Speaker: Hamad Algedaiby, MD
Institution: Department of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, Theresienkrankenhaus Mannheim, Germany
Abstract
This article presents a case of a 75-year-old male with a complex juxtarenal aortoiliac aneurysm, demonstrating the clinical application of a seven-vessel fenestrated/branched stent-graft combined with embolization strategies. Leveraging the technical advantages of Boston Scientific’s EMBOLD™ Fibered Coils, this study provides practical guidance and innovative insights for endovascular management of high-risk vascular pathologies.
Introduction
Juxtarenal aortic aneurysms with complex renal vascular anatomy pose significant challenges in vascular surgery. Traditional open repair carries high risks, particularly for patients with cardiac comorbidities. Endovascular aortic repair (EVAR) utilizing fenestrated/branched stent-grafts has emerged as a mainstream approach, yet it requires precise branch vessel management and prevention of endoleaks. Recent advancements in embolization devices, such as the EMBOLD™ Fibered Coils, have further enhanced procedural safety and efficiency.
Case Analysis: Individualized Application of Seven-Vessel Fenestrated Stent-Graft
Patient Profile
Age and Medical History: 75-year-old male with coronary artery disease (NYHA Class 3), post-PTCA (6 months prior), ASA Class 3 anesthesia risk.

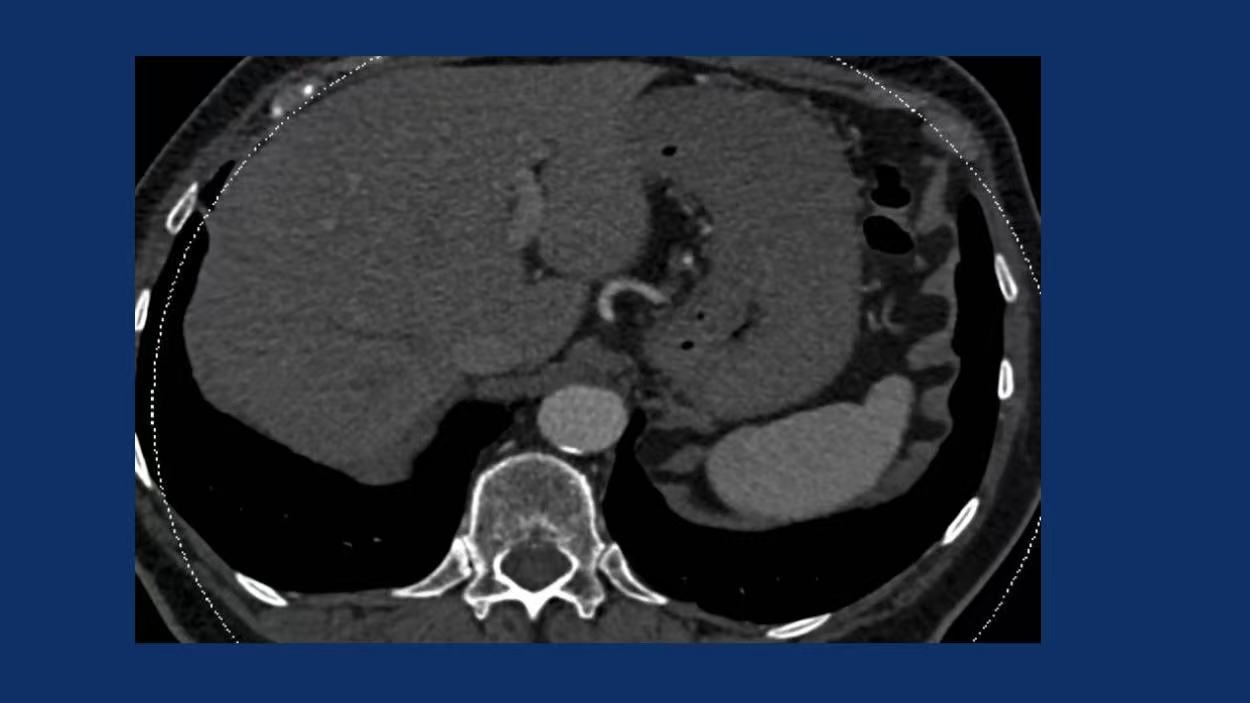
Vascular Pathology:
54 mm juxtarenal aortic aneurysm (6 mm growth in 6 months).
27 mm right common iliac artery aneurysm.
Therapeutic Challenges
Contraindication for Open Surgery: Poor cardiac function.
Anatomical Complexity: Preservation of bilateral renal arteries, superior mesenteric artery (SMA), and accessory renal arteries.
Surgical Strategy
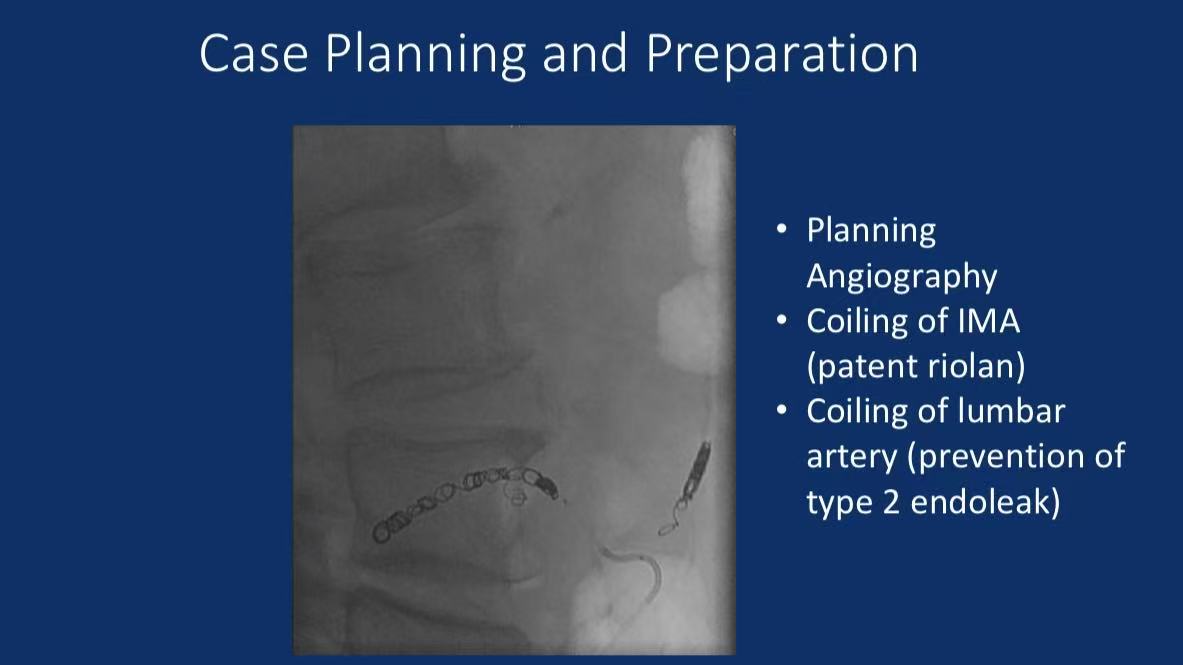
Preoperative Embolization (to prevent Type II endoleak):
Inferior Mesenteric Artery (IMA) Coiling: Blood flow occlusion using embolization coils.
Lumbar Artery Coiling: Reduction of collateral circulation-induced endoleaks.
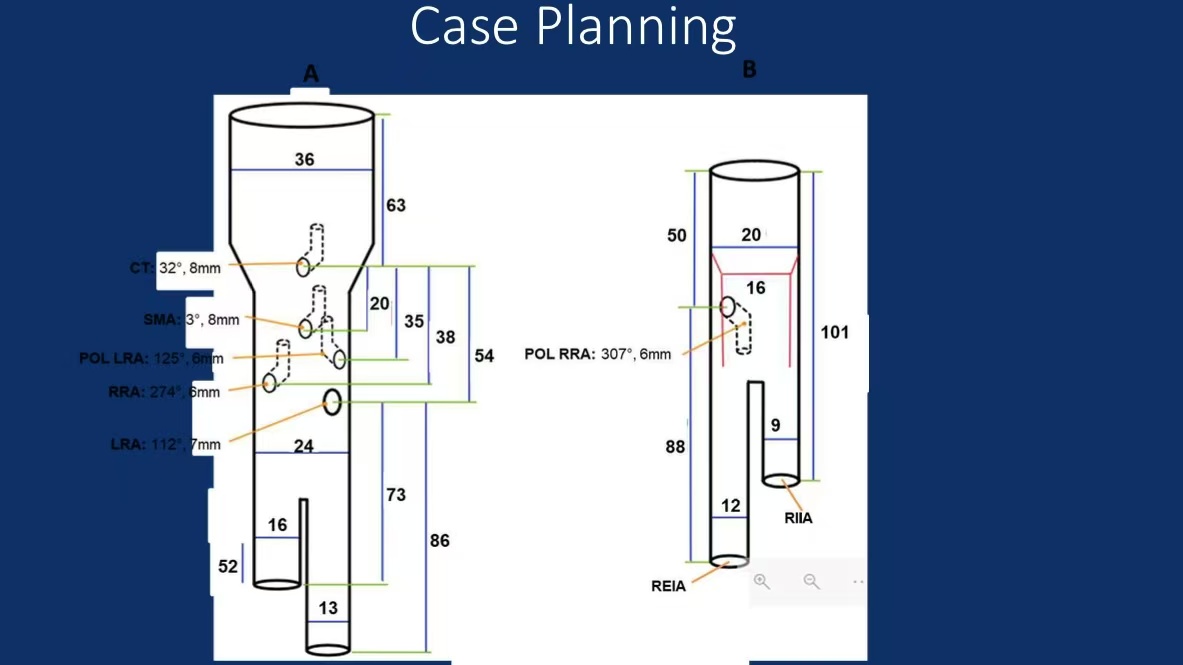
Seven-Vessel Fenestrated/Branched Stent-Graft Implantation:
Coverage of aortic and iliac aneurysms with preservation of renal arteries, SMA, and accessory branches.
Precise alignment of stent branches with target vessel ostia to ensure patency.
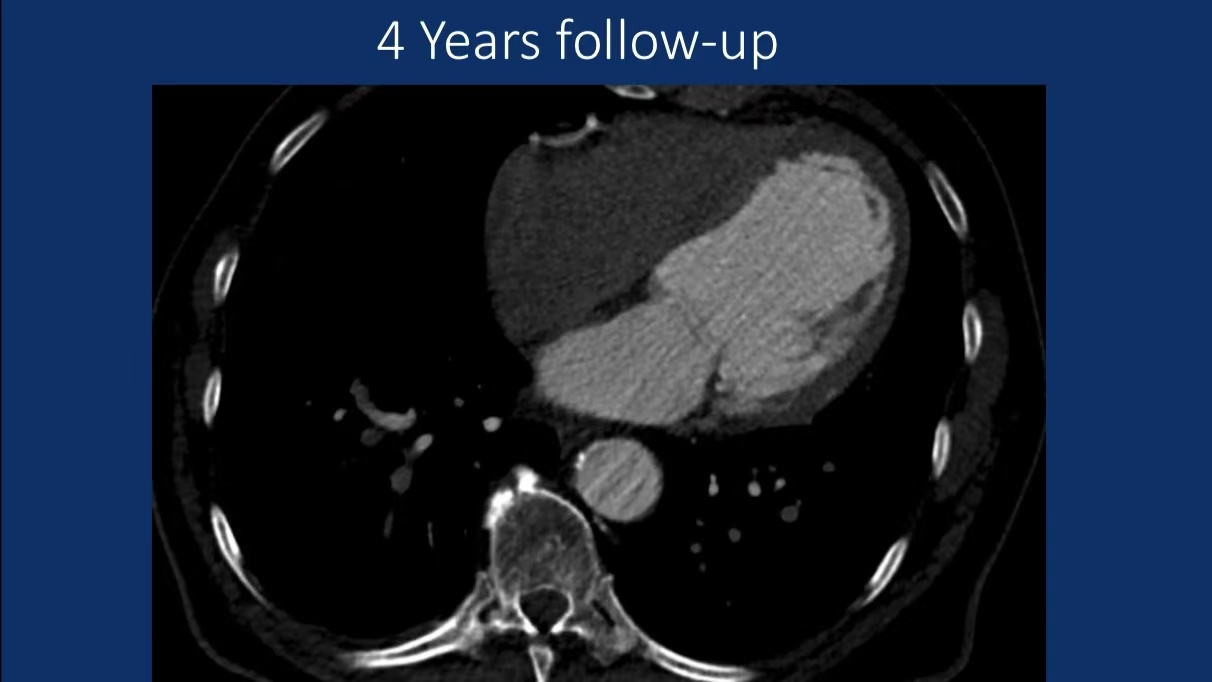
Postoperative Management:
Long-term dual antiplatelet therapy (aspirin + clopidogrel).

Regular CTA follow-up (no recurrence at 4 years).

Technical Highlights
Branch Vessel Alignment: Intraoperative angiography and 3D reconstruction for accurate positioning.
Endoleak Prevention: Critical role of preoperative IMA and lumbar artery embolization.
Product Innovation: EMBOLD™ Fibered Coils
Key advantages relevant to this case:
1.Full Controllability:Adjustable coil positioning prevents accidental embolization of critical branches (e.g., IMA).
2.Kink-Resistant:Design Nitinol delivery system navigates tortuous anatomy (e.g., lumbar arteries), reducing complications.
3.Catheter Compatibility:Compatibility with 0.021"–0.027" microcatheters accommodates diverse anatomical needs.
4.High Embolic:Efficacy PET fibers enhance thrombogenicity, ideal for occluding small collaterals or preventing endoleaks.

Conclusion
1.Personalized Stent Design: Complex aneurysms demand customized fenestrated/branched stent-grafts combined with preoperative embolization to mitigate endoleak risks.
2.Innovative Device Integration: Advanced tools like EMBOLD™ Fibered Coils optimize procedural efficiency and precision in embolization.
3.Long-Term Surveillance: Rigorous antiplatelet therapy and imaging follow-up are essential to monitor stent integrity and detect delayed complications.


