Author: Dr. Stephen Black
Institution: Vascular Surgery, King’s College London St Thomas’ Hospital
Summary
This article explores the mid- to long-term patency of venous stents and outlines strategies to maintain the effectiveness of stents through early intervention and post-operative follow-up. By analyzing clinical data, the study identifies the primary factors leading to stent failure and strategies for extending patency. The research concludes that early monitoring and timely re-intervention are key to ensuring long-term stent success.
Key Discussion Points
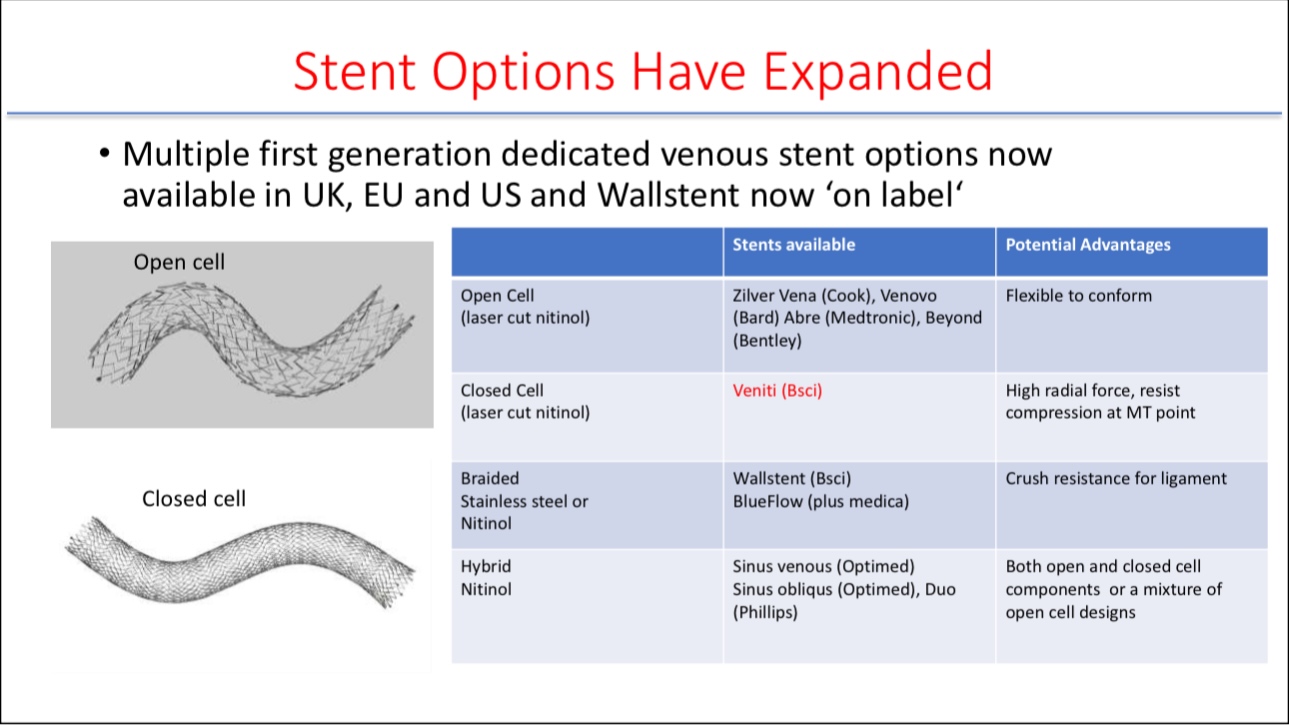
1.Venous Stent Selection:
•Different stent designs are available on the market, such as open-cell stents (e.g., Zilver Vena, Venovo, Abre) and closed-cell stents (e.g., Veniti). Open-cell stents offer greater flexibility, while closed-cell designs provide higher radial force and are suitable for areas requiring greater resistance.
2.Clinical Outcomes:
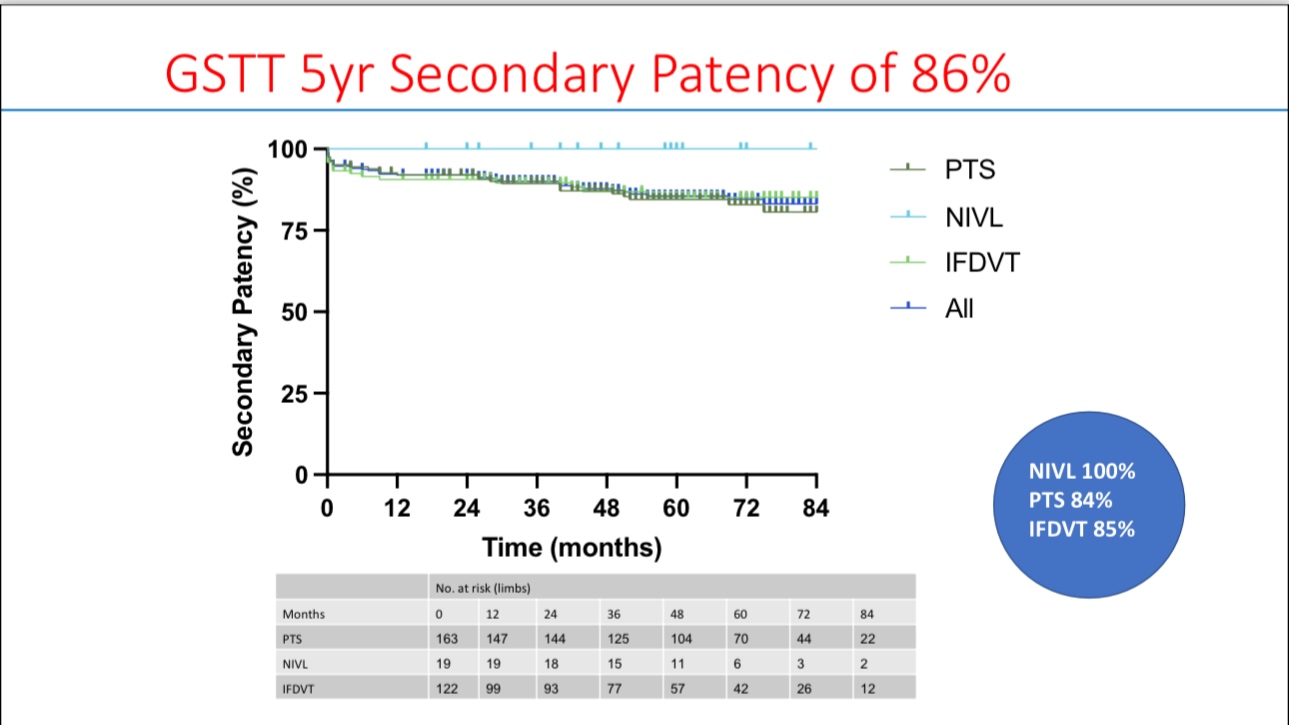
•Long-term data from St Thomas’ Hospital showed a secondary patency rate of 86% over five years. Different lesion types yielded varying patency rates, with post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS) showing an 84% patency rate, non-thrombotic iliac vein lesions (NIVL) reaching 100%, and iliac femoral deep vein thrombosis (IFDVT) at 85%.
3.Re-Intervention Strategy:
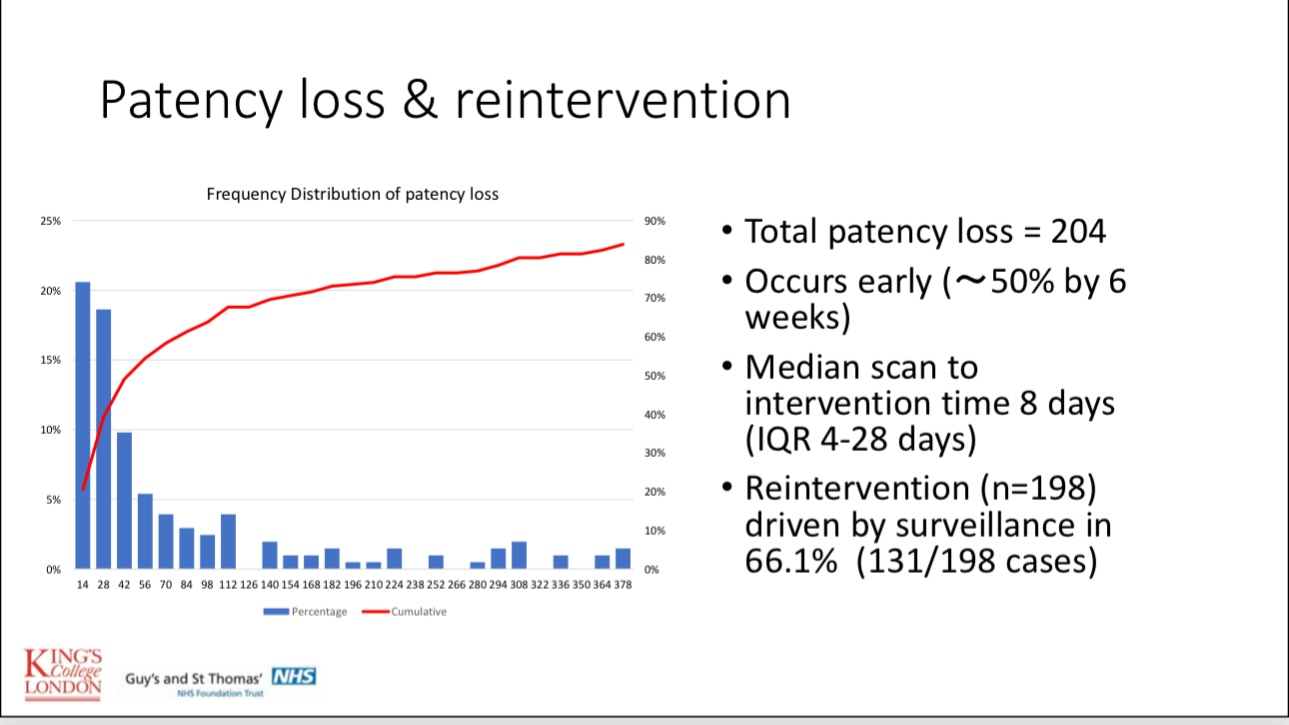
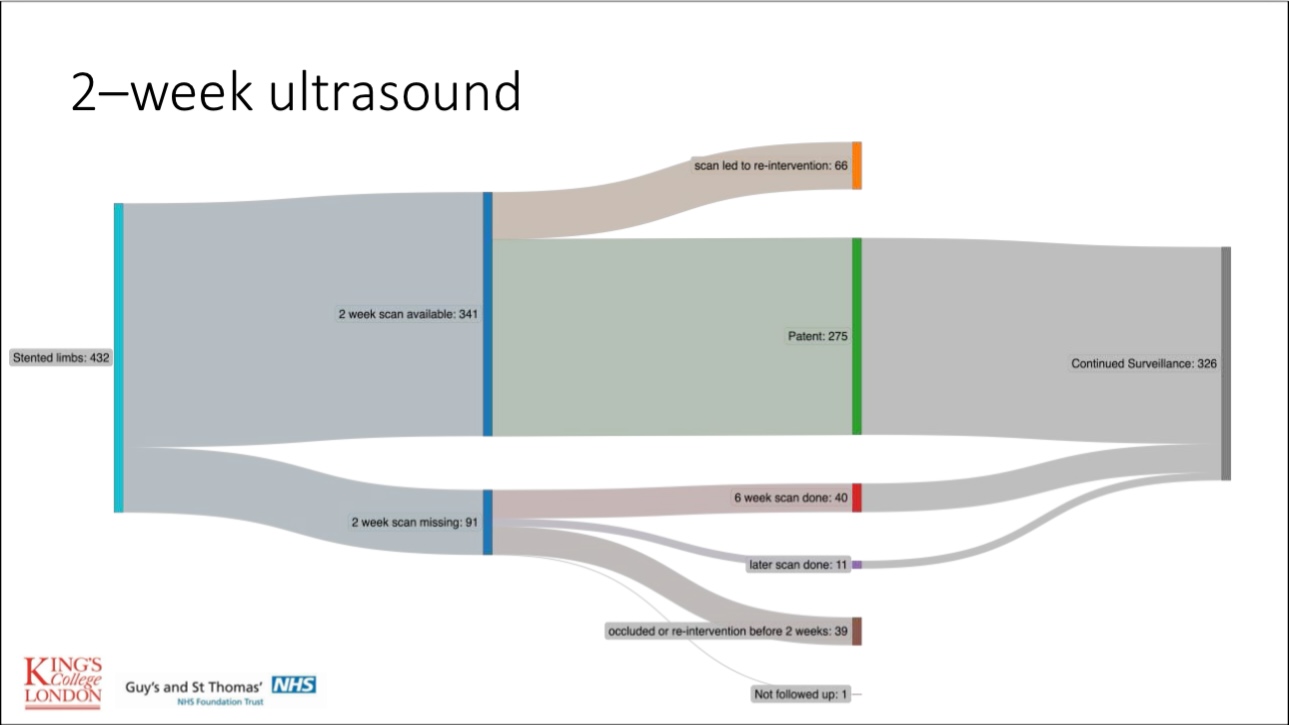
•Most stent failures occur within six weeks post-procedure due to thrombosis or inflow disease. Regular monitoring and timely re-interventions can restore patency in most cases.
Case Studies
•Case 1: A 57-year-old male with iliac vein stenting showed neointimal hyperplasia two weeks post-surgery. A successful balloon angioplasty restored patency, with no restenosis observed at the one-year follow-up.
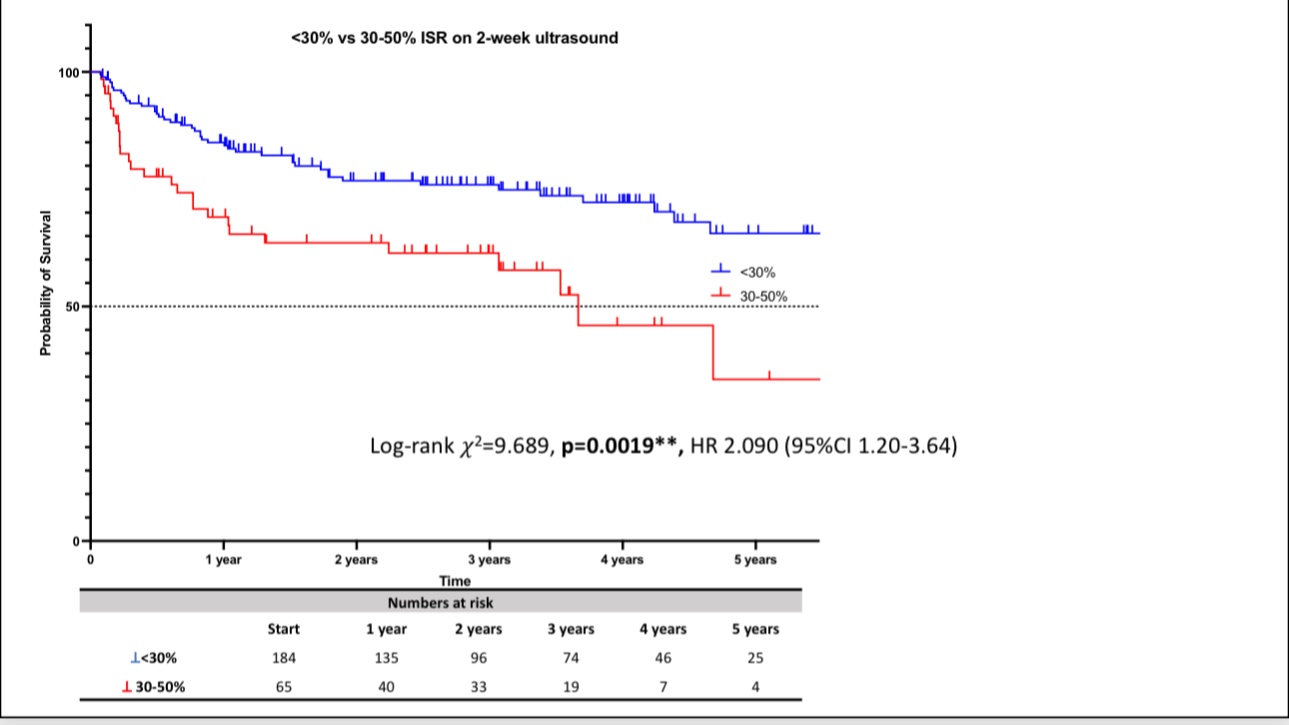
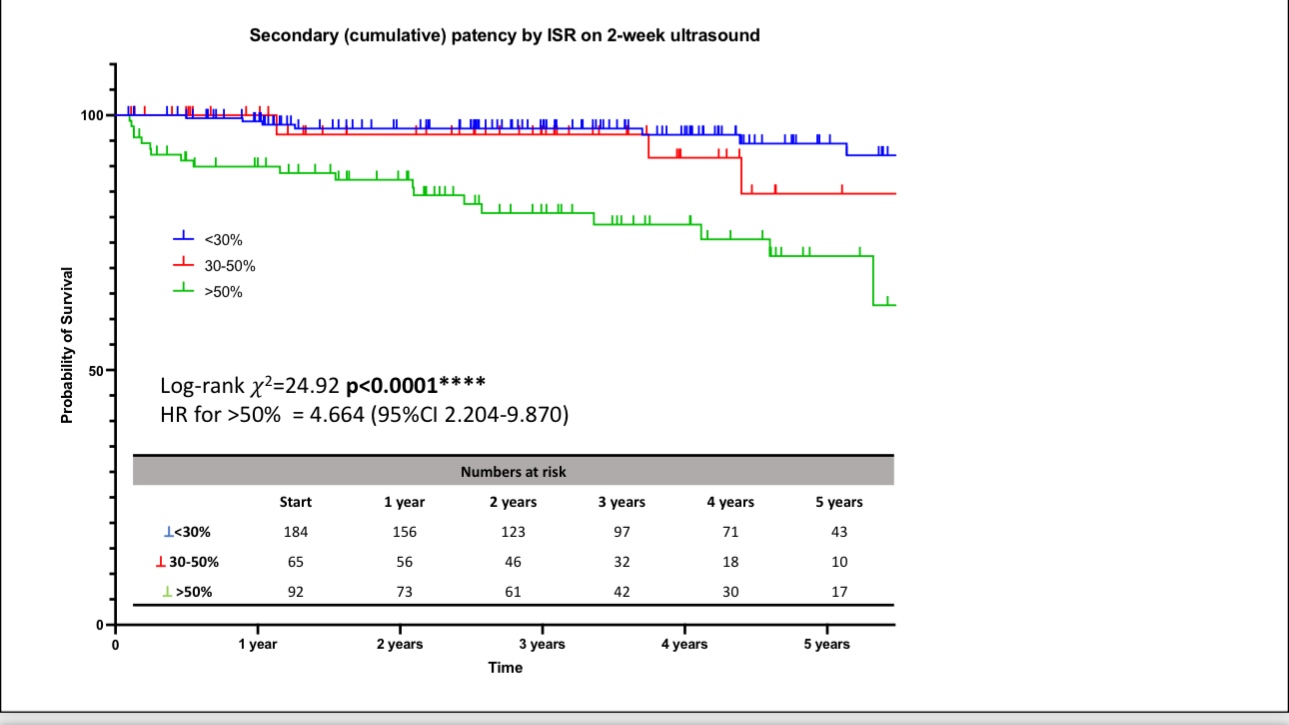
•Case 2: A 45-year-old female developed in-stent thrombosis six months post-stenting. Following re-intervention, patency was restored, and the stent remained functional during follow-up.
Conclusion
1.Early intervention, post-operative follow-up, and timely re-intervention are crucial for maintaining the long-term patency of venous stents.
2.While various stent technologies are available, patient management remains the key to long-term success.
3.Re-intervention should be considered part of ongoing stent maintenance rather than a failure, ensuring long-term outcomes through precise monitoring and intervention.

Contact Us
For submissions, please contact us at: endovascluar@simtomax.cn
Thank you for your attention, and let’s continue to safeguard health together!
More international information available at:
•www.vascularknight.com
•Facebook: Vasco Knight
•Instagram: knight_vasco


