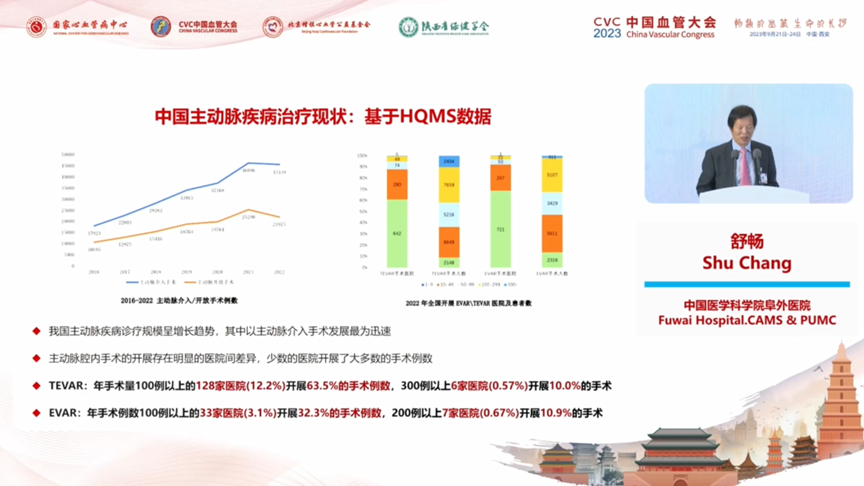
The scale of aortic disease diagnosis and treatment in China has shown a growth pattern, with the most rapid development of aortic interventional procedures. There are obvious inter-hospital differences in the development of aortic endoluminal surgery, with a small number of hospitals performing the majority of surgical cases.128 hospitals (12.2%) with an annual volume of more than 100 cases performed 63.5% of the surgical cases in TEVAR, and 6 hospitals (0.57%) with more than 300 cases performed 10.0% of the surgical cases.33 hospitals (3.1%) with an annual volume of more than 100 cases performed 32.3% of the surgical cases in EVAR, and 7 hospitals (0.67%) with more than 200 cases performed 32.3% of the surgical cases in EVAR. hospitals (3.1%) performed 32.3% of the surgical cases and 7 hospitals (0.67%) with more than 200 cases performed 10.9% of the surgical cases. In recent years, the number of hospitals performing aortic surgery in China has been on an overall upward trend The popularization and promotion of aortic surgery-related technologies has been effective In 2022, 1,304 hospitals (23.0%) performed interventional procedures on the aorta 518 hospitals (9.2%) performed open aortic surgeries.
Quality of Care Analysis of Aortic Disease in China
1, TEVAR, EVAR, Bentall and total arch replacement four aortic representative procedures
Between 2017 and 2022, the impact of the epidemic fluctuated slightly, with an overall increasing trend.TEVAR procedures increased from 13,709 to 24,076 (75.6% increase); EVAR procedures increased from 7,611 to 16,776 (120.4% increase); and Bentall procedures increased from 3,105 to 5,825 (87.6% increase); Total arch replacement increased from 3,707 to 10,268 (177.0% increase). The overall mortality rate of endoluminal surgeries showed a decreasing trend, and the rate of non-recovery discharge remained stable. The overall mortality rate of open surgeries showed a decreasing trend and the non-rehabilitation discharge rate showed an increasing trend. There were significant differences in medical outcomes between hospitals of different annual surgical volume sizes. The two major indicators, in-hospital mortality and in-hospital mortality plus nonrehabilitative discharge rates, both decreased with increasing annual surgical volume, consistent with the empirical accumulation pattern.

2. Quality of medical care in endoluminal surgery
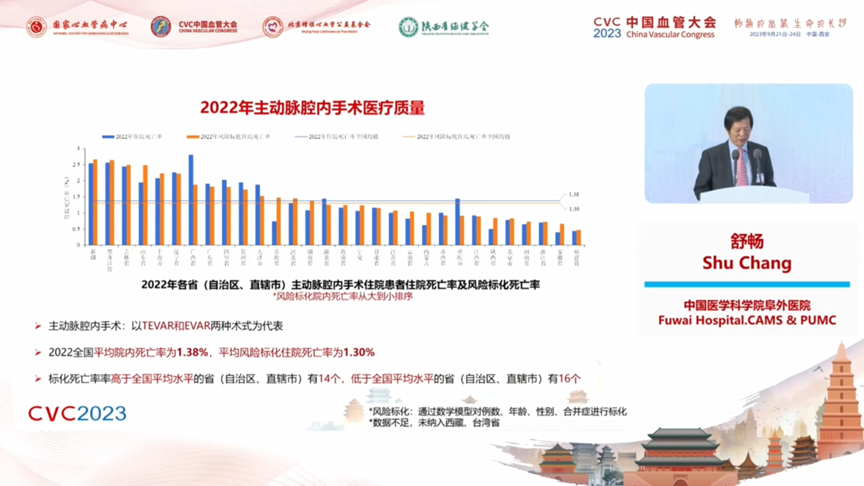
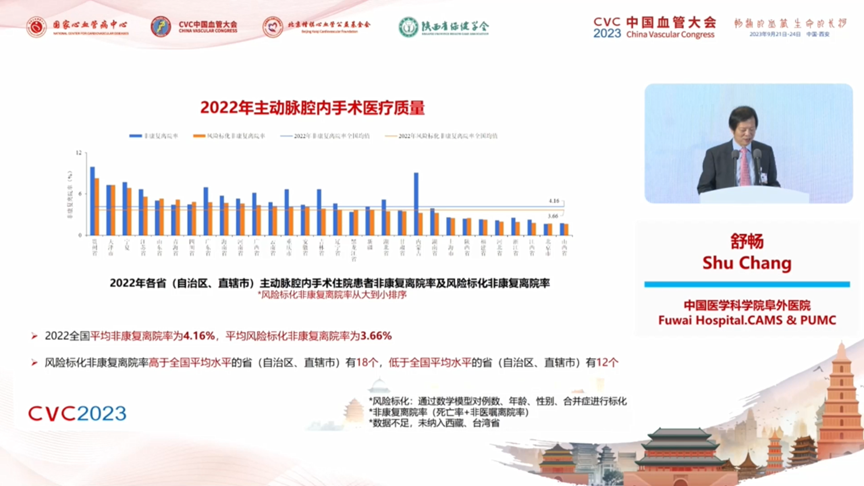
Aortic endoluminal surgery is represented by two types of procedures, TEVAR and EVAR, with a national average in-hospital mortality rate of 1.38% and an average risk-labeled in-hospital mortality rate of 1.30% in 2022. The number of provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government) with a standardized mortality rate higher than the national average is 14. The national average non-rehabilitation discharge rate in 2022 is 4.16%, and the average risk-scaled non-rehabilitation discharge rate is 3.66%. The number of provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government) with risky standardized non-rehabilitation discharge rates higher than the national average is 18, and the number of provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government) with rates lower than the national average is 12.
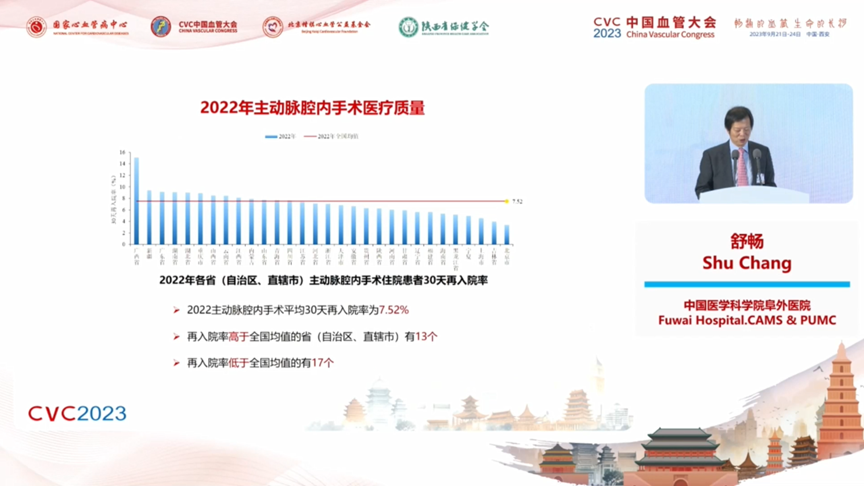
The average 30-day readmission rate for aortic endoluminal surgery in 2022 was 7.52%, with 13 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government) having a readmission rate higher than the national average, and 17 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government) having a readmission rate lower than the national average.
Between 2018 and 2022, the average length of stay declined from 16 to 14.3 days, and the median length of stay declined from 14 to 12 days. 10 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government) will have a median length of stay in 2022 that is lower than the national average, 12 will have a median length of stay higher than the national average, and 8 will have a median length of stay that is the same as the national average.

There are 15 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government) where the non-rehabilitation discharge rate is lower than the national average, with small differences between hospitals within the region; 10 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government) where the non-rehabilitation discharge rate is high, with large differences between hospitals within the region; 3 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government) where the non-rehabilitation discharge rate is high, with small differences between hospitals within the region; and 2 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government) with low non-rehabilitation discharge rates, with large differences between hospitals within the region.

3. Quality of medical care in open surgery
2022 The national average in-hospital mortality rate was 4.76%, and the average risk-labeled in-hospital mortality rate was 3.61% There were 15 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government) with risk-labeled in-hospital mortality rates higher than the national average, and 13 with rates lower than the national average.2022 The national average non-rehabilitation discharge rate was 10.13%, and the average risk-labeled non-rehabilitation discharge rate was 8.25%. The number of provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government) with a risk-marked non-rehabilitation discharge rate higher than the national average is 12, while the number of provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government) with a rate lower than the national average is 16.
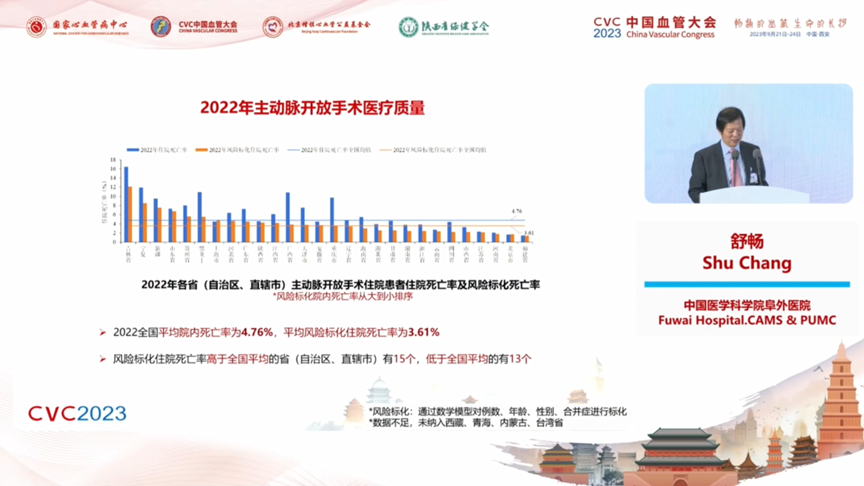
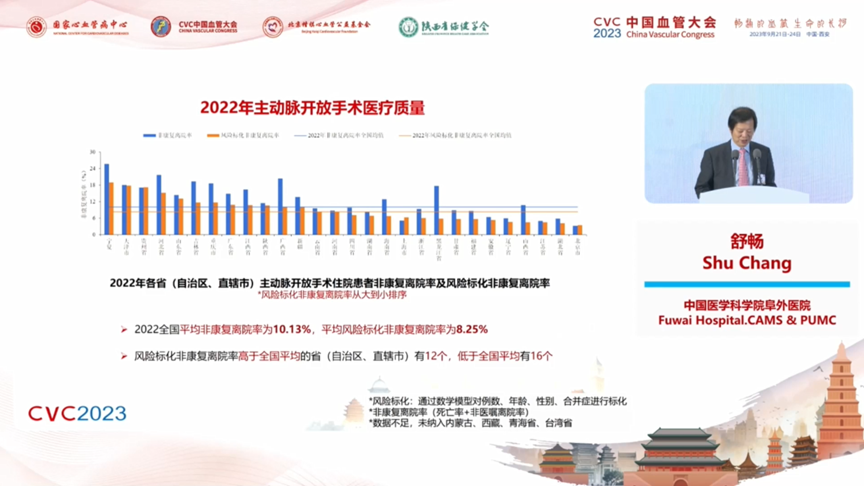
2022 The national average 30-day readmission rate for open surgery was 8.84%, with 18 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government) having a readmission rate higher than the national average and 12 having a readmission rate lower than the national average.
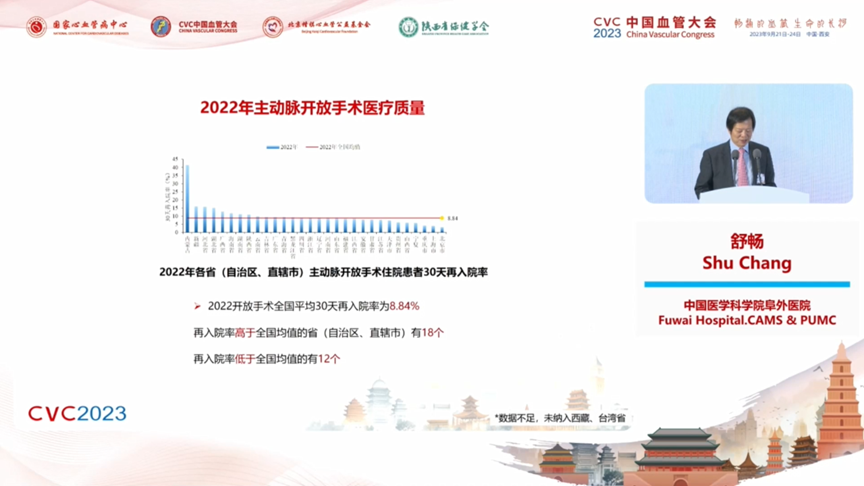
In 2022, the national average length of stay for open surgery patients was 21.4 days, and the median length of stay was 19 days. The median length of stay was lower than the national average in 12 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government), higher than the national average in 13, and flat in 5.

Aortic Disease Report
HQMS data shows that 3,722 hospitals practice aortic disease, admitting a total of 127,545 hospitalizations. Among aortic diseases, aortic coarctation (48.20%) and aortic aneurysm (23.10%) still accounted for the largest share.
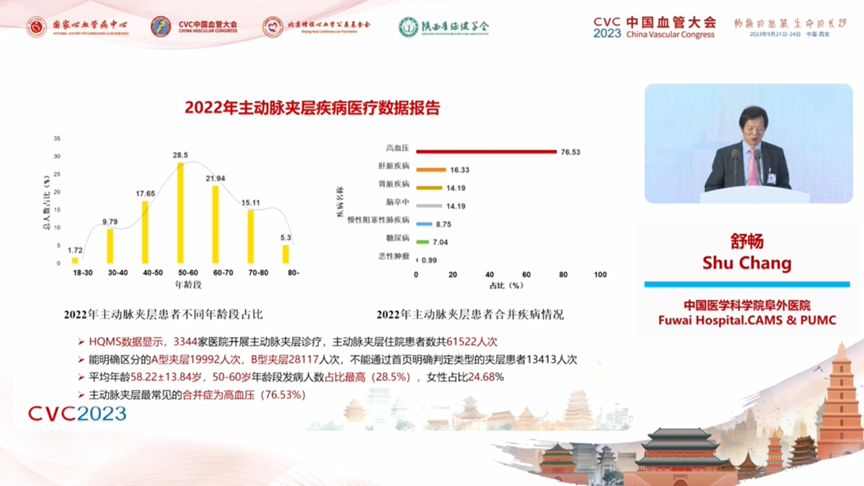
1. A report on the medical data of aortic coarctation disease shows that 3,344 hospitals carry out aortic coarctation treatment, and the number of patients hospitalized with aortic coarctation totaled 61,522. There were 19,992 patients who could be clearly distinguished as type A, 28,117 as type B, and 13,413 patients who could not be clearly determined by the homepage. The average age of the patients was 58.22±13.84 years, with the highest number of cases occurring in the 50-60 year age group (28.5%) and 24.68% in women. The most common comorbidity of aortic coarctation was hypertension (76.53%). Emergency was the main admission route for patients hospitalized with aortic coarctation (60.51%). The incidence of aortic coarctation is seasonally related, with a significant increase in admissions during the cold season. Nationally, aortic coarctation had an in-hospital mortality rate of 4.81% and a non-rehabilitated discharge rate of 16.57%: type A coarctation had an in-hospital mortality rate of 7.38% and a non-rehabilitated discharge rate of 24.04%; type B coarctation had an in-hospital mortality rate of 1.73% and a non-rehabilitated discharge rate of 10.82%. Mortality rate for non-operated patients 6.4%, non-rehabilitated discharge rate 24.9%; mortality rate for operated patients 3.2%, non-rehabilitated discharge rate 8.0%. The mortality rate for endoluminal surgery was 1.0% and the non-rehabilitative discharge rate was 3.9%; the mortality rate for open surgery was 6.5% and the non-rehabilitative discharge rate was 14.3%.
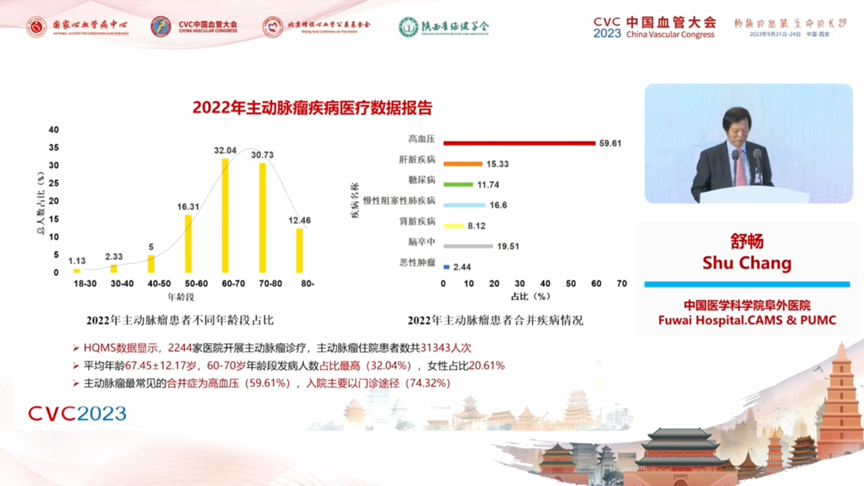
2. The medical data report of aortic aneurysm disease showed that 2,244 hospitals carried out aortic aneurysm diagnosis and treatment, and the number of aortic aneurysm hospitalized patients totaled 31,343. The average age was 67.45±12.17 years old, with the highest proportion of incidence in the age group of 60-70 years old (32.04%), and the proportion of females was 20.61%. The most common comorbidity of aortic aneurysm was hypertension (59.61%), and the admission was mainly by outpatient route (74.32%). The majority of aortic aneurysm patients (including thoracic and abdominal aortic aneurysms) in the country were treated with endoluminal surgery (70.18%).
3. Carotid artery stenosis occlusive disease medical data report shows:
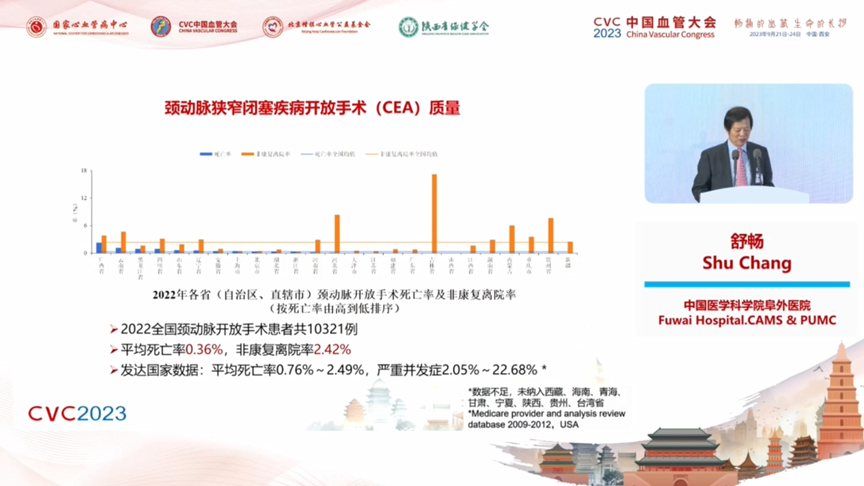
a. Carotid artery stenosis and occlusive disease open surgery (CEA) quality: CEA volume is correlated with regional morbidity and medical resources, with 9 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government) having fewer than 100 surgical cases (data from Tibet and Taiwan are not available at this time).2022 The total number of patients undergoing open carotid artery surgery nationwide was 10,321. The average mortality rate was 0.36%, and the non-rehabilitation discharge rate was 2.42%. Data from developed countries: average mortality rate 0.76% to 2.49%, serious complications 2.05% to 22.68%.
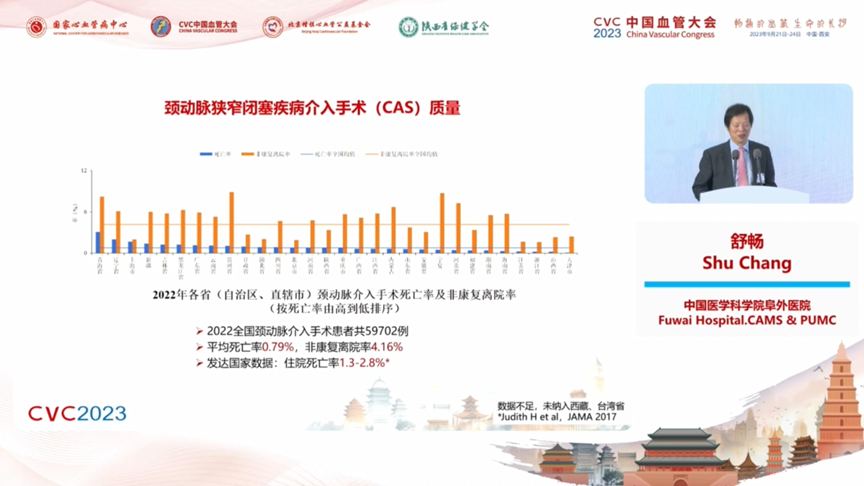
b. Carotid Artery Stenosis Occlusive Disease Endoluminal Surgery (CAS) Quality: CAS volume correlates with regional morbidity and healthcare resources.2022 Nationally, there were 59,702 carotid artery interventional patients. The average mortality rate was 0.79% and the nonrehabilitative discharge rate was 4.16%. Data from developed countries: hospitalized mortality rate 1.3% to 2.8%.
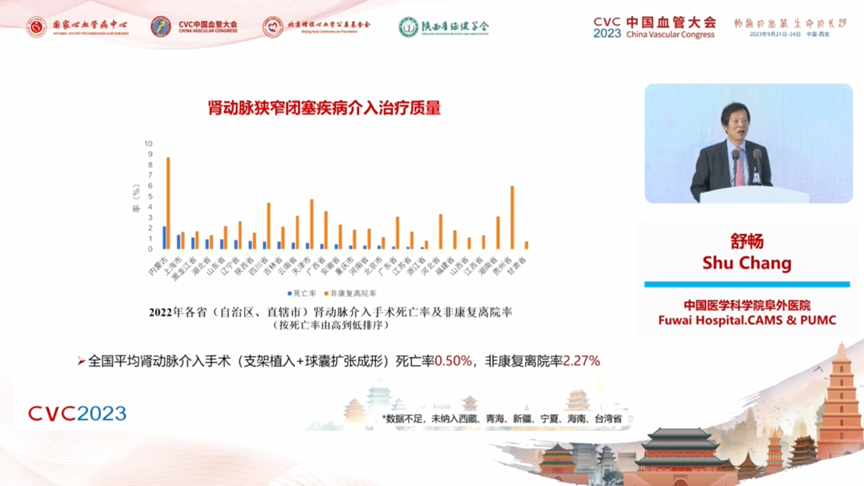
4. Quality of interventional treatment for renal artery stenosis and occlusive disease: the volume of renal artery interventional procedures is related to medical resources. 4 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government) have less than 100 cases (Tibet, Qinghai, and Taiwan are not included). The national average mortality rate of renal artery interventional procedures (stent implantation + balloon dilatation and molding) is 0.50%, and the rate of non-rehabilitative discharge is 2.27%.
5. Quality of treatment for ilio-femoral-popliteal stenosis and occlusive diseases: open surgery was carried out in 476 hospitals with a total of 1,438 cases, a mortality rate of 1.60%, and a non-rehabilitation discharge rate of 6.68%; interventional surgery was carried out in 1,058 hospitals with a total of 7,486 cases, a mortality rate of 0.41%, and a non-rehabilitation discharge rate of 2.56%.
6. Varicose veins of the lower limbs: 4,098 hospitals nationwide are carrying out diagnosis and treatment. Stripping surgery was carried out in 3,761 hospitals with 130,827 cases; ablation surgery was carried out in 561 hospitals with 17,381 cases; laser surgery was carried out in 1,154 hospitals with 37,822 cases.
Summary
1. In recent years, the number of hospitals performing aortic surgery and the number of surgical cases have been on the rise nationwide, with the scale of aortic endoluminal surgery growing even more rapidly.
2. There are obvious inter-hospital differences in the conduct of aortic surgery, with a small number of hospitals performing most aortic surgeries.
3, the medical quality of aortic surgery is related to the hospital's surgical volume, and the incidence of in-hospital adverse outcomes is higher in hospitals with less annual surgical volume. It is necessary to provide more technical guidance and quality control to hospitals with new aortic surgeries and smaller surgical scales, which needs to be emphasized in the future quality control work.
4. Peripheral vascular diseases have many types of diseases and involve many disciplines, and the use of the national unified data platform for quality analysis and control will help to grasp the overall quality of medical care.
转载至《门诊》杂志


