
Thoracic endovascular aortic therapy (TEVAR) has been present for 25 years, and this process is inseparable from the increasing popularity of endovascular treatment methods, continuous innovation and breakthroughs in surgical instruments and techniques. GORE ® TAG ® thoracic aortic covered stent is a stent product specially designed for endovascular treatment of thoracic aortic diseases. The latest research progress and results of the GORE ® TAG ® Branch Thoracic Aortic Covered Endovascular Stent System (TBE) were presented at the International Congress of Vascular and Endovascular Angiology (VEITH symposium) held at the Hilton Hotel, Central New York, USA, from November 14 to 17, 2023.
Recent Clinical Advances in the GORE ® TAG ® Branched Thoracic Endovascular Graft System
Michael D. Dake

Thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR) has become the treatment of choice for descending aortic aneurysms. For the treatment of aortic arch aneurysms involving Zone2 and the left subclavian artery (LSA), there are still some challenges. How to simplify the operation of endovascular aortic arch repair and improve the patency rate and safety of branch vessels, branch thoracic aortic stent grafts provide a brand-new solution. The GORE ® TAG ® Thoracic Branch Graft (TBE) is a finished stent intended for endovascular treatment of aortic arch lesions with primary reconstruction of blood flow in aortic arch branches and is currently approved by the US FDA. Professor Michael D. Dake of Arizona University of Health Sciences presented the latest clinical data on the TBE stent at the meeting, showing its excellent performance in the treatment of aortic arch lesions.
GORE ® TAG ® Branch Thoracic Endovascular Graft (TBE) Design
The use of branched aortic stents is the preferred option to address lesions involving the Zone2 region in aortic arch arteries. The GORE ® TAG ® Branch Thoracic Endovascular Graft (TBE) consists of three modules (Figure 1-1):
(1)Aortic main body stent (AC): diameter range 21 to 45 mm.
(2)Branch stents (SBs): 8 to 20 mm in diameter.
(3)Aortic extension (AE): Optional use, diameter range 21 to 45 mm, length range 3.6 to 4.6 cm.
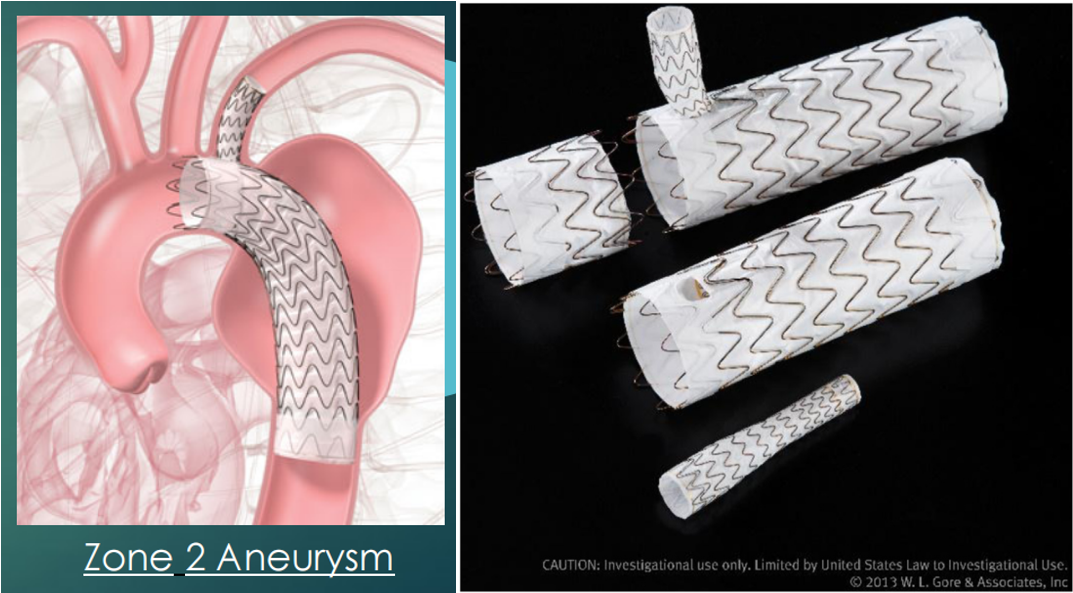
Figure 1-1. Schematic diagram of TBE device
Operating Procedure for TBE Use in Z2 Area
The operation steps used for TBE in Z2 area are as follows (Figure 1-2):
(1)A guidewire was placed in the aorta and branch vessels.
(2)Introduce the main body stent assembly over two guide wires into the aortic arch.
(3)Release the body stent and withdraw the delivery catheter.
(4)Branch stent components are placed and released through a pre-positioned guidewire in the branch vessel.
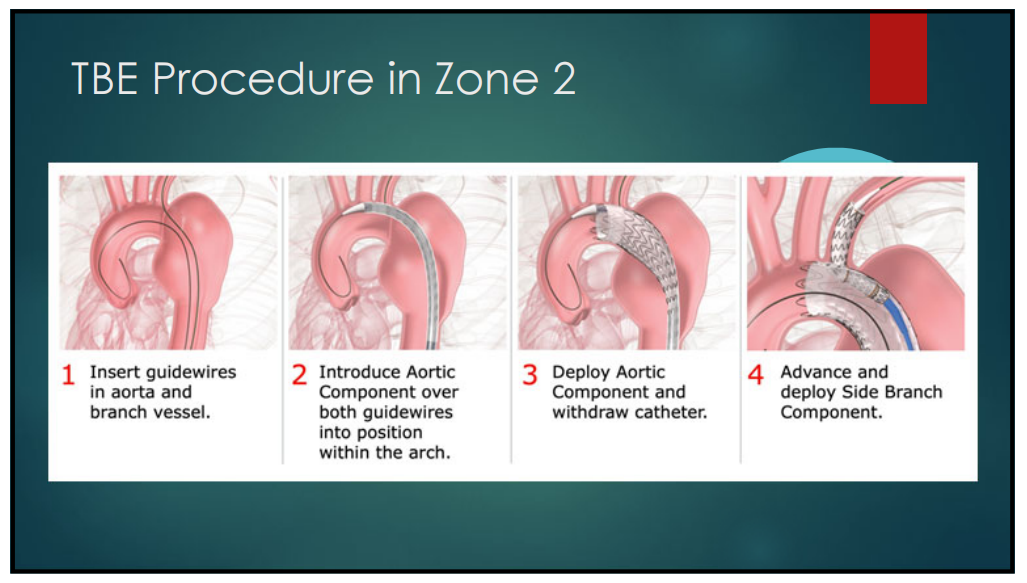
Figure 1-2. TBE Operating Procedures
TBE Associated Studies and Recent Results
TBE related studies and recent results This presentation presents two studies on TBE, one feasibility study and the other pivotal study, and compares their results (Figures 1-3). According to the results of both studies, the FDA approved Z2 region as a therapeutic indication for TBE in May 2022, and whether Z0/1 region is an indication remains in clinical trials.
The feasibility study was a multicenter, nonrandomized, prospective study that included 31 patients with distal aortic arch aneurysms at 6 sites. This study used TBE as a treatment to ensure blood perfusion in the LSA by implanting branch stents in the LSA.
The pivotal study was a multicenter, nonrandomized, prospective study of 84 patients with zone Z2 aneurysms from 34 centers between September 2014 and October 2019. Non-statistical arms (dissection cohort, traumatic transection cohort, and solitary lesion cohort) were also analyzed in this study.
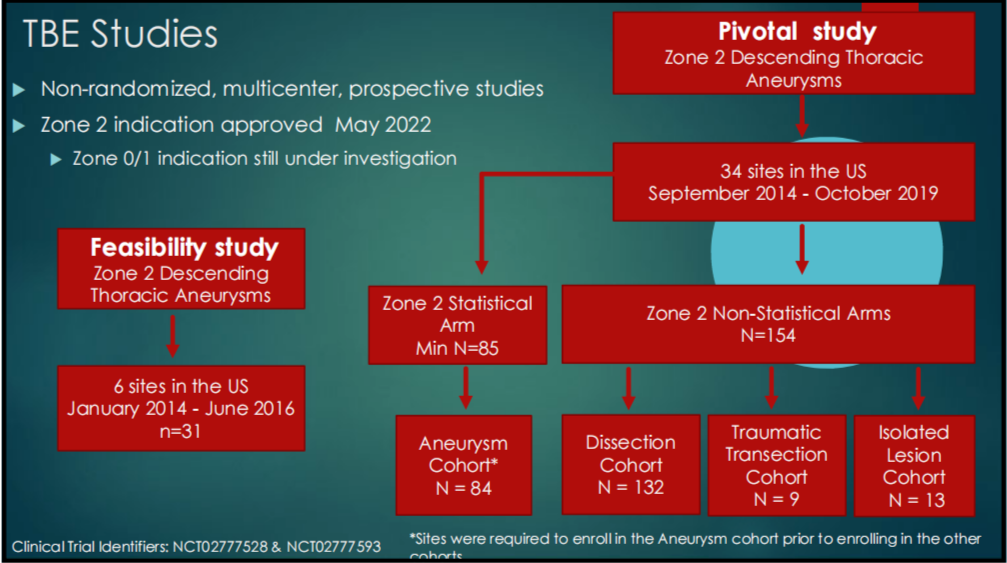
Figure 1-3. TBE Feasibility Study and Critical Study Flow
Latest Result Comparison:
1. BASELINE CHARACTERISTICS: Baseline demographics (Table 1-1) and risk profiles (Table 1-2) were similar in both trials.
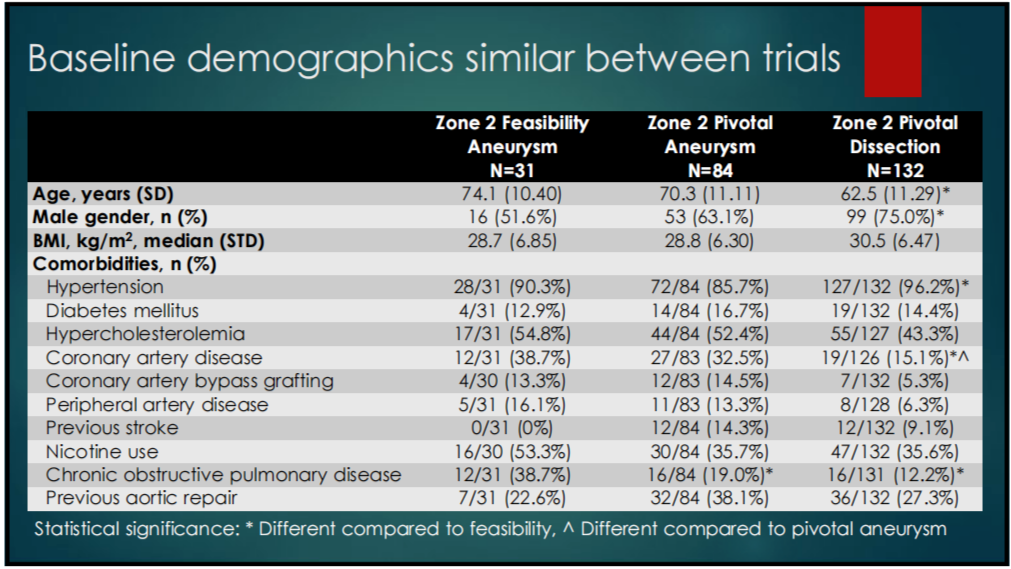
Table 1-1. Baseline Characteristics of the 2 Studies
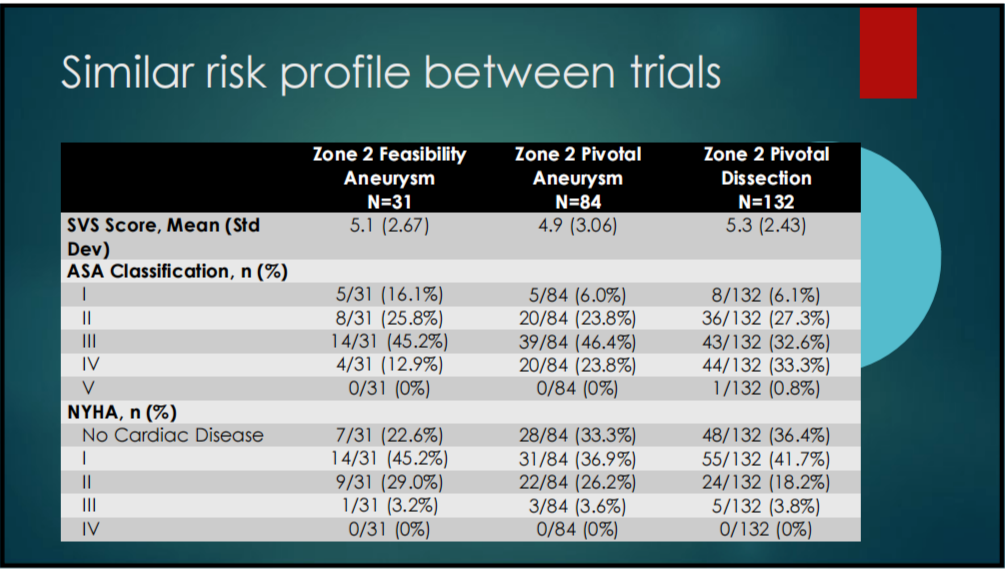
Table 1-2. Risk Profile
2. DEVICE RELATED EVENTS: The pivotal studies had lower patency loss, rupture, and aortic dilation rates and superior clinical outcomes compared to the feasibility studies (Tables 1-3).
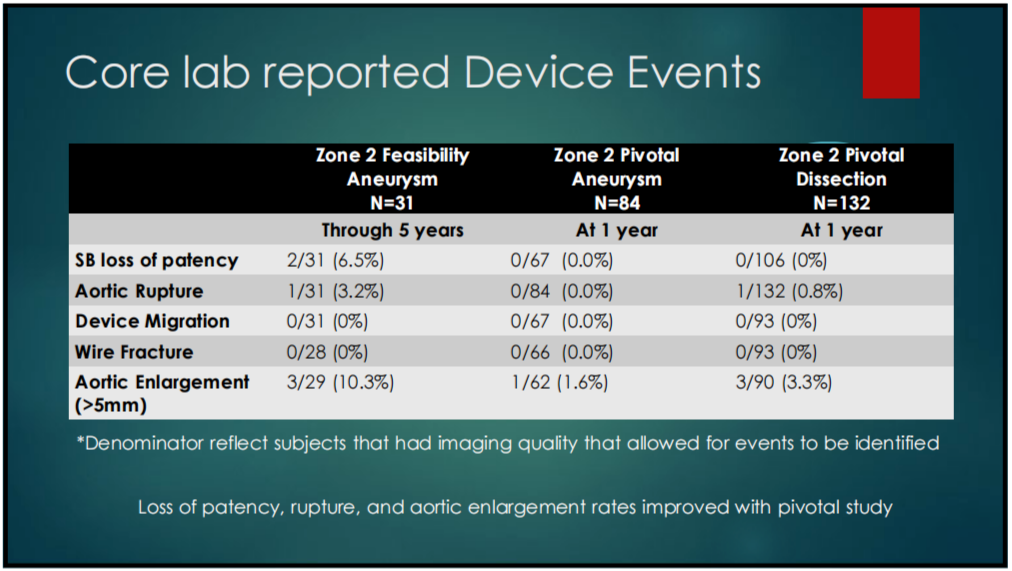
Table 1-3. Core Lab Reported Device Related Events
3. ANEURYSM REINTERVENTION RATE: In the pivotal study, aneurysm reintervention results were superior to the feasibility study.
(1)In the 5-year results of the Z2 feasibility study, two patients underwent reintervention 130 and 133 days after surgery, respectively, and one of the subjects underwent thrombectomy 0 and 1 day after intervention due to treatment of left lower extremity and left upper extremity ischemia during reintervention.
(2)In the Z2 pivotal study, as of 1 year, 1 patient was observed to have undergone reintervention for a type III endoleak that developed one week after surgery.
4. PIVOTAL STUDY DISSECTION COHORT ANALYSIS: Dissection false lumen thrombogenicity status continued to improve through 1 year in the pivotal studies (Table 1-4). Six patients with dissection required reintervention, all within 6 months of the procedure and no reintervention thereafter.
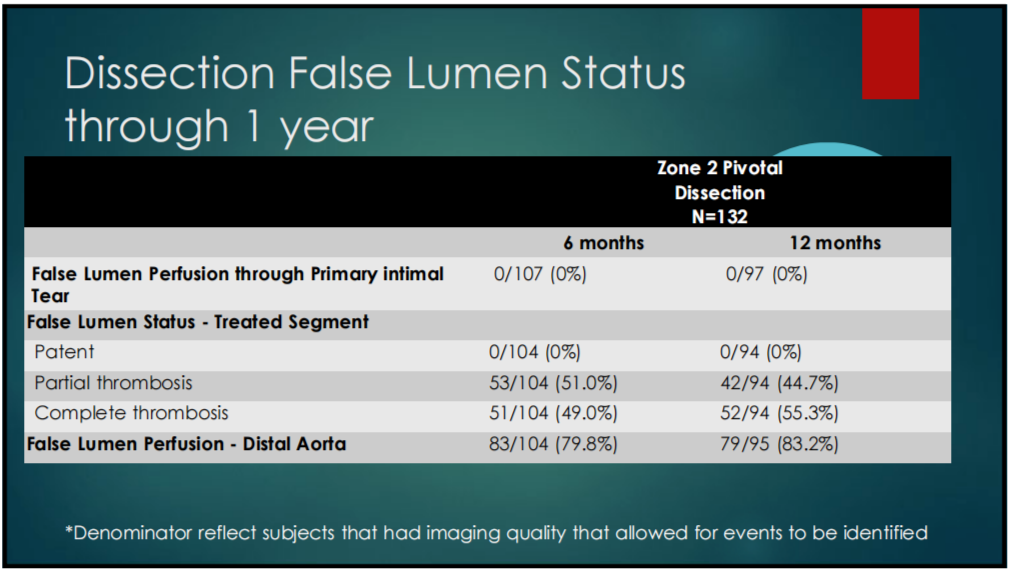
Table 1-4. Dissection Cohort – Thrombosis of the False Lumen
5. MORTALITY AND STROKE INCIDENCE: There was no significant difference in mortality and stroke incidence between the 1-year pivotal study and the 5-year feasibility study.
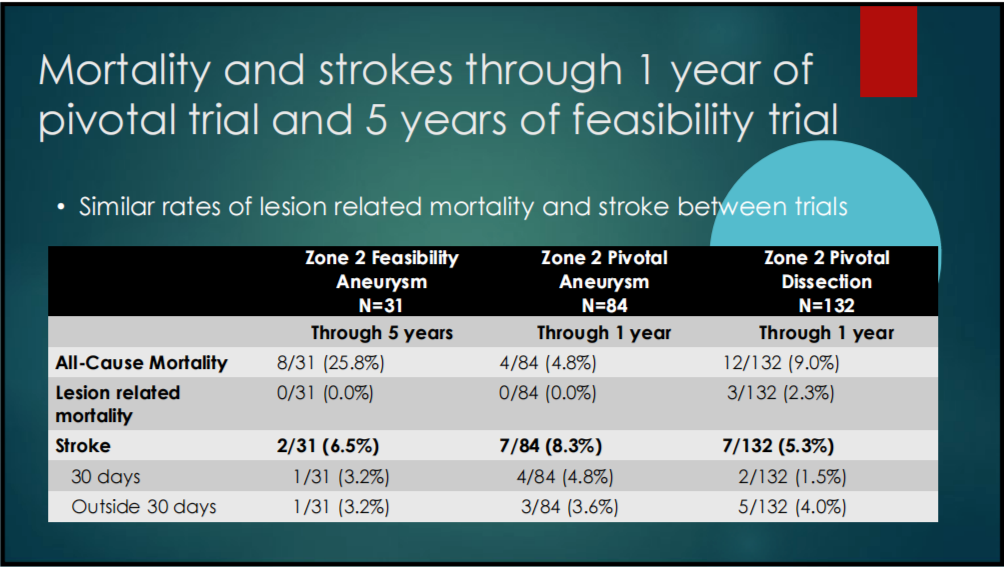
Table 1-5. Incidence of Mortality and Stroke in the 1-year pivotal and 5-year feasibility studies
Summary
1、Data from the TBE feasibility study showed a low incidence of device-related events within 5 years of surgery, with the majority occurring within 24 months of surgery.
2、Data from the pivotal TBE study in patients with Z2 aneurysms showed a low incidence of device-related events within one year of the procedure. Lesion-related mortality and stroke rates did not differ significantly between trials. The rate of patency loss, aortic rupture, and aortic dilation improved in the pivotal study.
3、As the first commercially approved branched aortic stent by FDA, its clinical benefit and efficacy need to be observed in long-term follow-up.


