Author: Dr. Richard Bulbulia
Institution: Nuffield Department of Population Health, University of Oxford, Co-Principal Investigator of ACST-2
Summary
This presentation analyzes 40 years of data on carotid trials, examining the efficacy of carotid endarterectomy (CEA) and carotid artery stenting (CAS) in treating symptomatic and asymptomatic carotid stenosis. Findings indicate that while carotid surgery is reliable for stroke prevention, CAS holds potential in younger patients. With advancements in technology and surgical strategies, CAS has shown advantages in specific anatomical structures and high cardiac risk patients.
Research Progress in Carotid Treatment
• Surgical Comparison for Symptomatic Lesions: According to trials such as ICSS, SPACE, and EVA-3S, CEA demonstrates better procedural safety than CAS for symptomatic patients, especially those over 70. However, improvements in CAS (e.g., flow reversal and selective protection filters) are narrowing the safety gap, making CAS increasingly comparable to CEA.
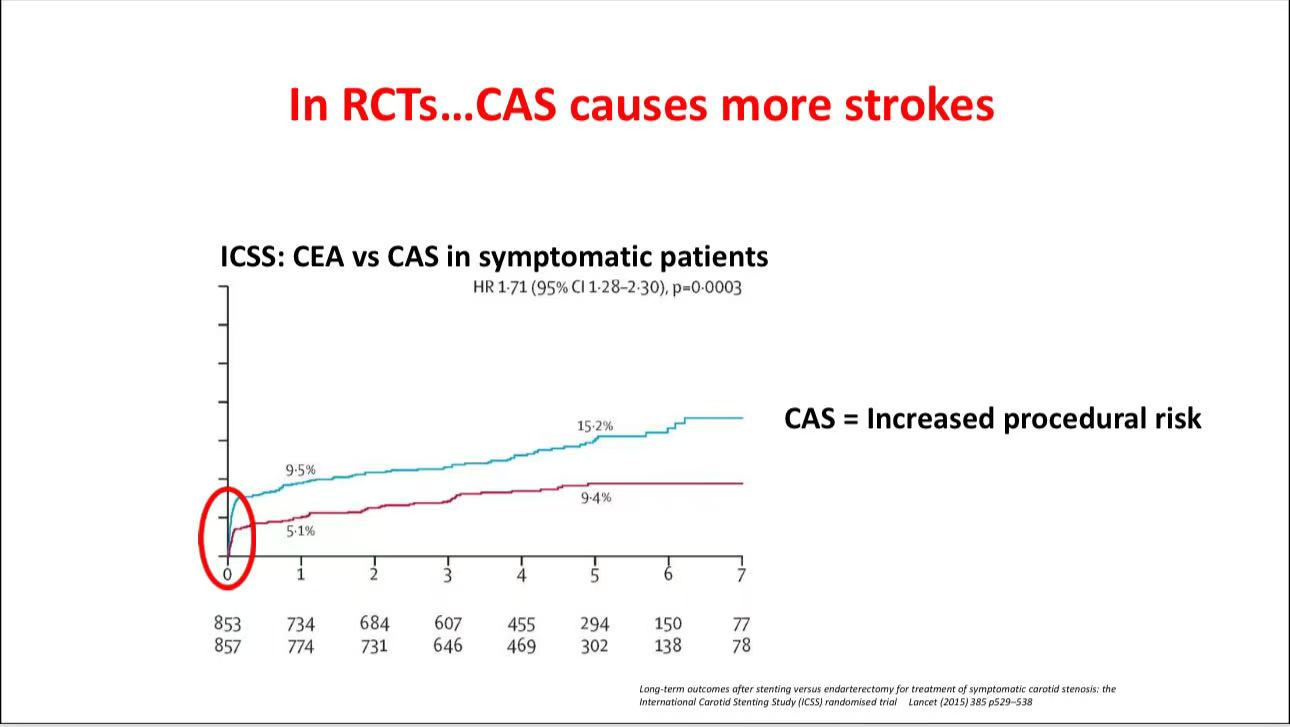
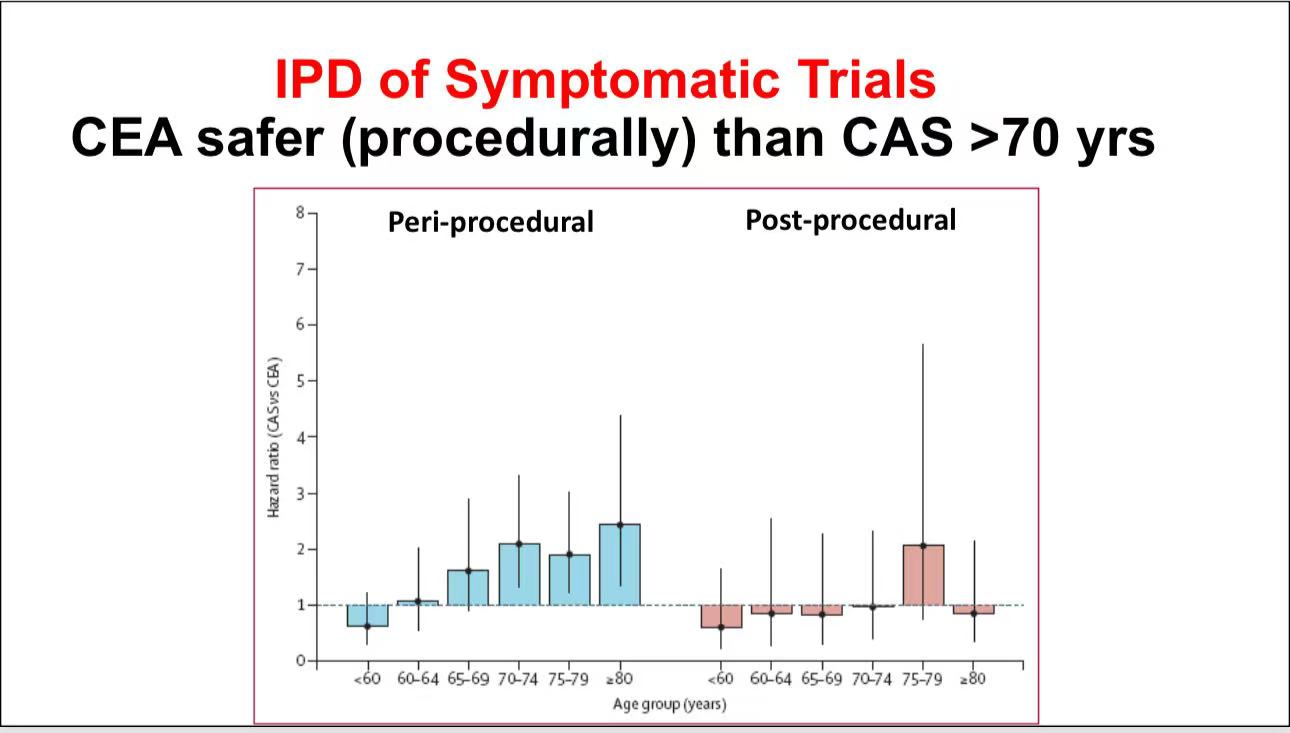
• Controversy in Asymptomatic Lesions: For asymptomatic patients, studies like ACST-2 and CREST-2 weigh surgery against non-surgical treatment. Advances in medical therapy may reduce the absolute treatment effect, suggesting a need for further evidence to confirm its relevance in a modern context.
Application of Contemporary CAS Techniques
• Outcomes of Modern CAS: Recent data indicate significant reductions in mortality and stroke rates with new-generation stents (e.g., C-Guard, Roadsaver) and protection techniques (e.g., MoMa flow reversal). Some centers report stroke rates as low as 0.9%.
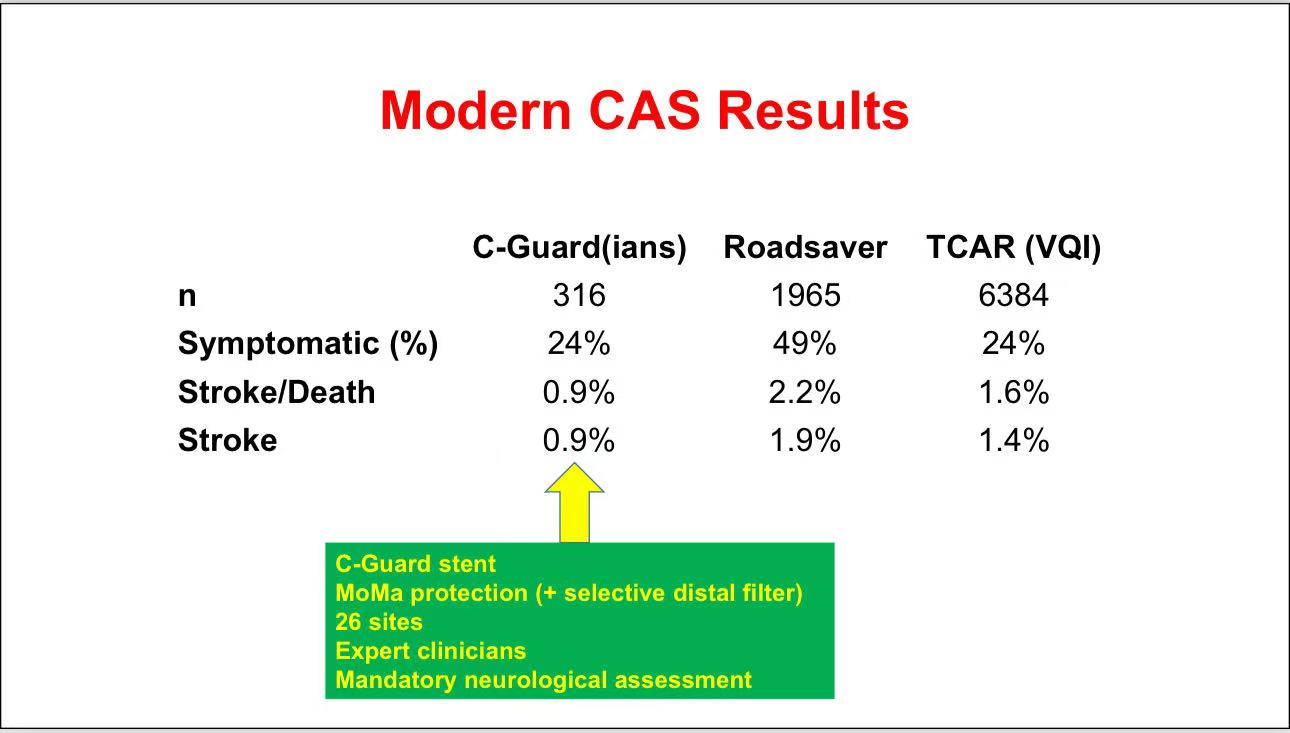
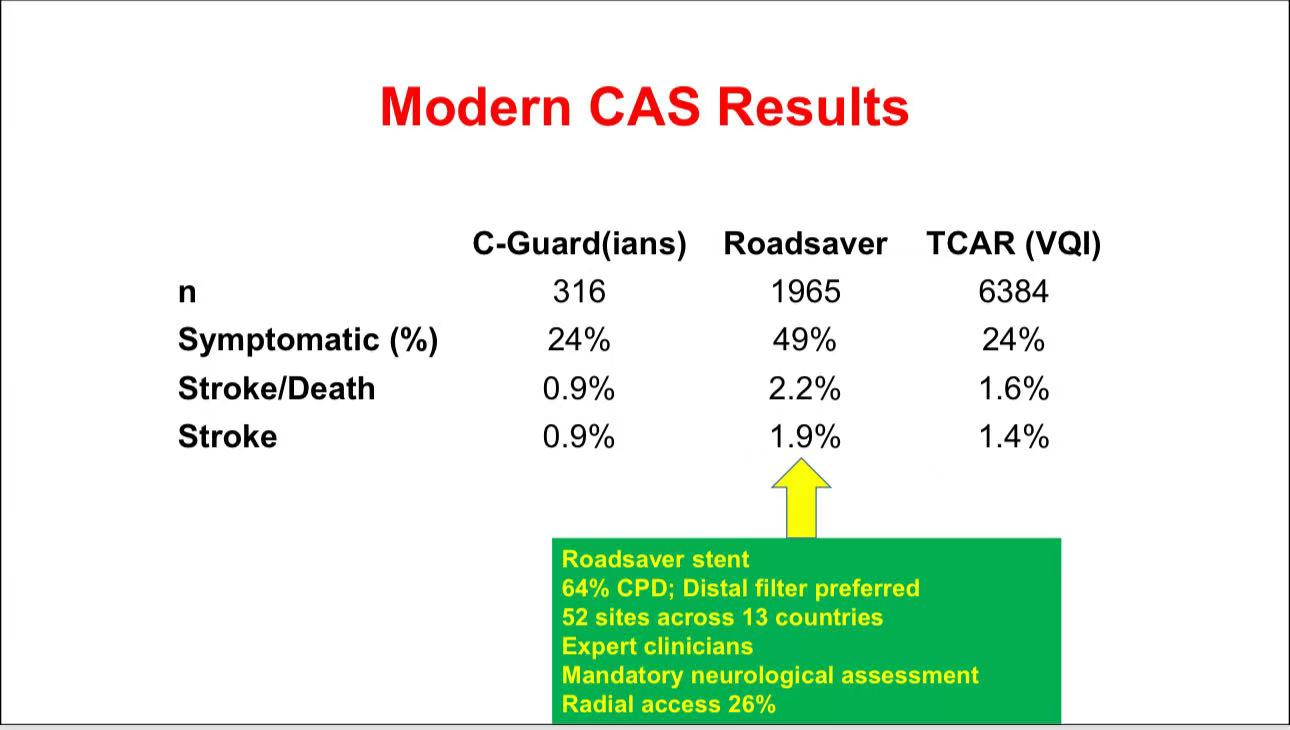
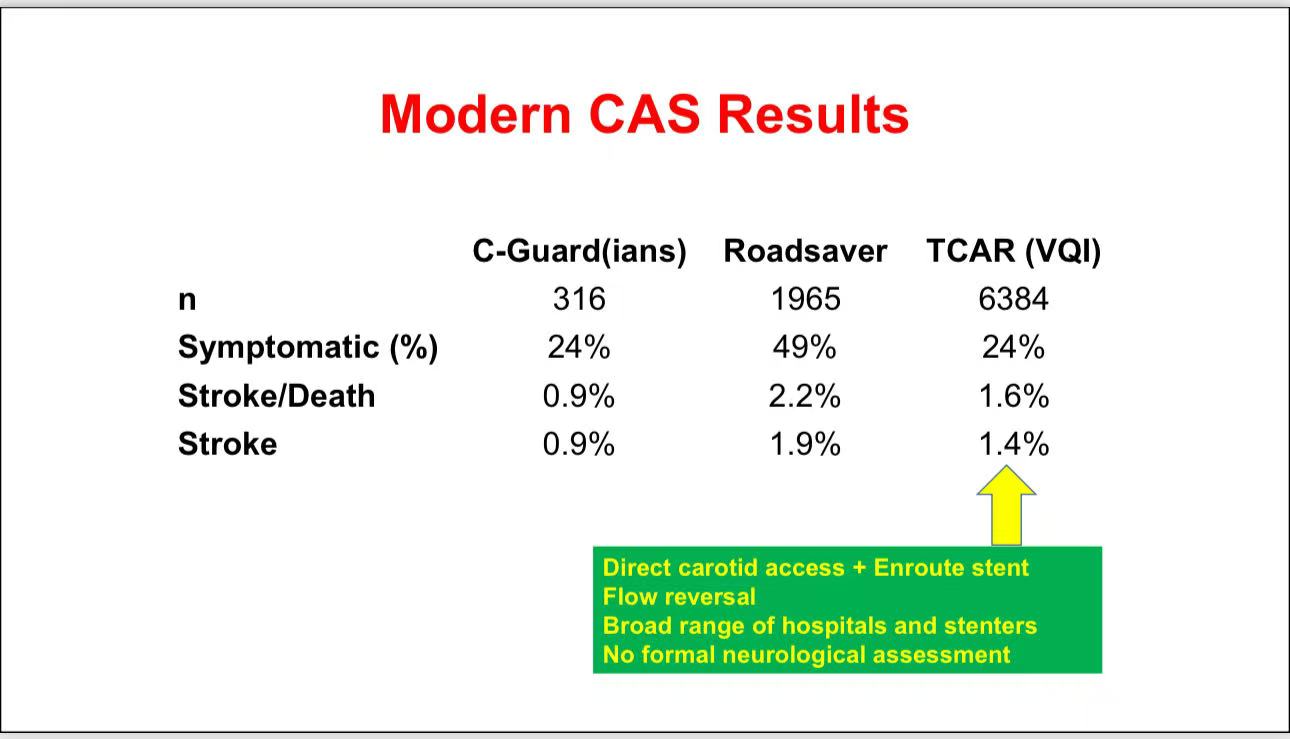
• Target Population: Although CAS shows promise in symptomatic patients, it is best suited for younger patients with favorable anatomy and high cardiac risk patients intolerant to surgery. Optimizing CAS expertise and equipment may further narrow the gap with CEA.

Future Challenges
1. Expanding Technology and Risk Matching: Future CAS challenges lie in reducing procedural risks and ensuring reproducibility across suitable patient populations.
2. Cost Control: Widespread adoption of modern CAS requires consideration of cost-effectiveness to enable broader clinical application.
3. Data Accumulation: More randomized controlled data is needed to validate CAS’s long-term effectiveness and refine carotid revascularization strategies.

Contact Us
• Email: endovascluar@simtomax.cn
The English content has been synchronized with the Vasco Knight account. For more international information, please visit:
• www.vascularknight.com
• Facebook: Vasco Knight
• Instagram: knight_vasco
Let’s safeguard health together and showcase your brilliance to the world!


