
Endothelial hyperplasia is a determinant of the prognosis of SFA stenting. Any placement of a stent can stimulate a proliferative response in the endothelium, leading to restenosis. Currently, the creation of covered stents and drug-eluting balloons has been an important advancement in the search for an ideal endoluminal treatment for SFA.
Covered stents (CS) can limit the inward growth of the endothelium in the treated segment to a certain extent, thus improving vessel patency. The principle behind the use of covered stents to limit restenosis is to isolate plaque from the arterial lumen by creating a mechanical barrier that keeps smooth muscle cells independent of the circulation, thus preventing their stimulatory effects and migration into the open stent. In contrast to conventional stents, CS can prevent restenosis through a mechanical barrier combined with direct radial resistance.
The more studied drug-eluting balloon (DEB), such as paclitaxel-eluting balloon, is filled with paclitaxel in micropores on the surface of the balloon, and enters the lesion area through the delivery system of PTA. Folding of the balloon before expansion prevents premature loss of drug, which can be infiltrated into the arterial wall tissue by expanding the balloon for 45-60 s. The balloon is then released into the arterial wall. When the balloon is released, part of the drug is washed away by the blood flow, and the remaining 75% of the drug can be immersed into the localized diseased arteries, which can be used to prevent endothelial hyperplasia.
The results of many clinical studies at home and abroad have shown that the therapeutic effects of CS and DEB are favorable, but there is a lack of comparative studies on the efficacy of CS and DEB. In this regard, we conducted a single-center study to compare the clinical outcomes of CS and DEB in patients with SFA lesions.
Research methodology
This study retrospectively analyzed 53 patients with SFA lesions treated with CS and DEB between June 2015 and June 2017, including 32 patients in the CS group and 21 patients in the DEB group (Tables 1-2). Patient inclusion criteria: patients with severe limb ischemia and partial intermittent claudication (Rutherford classification 2-5); patients with primary coronary artery lesions (Denovo) with in-stent restenosis lesions (ISR); and SFA occlusion lengths >10 cm. postprocedural clopidogrel 75 mg in combination with aspirin 100 mg treatment.
Table 1、Baseline Patient Characteristics
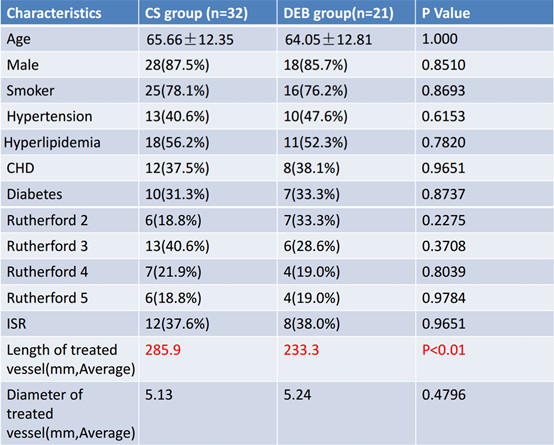
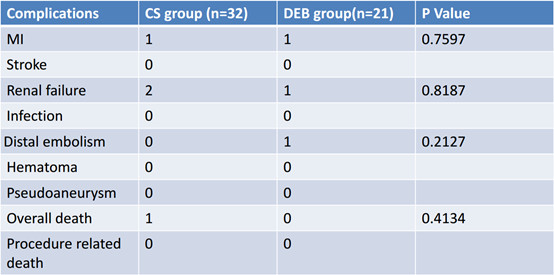
Table 2、Perioperative complications
Results of the study
There were no postoperative amputations in patients. A total of 3 patients died, and no surgery-related deaths occurred. The 1-year postoperative stage I patency rate was 50% in the CS group and 61.9% in the DEB group, and the stage II patency rate was 81.2% in the CS group and 85.7% in the DEB group.The length of the lesions in patients in the CS group was greater than that in the DEB group. There was no statistically significant difference in treatment outcomes between the two groups (Tables 3-4).
Table 3、Results of the study
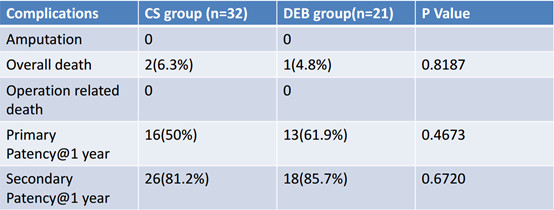
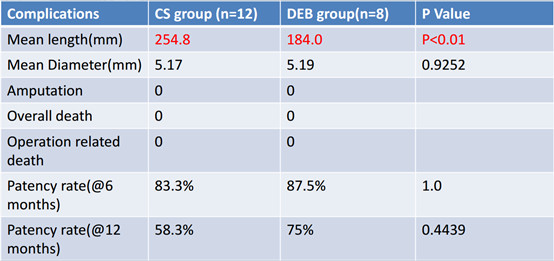
Table 4、Results of the ISR subgroup study
Discussions
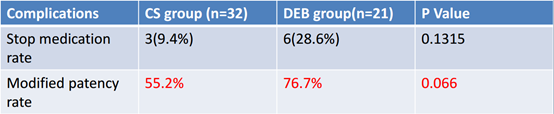
The 12-month recanalization rates of 50% and 61.9% for CS and DEB, respectively, were lower than in other studies in the literature (Table 5). This may be related to the longer length of diseased vessels and higher percentage of chronic total occlusion (CTO) of coronary arteries in the included patients.The higher patency rate in the DEB group than in the CS group may be related to the postoperative patients' medication adherence. According to the clinical research, the poorer postoperative medication compliance in the CS group may be due to psychological factors, which may have contributed to the lower patency rate in the CS group than in the DEB group (Table 6).
Table 5、Other relevant research data
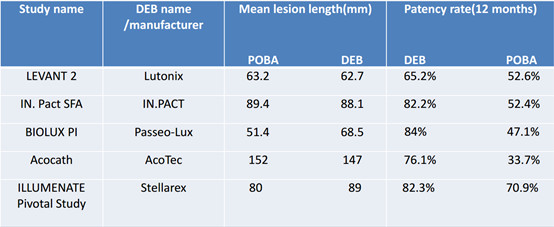
Table 6、Comparison of discontinuation and patency rates in the CS and DEB groups
Summary
Comparison of the therapeutic effects of CS and DEB in clinical practice needs to be combined with a specific diagnostic procedure. The results of this study show that DEB is superior to CS in the treatment of long segments of SFA occlusions >10 cm, but CS still plays an important role in the treatment of peripheral arterial disease, especially in patients with ISR. The results of CS and DEB need to be supported by additional clinical data and longer follow-up.


