Author: Dr. Manuela Konert
Institution: Leipzig University Hospital, Germany
Summary
This presentation discusses new techniques and treatment strategies for preventing post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS) in patients with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). By analyzing the epidemiology, risk factors, and clinical studies of venous thromboembolism (VTE), the author highlights the role of residual venous obstruction (RVO) and explores mechanical thrombectomy as a safe and effective method of treatment.
Key Points in Preventing PTS
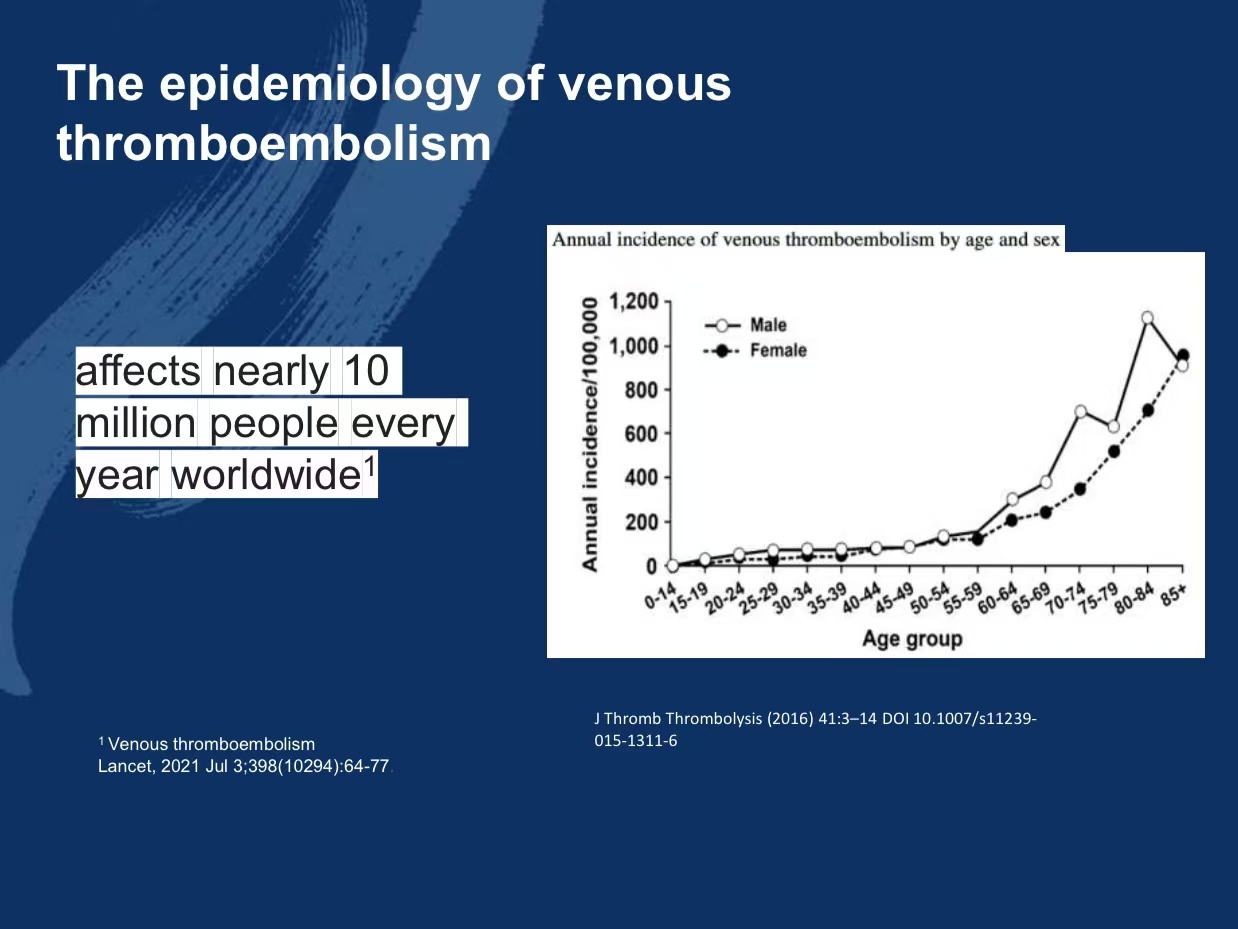
•Impact of Venous Thromboembolism: Annually, approximately 10 million cases of venous thromboembolism (VTE) occur worldwide, with PTS developing in up to 50% of cases.
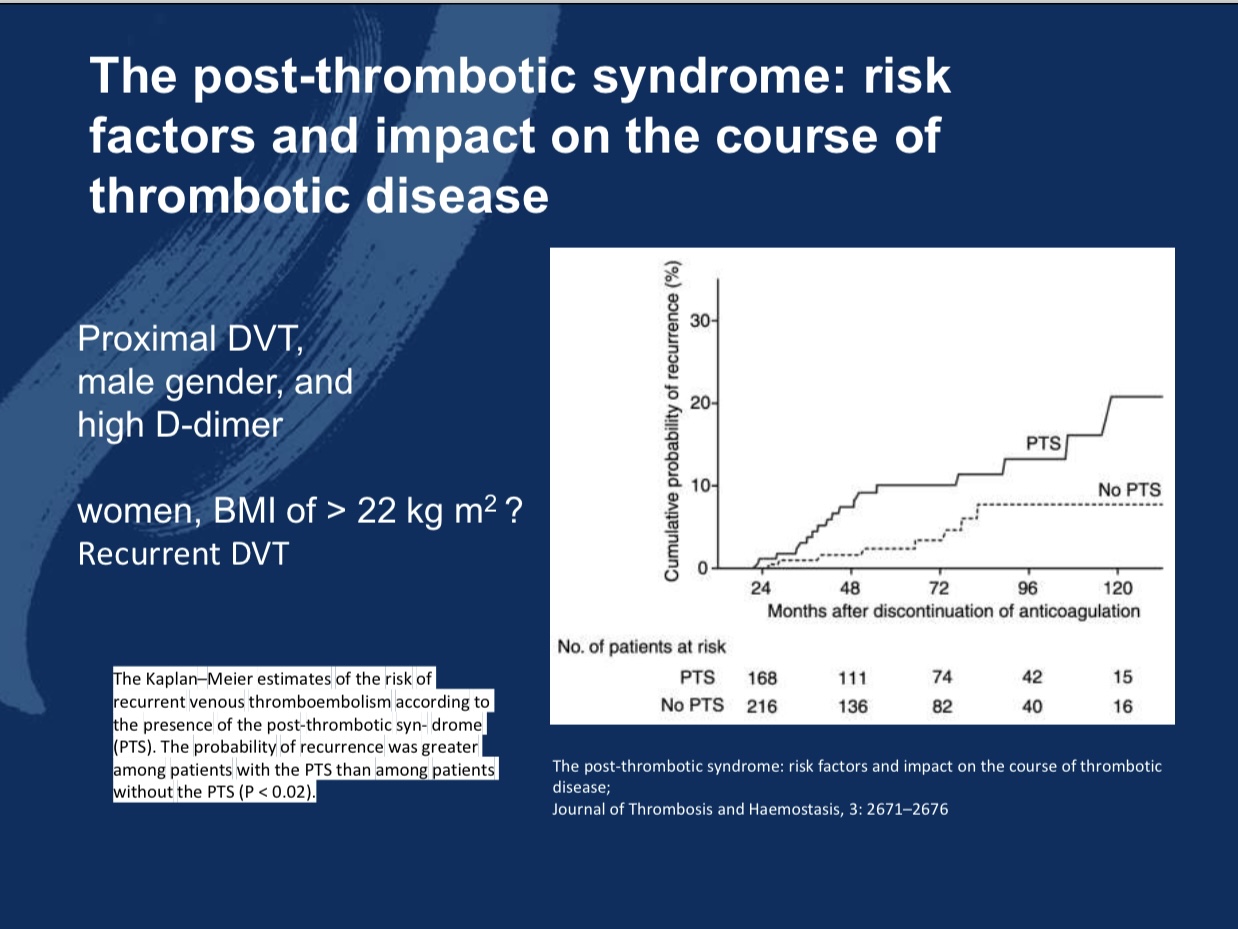
•Major Risk Factors: Proximal DVT, male gender, elevated D-dimer levels, and a BMI over 22 kg/m² are high-risk factors for developing PTS.
Treatment Approaches
• Application of Mechanical Thrombectomy: Studies show that mechanical thrombectomy is an effective device for reducing residual thrombus, lowering the incidence of PTS and recurrent DVT.
• Efficacy of Embolization Interventions: Multiple studies support embolization interventions in reducing PTS risk, especially in femoral vein obstruction, where cumulative primary and secondary patency rates have been positive.
Clinical Case Analysis
• Clinical Case: A 68-year-old male patient treated for femoral vein obstruction successfully restored blood flow following mechanical thrombectomy, preventing the development of PTS.


Conclusion
1. Effectively managing residual venous obstruction is key to preventing PTS.
2. Mechanical thrombectomy is a safe and effective treatment option that reduces the risk of recurrent DVT.
3. Further reliable data is needed to assess the role of the femoral vein in PTS prevention.

Contact Us
•Email: endovascluar@simtomax.cn
More international information available at:
•Facebook: Vasco Knight
•Instagram: knight_vasco


