Author: Bart Sanders
Institution: STENTiT B.V., Eindhoven, Netherlands
Summary:
This presentation introduces the innovative application of Resorbable Fibrillated Scaffold (RFS) technology developed by STENTiT B.V. in vascular regeneration, specifically for treating ischemic limb lesions. RFS aims to stimulate “endogenous” new vessel formation through intimal regeneration, reducing the need for reintervention and minimizing complication risks. Preclinical trials in animal models have shown that RFS exhibits good flexibility, low hyperplasia, and high patency rates.
Clinical Advantages of RFS Technology
1.Regenerative Capability: The micro-fibril structure of the RFS promotes vascular remodeling post-implantation, reducing the risk of late-stage thrombosis.
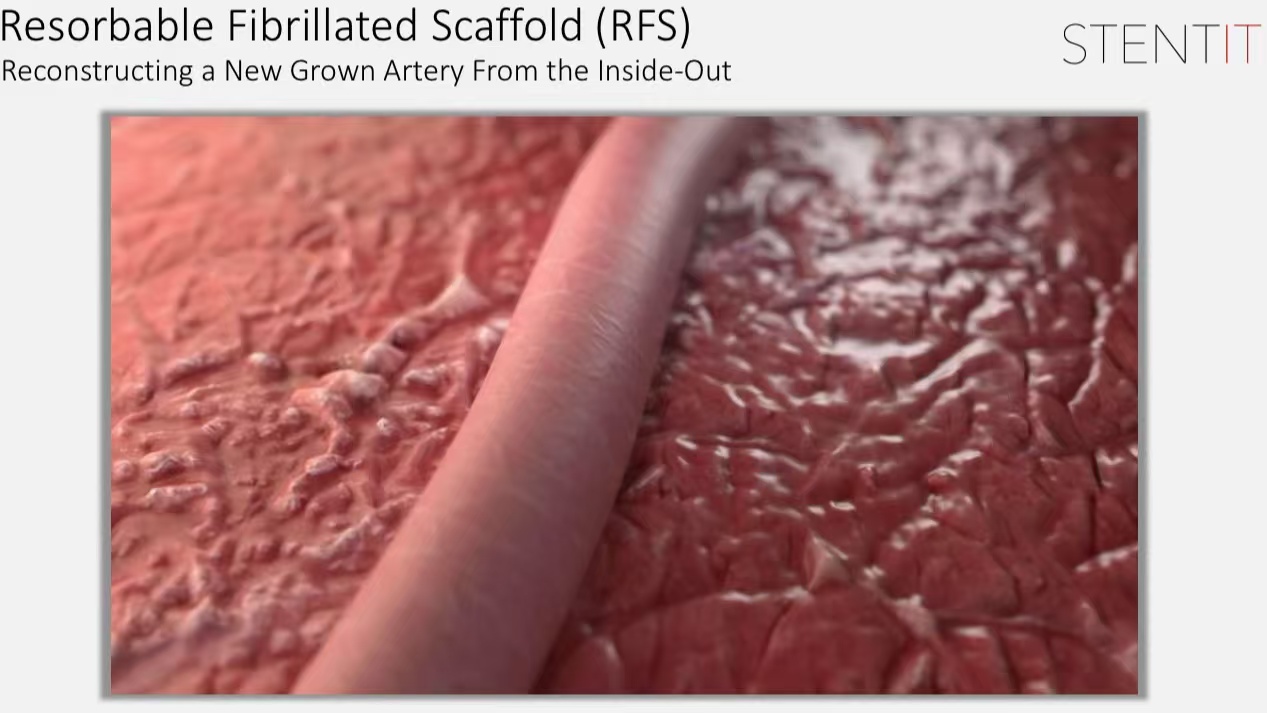
2. Resorbability: The scaffold gradually absorbs over 3 to 6 months, allowing for future reinterventions if necessary.
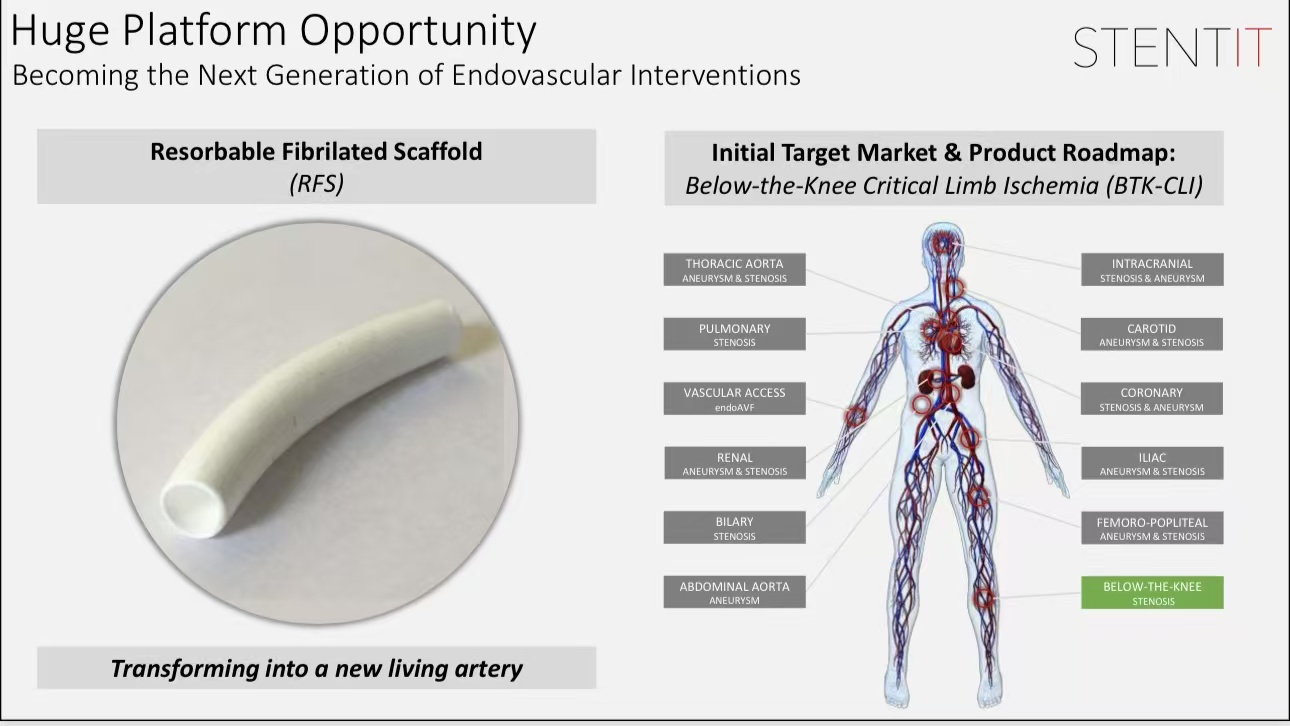
3.Flexibility: It adapts to the natural curvature of vessels, showing promising clinical outcomes in patients with below-the-knee critical limb ischemia (BTK-CLI).
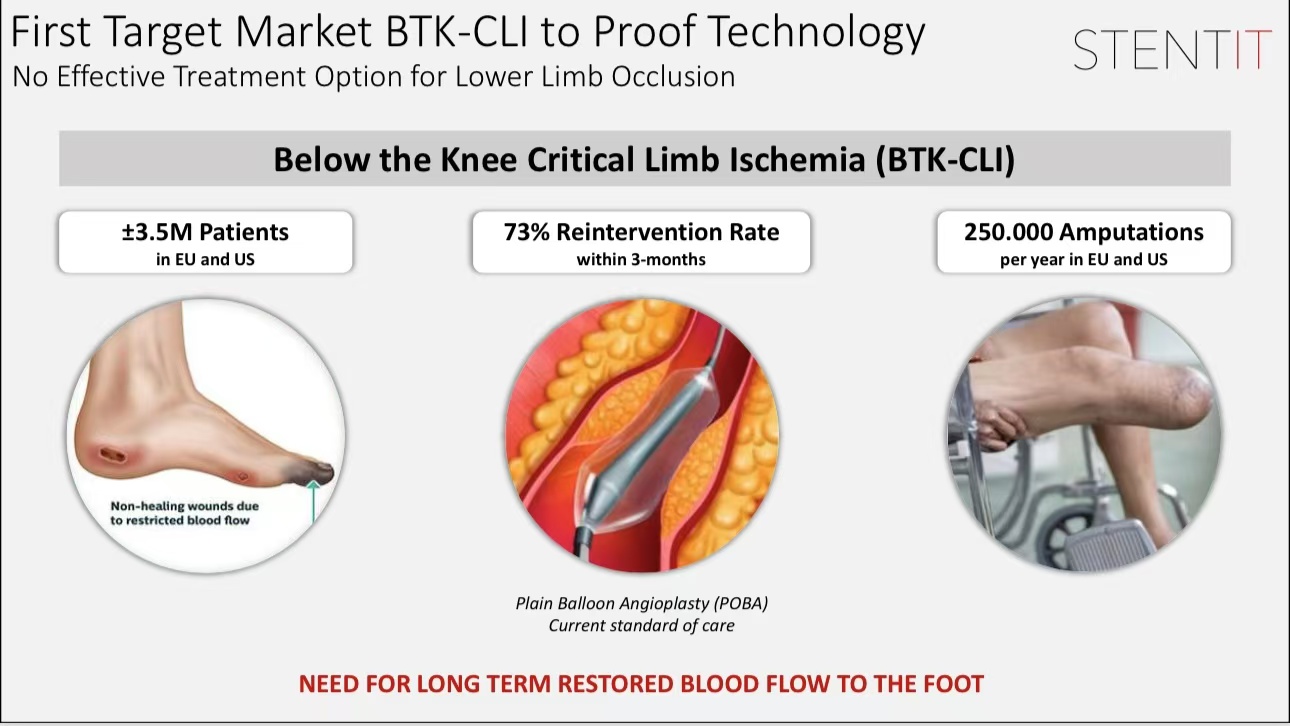
Key Preclinical Research Data
•Elastic Regeneration: The RFS scaffold achieved initial elastic remodeling within 3 months, with full vascular wall regeneration observed by 6 months.
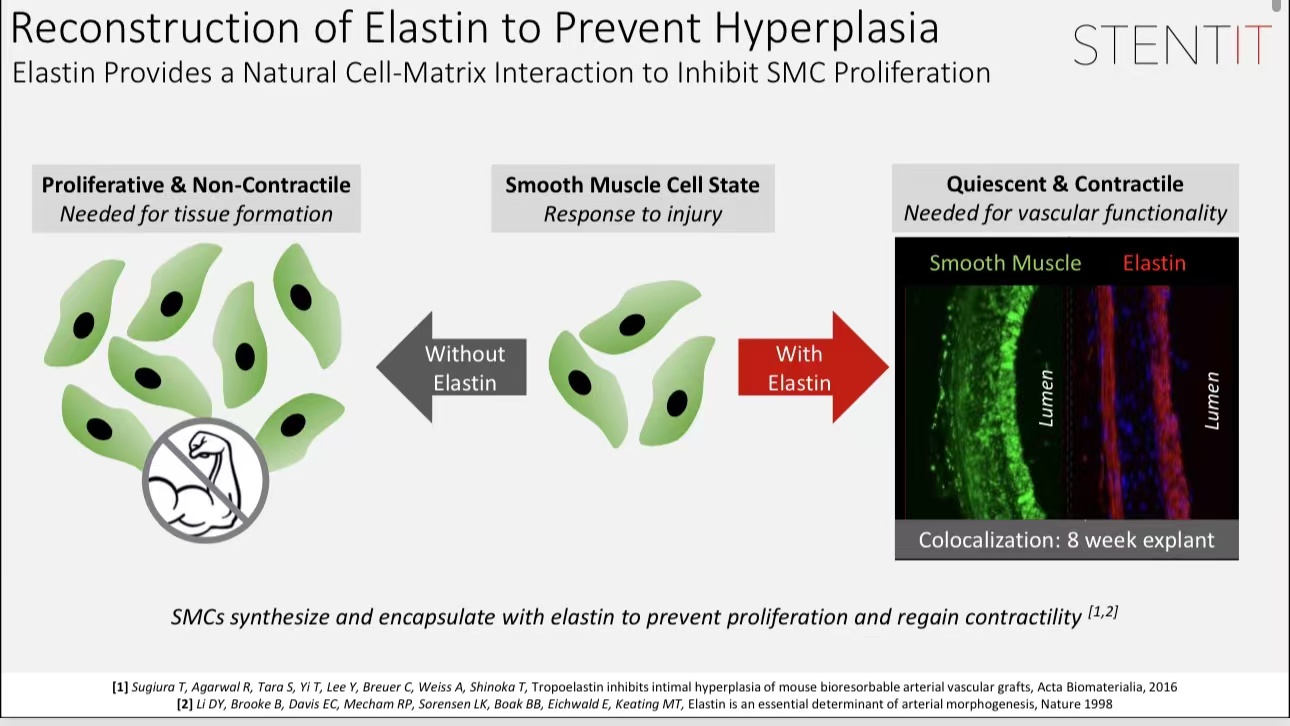
•Safety and Efficacy: Experiments in medium-sized animal models showed no significant inflammatory response post-implantation, with ideal patency rates.
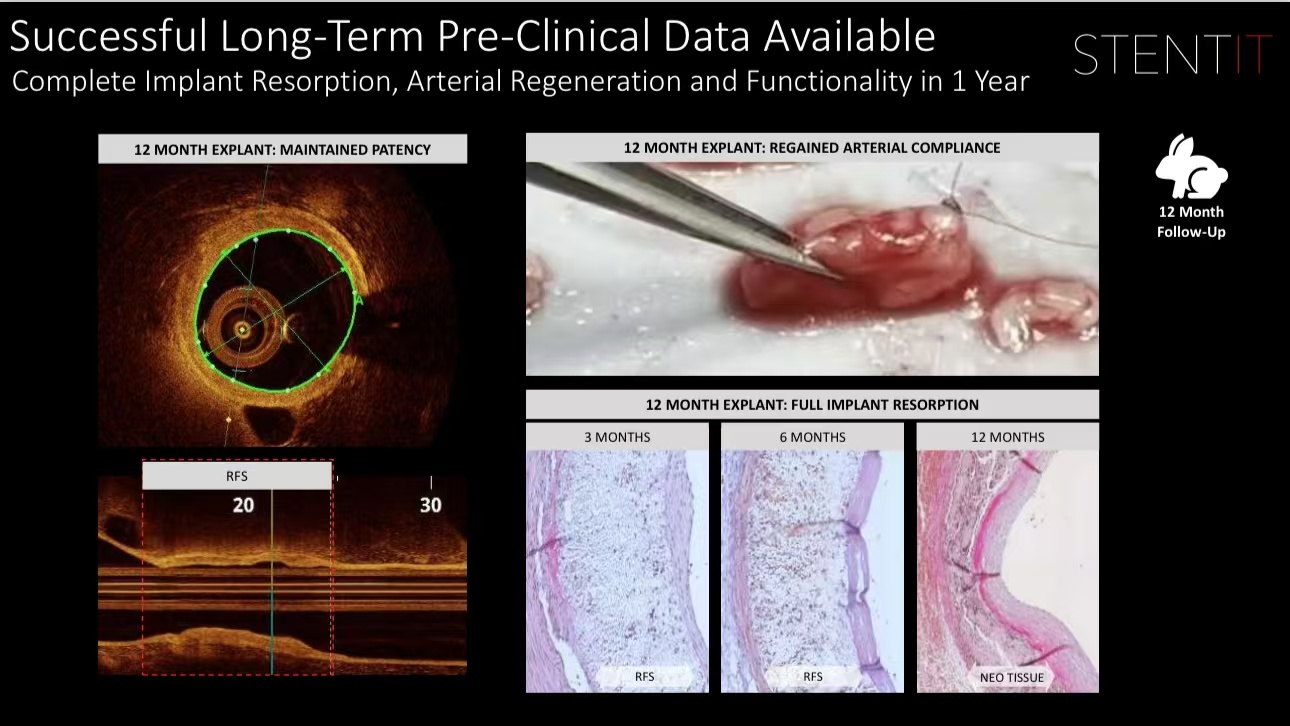
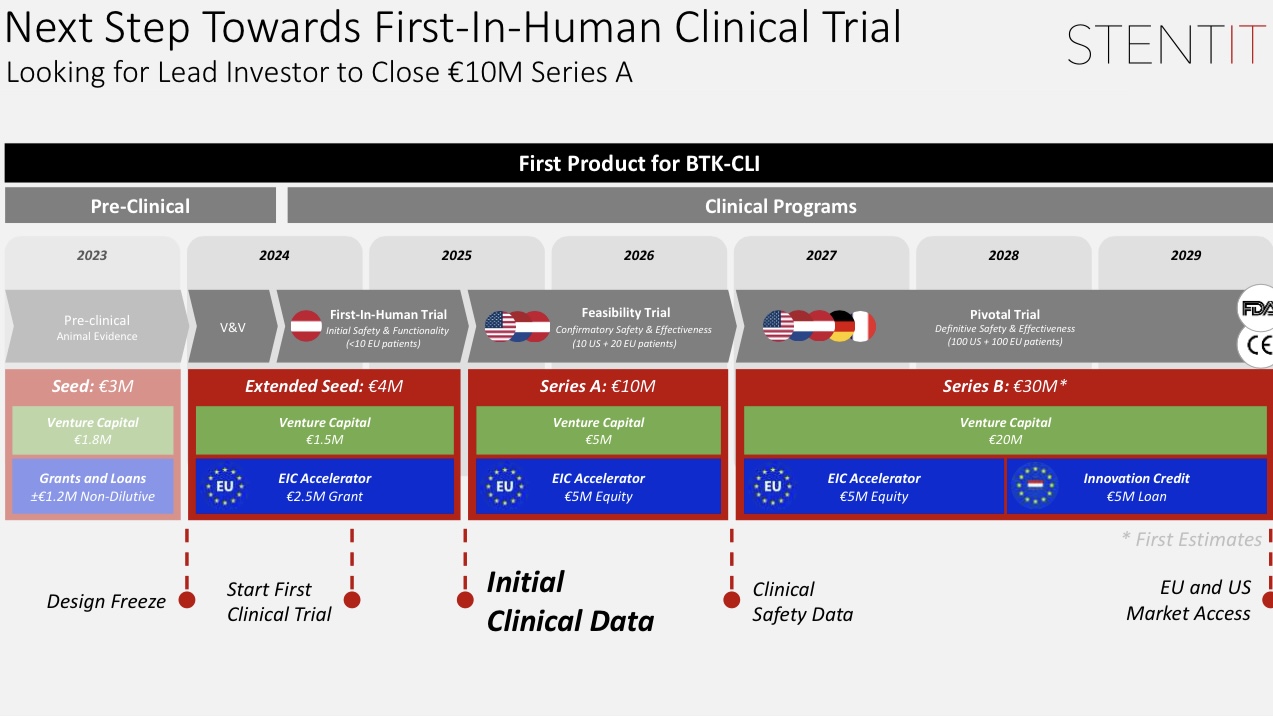
Clinical Translation and Market Outlook
STENTiT B.V. plans to begin first-in-human trials for BTK-CLI patients in 2024, with a targeted market launch in the EU and the US by 2029. RFS technology has the potential to become a standard next-generation treatment for vascular disease, addressing long-term blood flow issues through its regenerative mechanism.