Presenter: Thatchawit Urasuk, MD (FRCST)
Department of Vascular Surgery, Phramongkutklao Hospital, Thailand
Abstract
This study examines a complex case of ruptured infected iliac artery aneurysm with disseminated Burkholderia pseudomallei infection in a 64-year-old male, exploring the rescue strategy combining emergency endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) and open surgical intervention. The clinical data from CE-marked AFX-2 stent graft system (Endologix) provides practical evidence for treating infected aneurysms.
Introduction
Infected aneurysms (including melioidosis-associated cases) represent critical vascular emergencies. Traditional open repair requiring infected tissue excision and vascular reconstruction carries high morbidity in patients with systemic infection or comorbidities. The emerging paradigm of EVAR combined with antimicrobial therapy has shown viability for high-risk patients. The AFX-2 stent graft system demonstrates unique technical advantages supported by clinical validation for complex infected aneurysm management.
Case Presentation: Emergency AFX-2 Application
Patient Profile
Demographics: 64-year-old male construction worker

Comorbidities: Chronic smoking, hypertension, dyslipidemia
Chief Complaint: 3-month history of right lower quadrant pulsatile pain with intermittent fever, acute exacerbation within 1 week
Diagnostic Findings
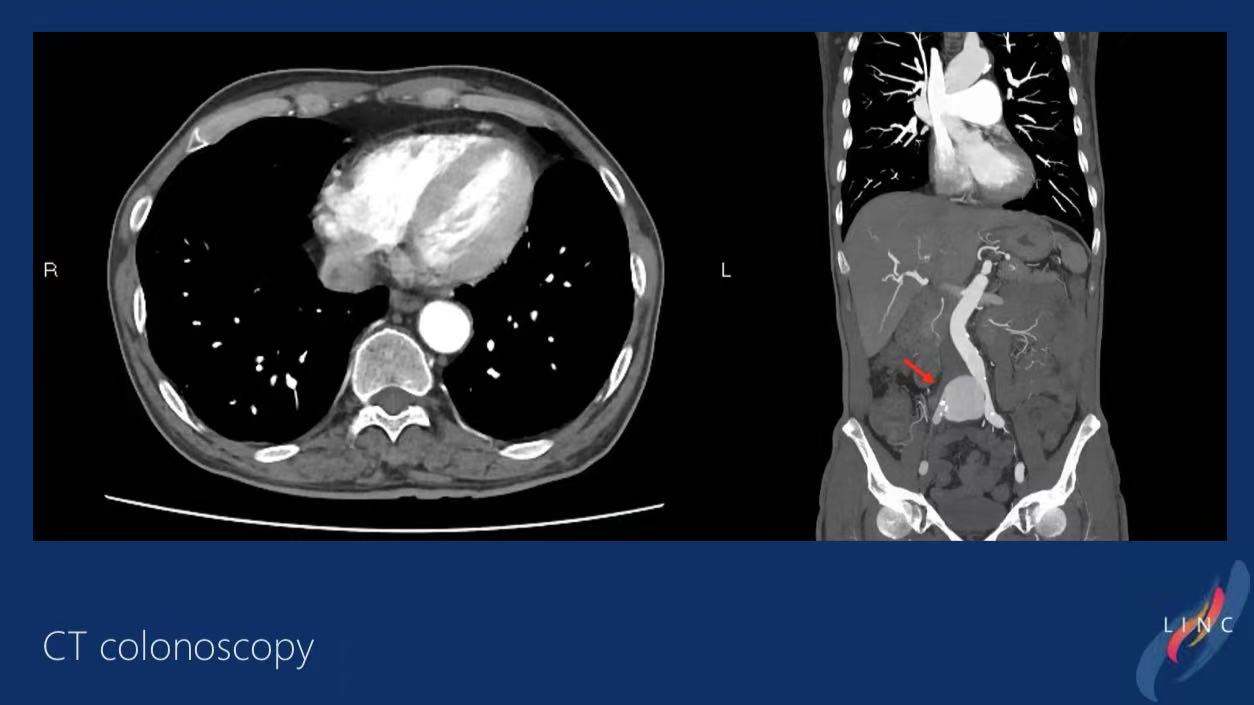
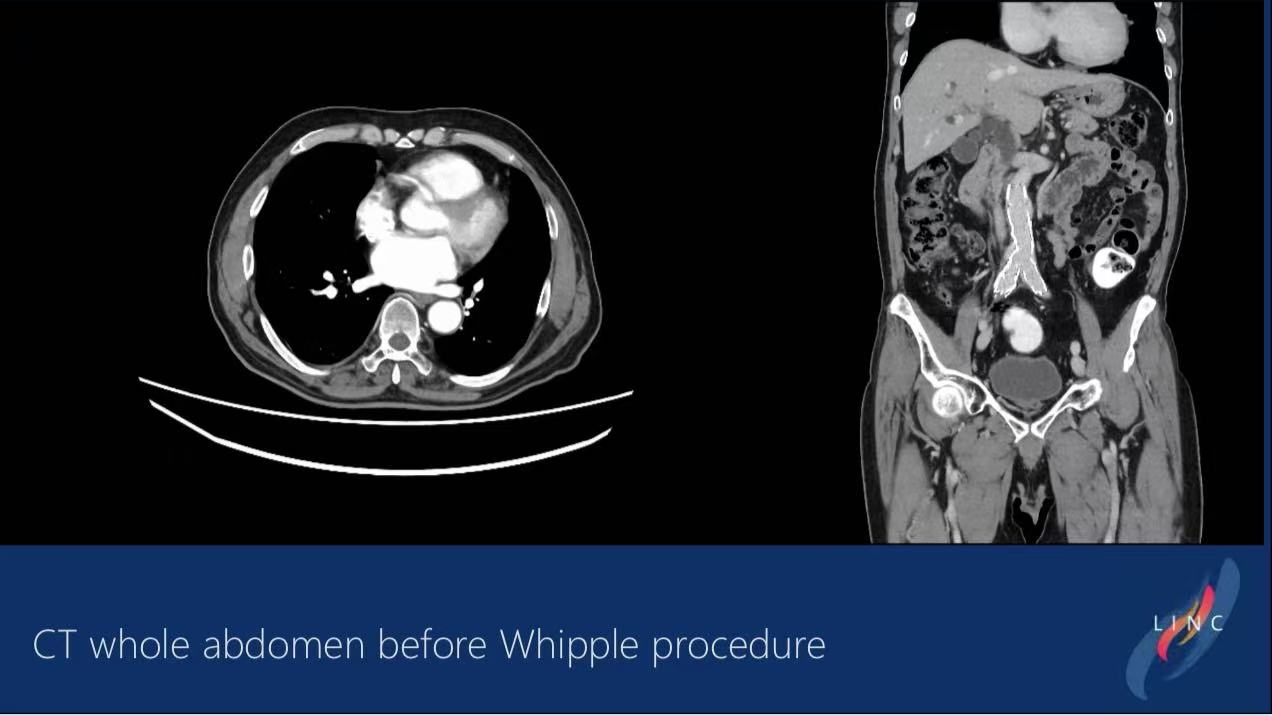
CT Angiography:
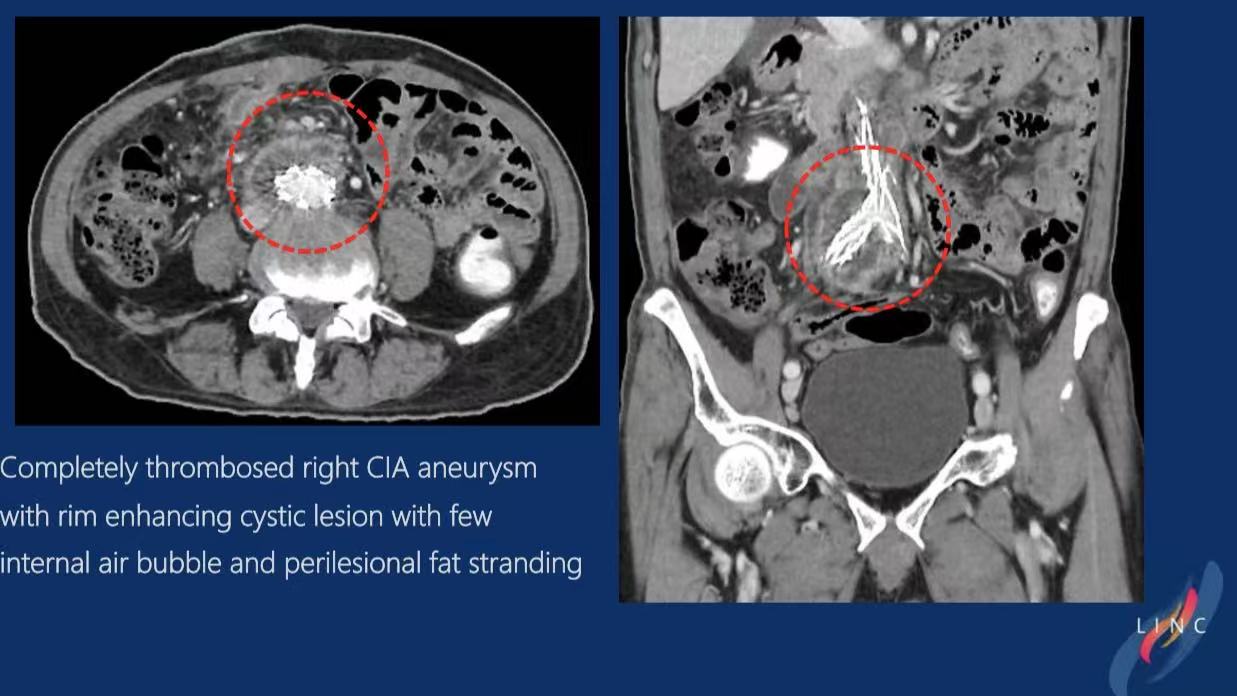
1.Complete thrombosis of right common iliac artery aneurysm
2.Peri-aneurysmal ring-enhancing cystic lesion with minimal gas (suggestive of infected aneurysm)
3.Multiple splenic low-density calcified lesions (disseminated melioidosis)
Final Diagnosis:
Ruptured infected right common iliac artery aneurysm with systemic Burkholderia pseudomallei infection
Therapeutic Challenges
1.Acute rupture requiring urgent intervention
2.High surgical risk due to systemic sepsis
3.Coexisting splenic abscess requiring multi-organ management
Surgical Strategy
Emergency EVAR:
AFX-2 stent graft deployment covering ruptured segment

8Fr/25cm delivery system with precise placement
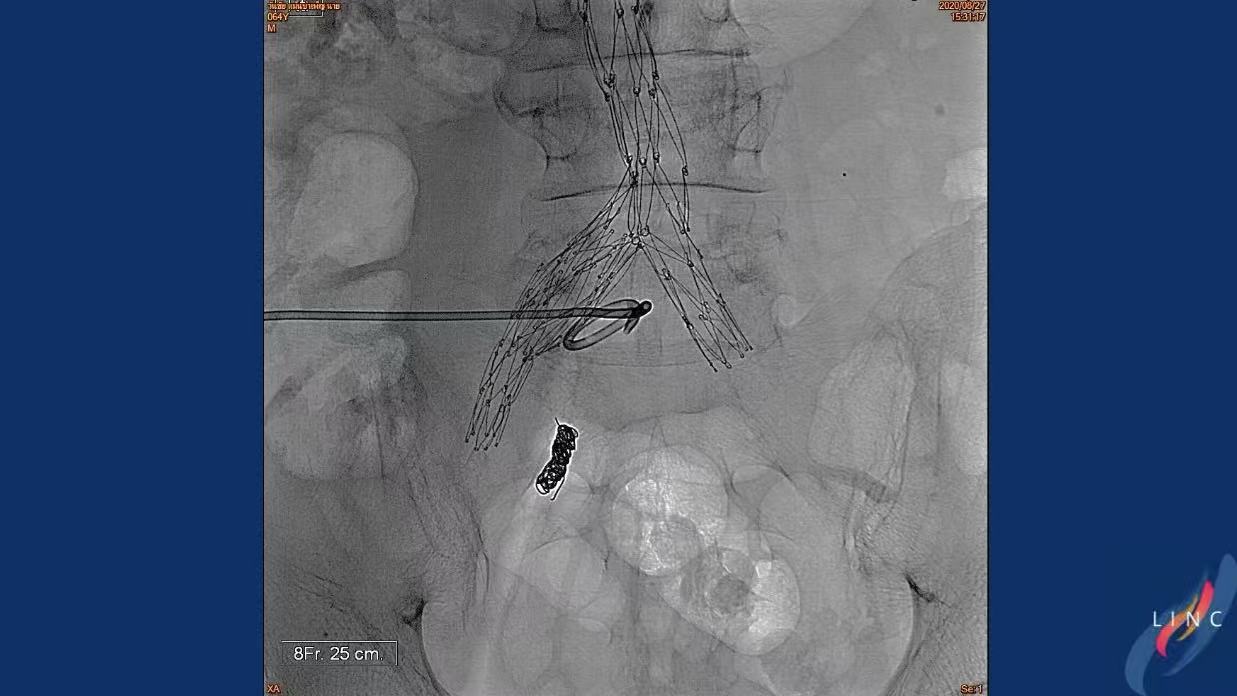
Post-deployment angiography confirmed exclusion without endoleak
Open Surgery:Concurrent splenectomy and abscess drainage
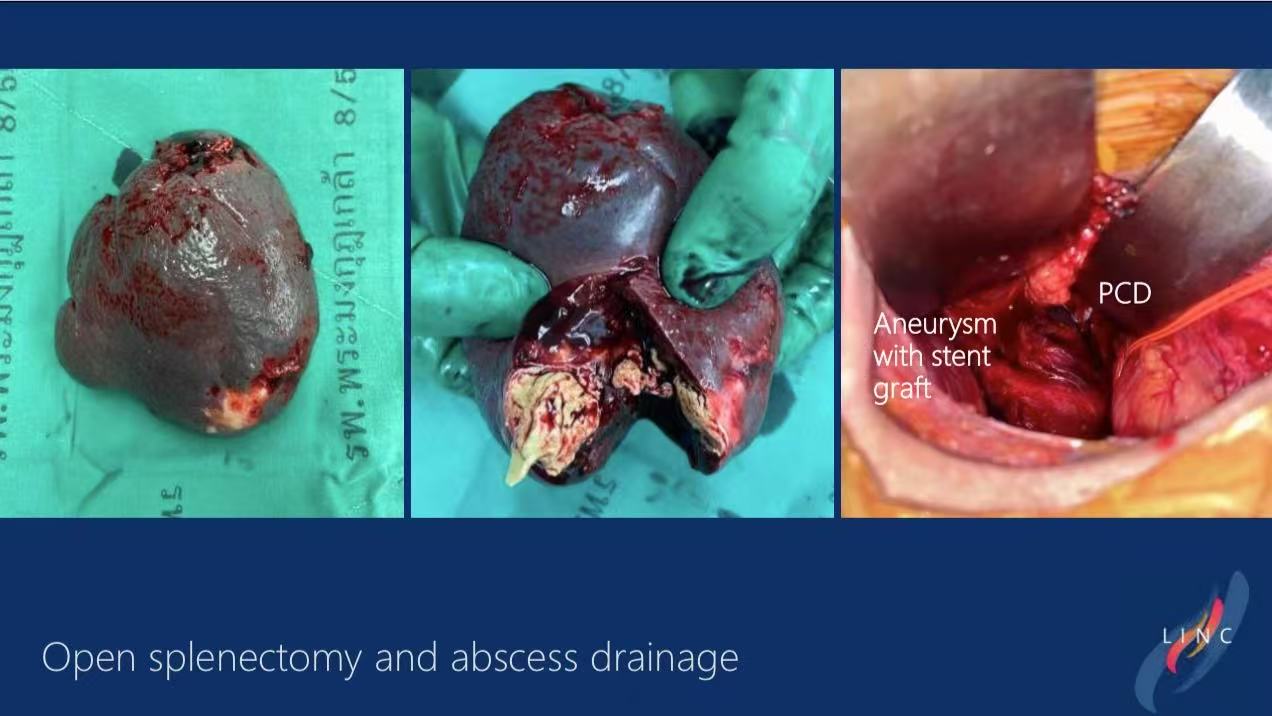
3.Postoperative Management:
Prolonged IV antimicrobial therapy (ceftazidime + co-trimoxazole)
Infection monitoring protocol
Postoperative Outcomes
Short-term:
CT verification showed complete aneurysm exclusion
Splenic abscess resolution confirmed
Intermediate Follow-up:
Symptomatic improvement
No recurrence of rupture or graft infection (duration unspecified)
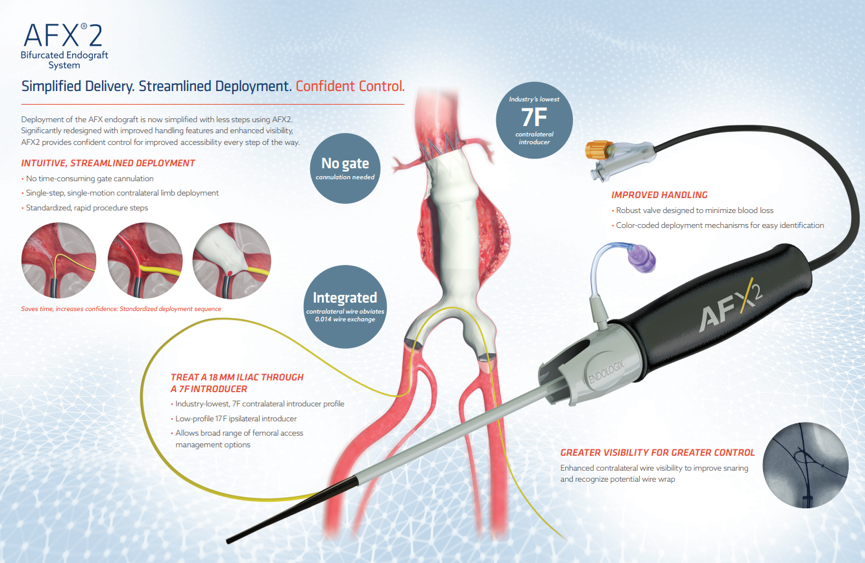
Technical Advantages of AFX-2 Stent Graft
Feature Clinical Significance
Anatomic Fixation Design:
Optimized apposition to vessel wall
Reduced endoleak risk (particularly valuable in infected cases)
Modular Delivery System:
8Fr low-profile profile compatible with complex iliac anatomy
Enhanced procedural precision
Proven Durability:
CE Mark supported by LEOPARD RCT data
5-year outcomes demonstrate comparable complication rates to open repair
Infection Mitigation:
Biocompatible graft material reduces bacterial adherence
Synergistic with antimicrobial therapy
Clinical Implications
1.Treatment Algorithm:
Multidisciplinary approach essential for infected aneurysm rupture
EVAR combined with radical debridement shows mortality benefit in high-risk patients
AFX-2 system demonstrates emergency viability in acute settings
2.Infection Control:
Extended antibiotic regimens (minimum 6-12 weeks) required for B. pseudomallei
Mandatory surveillance for graft infection (CT/MRI with contrast every 3 months)
3.Device Selection:
AFX-2’s modular architecture and anti-endoleak performance
Preferred option for anatomically challenging infected aneurysms



