Introduction
Dr. Olivier Hartung from the Vascular Surgery Department at University Hospital of Marseille, France, presented an in-depth analysis of the complications associated with endovascular treatments for pelvic venous disease (PVD) at LINC 2024. While PVD is not life-threatening, its functional symptoms can severely affect patients’ quality of life. This presentation highlighted the primary complications such as stent migration, restenosis, and thrombosis, along with preventive strategies.
Key Points
1. Complications in Embolization Therapy:
•Contrast Extravasation: During pelvic vein embolization, the use of foam or glue is discouraged due to the risk of causing pain or retroperitoneal fibrosis. Though rare, contrast extravasation can occur, particularly when coils migrate near the renal vein.

•Coil Migration: While the incidence of coil migration is low, its risk increases depending on the coil’s positioning. Extra care is needed during coil deployment in the main iliac vein trunk.
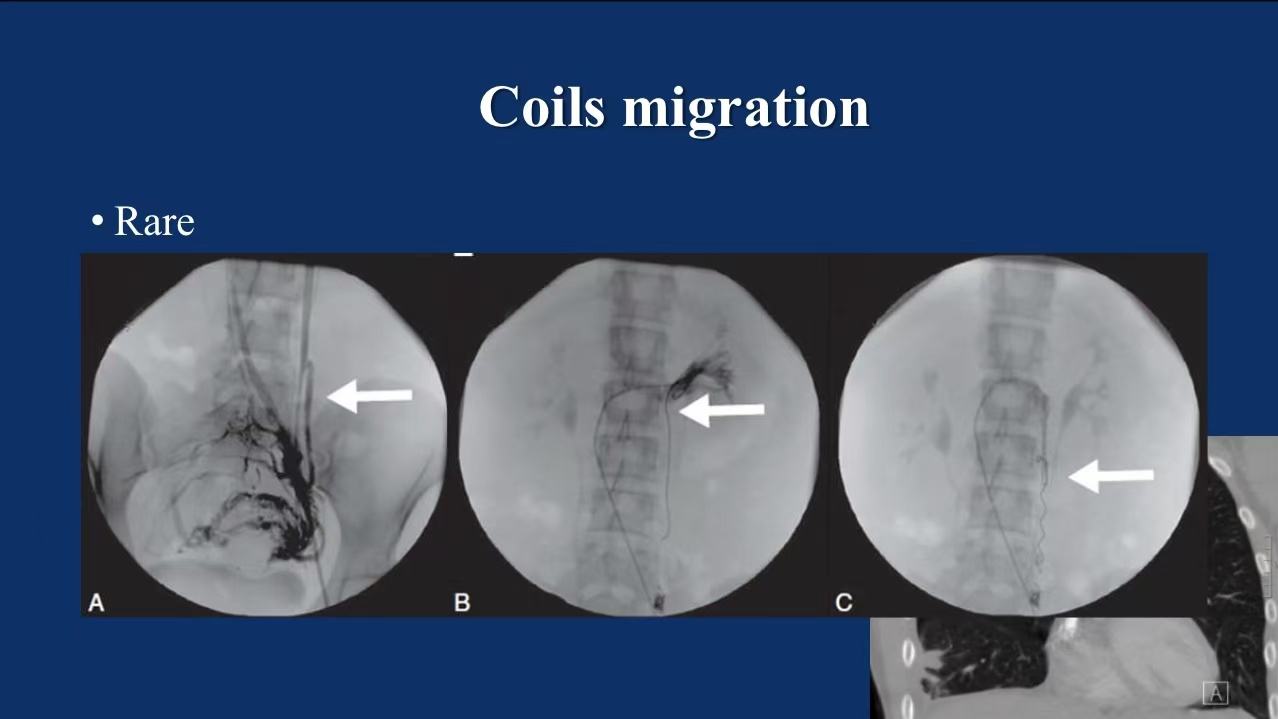
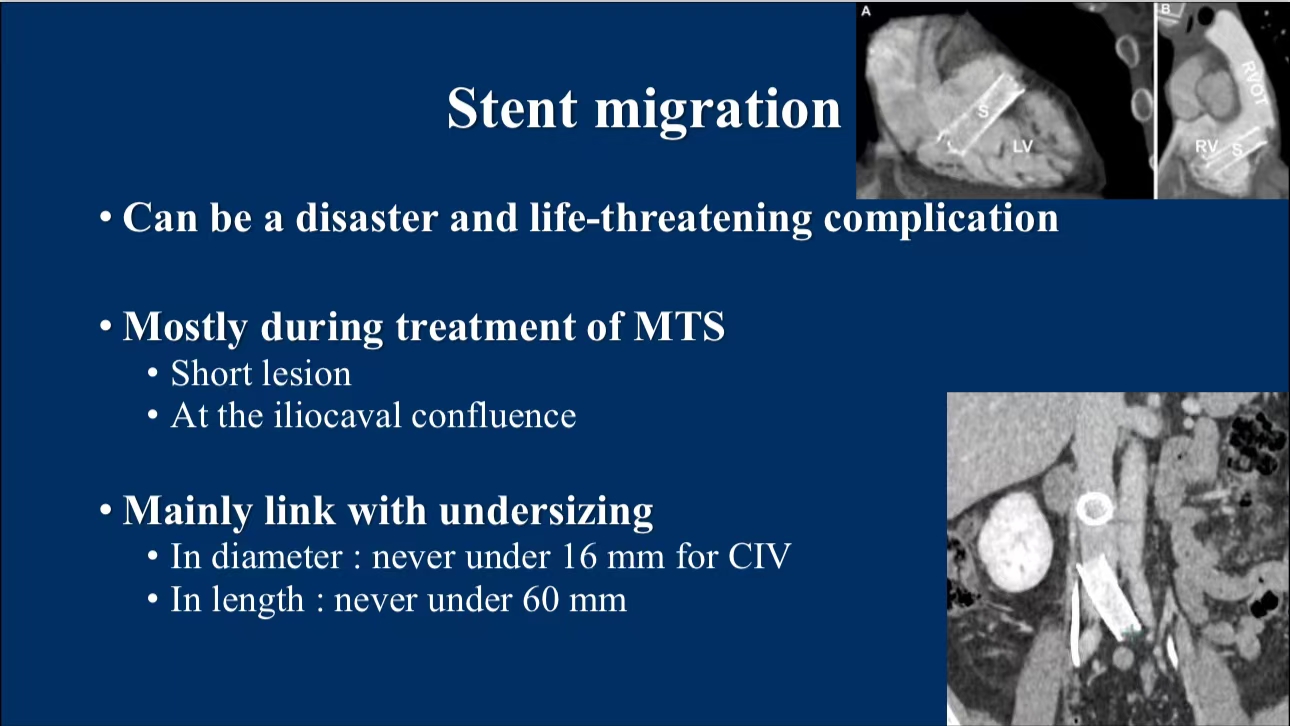
2. Complications with Iliac Vein Stenting:
•Stent Migration: One of the most severe complications, particularly in the treatment of May-Thurner Syndrome. This often occurs at the iliac vein confluence, especially when short-segment stents are used. A recommended stent diameter of at least 16mm and a length greater than 60mm help minimize this risk.
•Stent Compression and Fracture: Stents placed near the inguinal ligament are at a higher risk of compression and fracture. Adequate overlap between stents (at least 2cm) is essential to ensure stability.

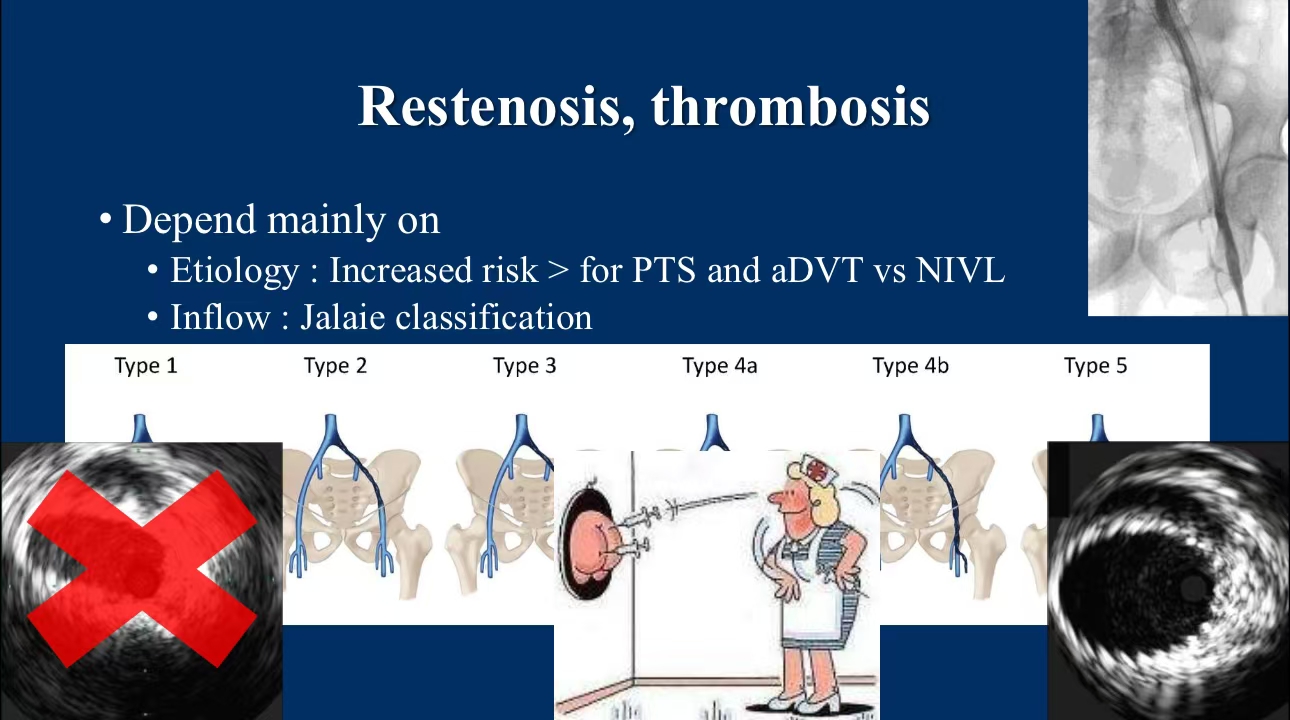
3. Restenosis and Thrombosis Management:
•Risk Factors:Restenosis and thrombosis are common complications, particularly in patients with post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS) and acute deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Jalaie classification can be helpful in assessing postoperative inflow issues. IVUS and postoperative anticoagulation therapy are critical in reducing these complications.
Conclusion
Endovascular treatment remains an effective solution for PVD but comes with specific complications, particularly when technical precision is lacking. To mitigate risks, it is recommended to avoid foam or glue embolization, properly size and place stents, and apply IVUS and anticoagulation postoperatively.
Contact Us
For submissions, please contact us at: endovascluar@simtomax.cn
Thank you for your attention, and let’s continue to safeguard health together!
More international information available at:
•Facebook: Vasco Knight
•Instagram: knight_vasco


